Author:
William Ramirez
Date Of Creation:
16 September 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- Steps
- Method 1 of 3: Pythagorean Theorem
- Method 2 of 3: Special Cases
- Method 3 of 3: The Sine Theorem
All right-angled triangles have one right angle (90 degrees), and the opposite side is called the hypotenuse. The hypotenuse is the longest side of the triangle and can be found in a variety of ways. In this article, we will tell you how to find the hypotenuse according to the Pythagorean theorem (when the lengths of the other two sides of the triangle are known), according to the sine theorem (when the length of the leg and the angle are known) and in some special cases (such tasks are often found on control and tests).
Steps
Method 1 of 3: Pythagorean Theorem
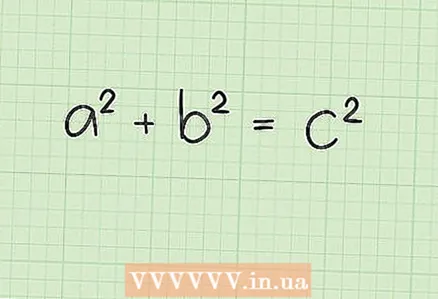 1 The Pythagorean theorem connects all sides of a right-angled triangle. According to this theorem, in any right-angled triangle with legs "a" and "b" and hypotenuse "c": a + b = c.
1 The Pythagorean theorem connects all sides of a right-angled triangle. According to this theorem, in any right-angled triangle with legs "a" and "b" and hypotenuse "c": a + b = c. 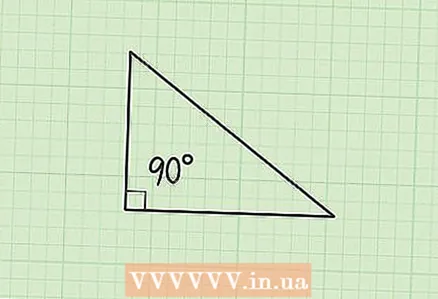 2 Make sure the triangle you are given is right-angled, as the Pythagorean theorem only applies to right-angled triangles. In right-angled triangles, one of the three angles is always 90 degrees.
2 Make sure the triangle you are given is right-angled, as the Pythagorean theorem only applies to right-angled triangles. In right-angled triangles, one of the three angles is always 90 degrees. - A right angle in a right triangle is indicated by a square icon.
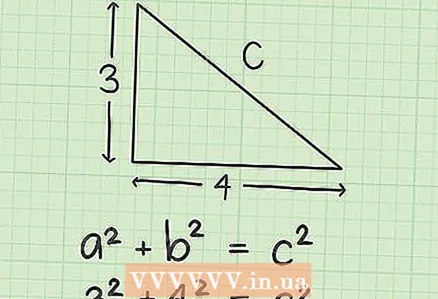 3 Add guidelines for the sides of the triangle. Label the legs as "a" and "b" (legs - sides intersecting at right angles), and the hypotenuse as "c" (hypotenuse - the largest side of a right triangle lying opposite a right angle). Then plug the given values into the formula.
3 Add guidelines for the sides of the triangle. Label the legs as "a" and "b" (legs - sides intersecting at right angles), and the hypotenuse as "c" (hypotenuse - the largest side of a right triangle lying opposite a right angle). Then plug the given values into the formula. - For example, the legs of a triangle are 3 and 4. In this case, a = 3, b = 4, and the formula looks like this: 3 + 4 = c.
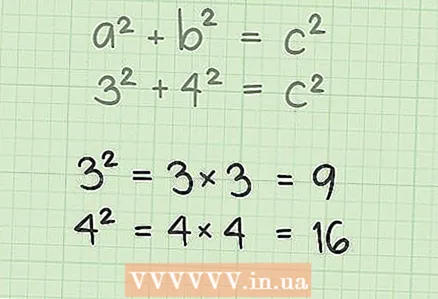 4 Square the leg values ("a" and "b"). To do this, simply multiply the number by itself:
4 Square the leg values ("a" and "b"). To do this, simply multiply the number by itself: - If a = 3, then a = 3 x 3 = 9. If b = 4, then b = 4 x 4 = 16.
- Plug these values into the formula: 9 + 16 = s.
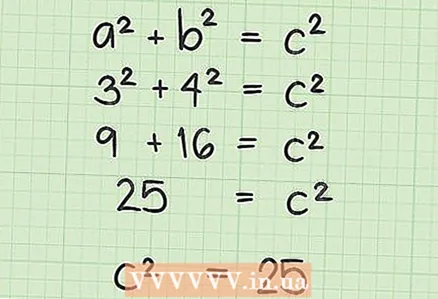 5 Add the found squares of the legs (a and b) to calculate the square of the hypotenuse value (c).
5 Add the found squares of the legs (a and b) to calculate the square of the hypotenuse value (c).- In our example 9 + 16 = 25, so c = 25.
 6 Find the square root of c. Use a calculator to find the square root of the found value. This will calculate the hypotenuse of the triangle.
6 Find the square root of c. Use a calculator to find the square root of the found value. This will calculate the hypotenuse of the triangle. - In our example c = 25... The square root of 25 is 5 (since 5 x 5 = 25, so √25 = 5). This means that the hypotenuse c = 5.
Method 2 of 3: Special Cases
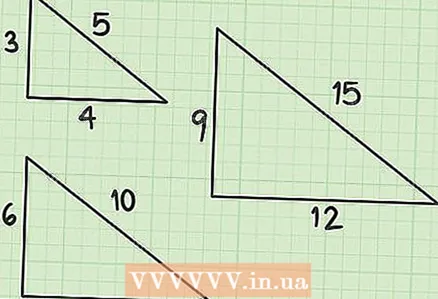 1 Definition of the Pythagorean triplet. The Pythagorean triple is three numbers (the lengths of three sides) that satisfy the Pythagorean theorem. Very often triangles with such sides are shown in textbooks and on tests. If you memorize the first few Pythagorean triples, you will save a lot of time on tests or exams because you can calculate the hypotenuse just by looking at the leg lengths.
1 Definition of the Pythagorean triplet. The Pythagorean triple is three numbers (the lengths of three sides) that satisfy the Pythagorean theorem. Very often triangles with such sides are shown in textbooks and on tests. If you memorize the first few Pythagorean triples, you will save a lot of time on tests or exams because you can calculate the hypotenuse just by looking at the leg lengths. - The first Pythagorean triplet: 3-4-5 (3 + 4 = 5, 9 + 16 = 25). Given a triangle with legs 3 and 4, then you can confidently state that the hypotenuse is 5 (without having to do any calculations).
- Pythagorean triplets work even when numbers are multiplied or divided by one factor. For example, if the legs are equal 6 and 8, the hypotenuse is 10 (6 + 8 = 10, 36 + 64 = 100). The same is true for 9-12-15 and even for 1,5-2-2,5.
- Second Pythagorean triplet: 5-12-13 (5 + 12 = 13, 25 + 144 = 169). Also, this triple includes, for example, the numbers 10-24-26 and 2,5-6-6,5.
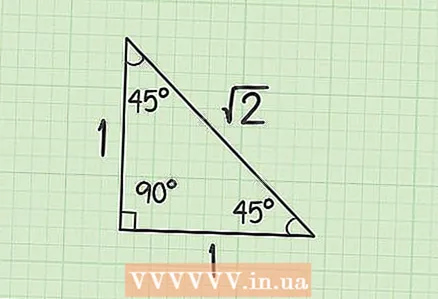 2 Isosceles right triangle. This is such a triangle, the angles of which are equal to 45.45 and 90 degrees. The ratio between the sides of this triangle is 1:1:√2... This means that the hypotenuse in such a triangle is equal to the product of the leg and the square root of 2.
2 Isosceles right triangle. This is such a triangle, the angles of which are equal to 45.45 and 90 degrees. The ratio between the sides of this triangle is 1:1:√2... This means that the hypotenuse in such a triangle is equal to the product of the leg and the square root of 2. - To calculate the hypotenuse of such a triangle, simply multiply the length of any leg by √2.
- This relationship is especially convenient when variables are given instead of numerical values in problems.
 3 Half an equilateral right-angled triangle. This is a triangle with angles equal to 30.60 and 90 degrees.The ratio between the sides of this triangle is 1:√3:2 or x: x√3: 2x... To find the hypotenuse in such a triangle, do one of the following:
3 Half an equilateral right-angled triangle. This is a triangle with angles equal to 30.60 and 90 degrees.The ratio between the sides of this triangle is 1:√3:2 or x: x√3: 2x... To find the hypotenuse in such a triangle, do one of the following: - If you are given a short leg (opposite to a 30 degree angle), simply multiply the length of that leg by 2 to find the length of the hypotenuse. For example, if the short leg is 4, then the hypotenuse is 8.
- If you are given a long leg (opposite to a 60 degree angle), simply multiply the length of that leg by 2/√3to find the length of the hypotenuse. For example, if the short leg is 4, then the hypotenuse is 4,62.
Method 3 of 3: The Sine Theorem
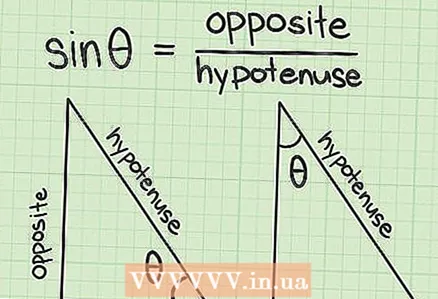 1 Understand what "sine" means. Sine, cosine, and tangent of an angle are the basic trigonometric functions that relate angles and sides in a right triangle. The sine of the angle is equal to the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse... The sine is denoted as sin.
1 Understand what "sine" means. Sine, cosine, and tangent of an angle are the basic trigonometric functions that relate angles and sides in a right triangle. The sine of the angle is equal to the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse... The sine is denoted as sin.  2 Learn to calculate sine. To calculate the sine, on the calculator find the key sin, click it, and then enter a value for the angle. In some calculators, you first need to press the function key, and then press sin... So experiment with the calculator or check its documentation.
2 Learn to calculate sine. To calculate the sine, on the calculator find the key sin, click it, and then enter a value for the angle. In some calculators, you first need to press the function key, and then press sin... So experiment with the calculator or check its documentation. - To find the sine of an angle of 80 degrees, press “sin”, “8”, “0”, “=” or press “8”, “0”, “sin”, “=” (answer: -0.9939).
- You can also find an online calculator by searching for "calculate sine" (without quotes).
 3 Memorize the theorem of sines. The Sine Theorem is a useful tool for calculating the angles and sides of any triangle. In particular, it will help you find the hypotenuse of a right triangle if you are given a leg and an angle other than a right angle. According to the sine theorem, in any triangle with sides a, b, c and corners A, B, C equality is true a / sin A = b / sin B = c / sin C.
3 Memorize the theorem of sines. The Sine Theorem is a useful tool for calculating the angles and sides of any triangle. In particular, it will help you find the hypotenuse of a right triangle if you are given a leg and an angle other than a right angle. According to the sine theorem, in any triangle with sides a, b, c and corners A, B, C equality is true a / sin A = b / sin B = c / sin C.- The sine theorem applies to any triangles, not just right-angled triangles (but only a right-angled triangle has a hypotenuse).
 4 Label the sides of the triangle with "a" (known leg), "b" (unknown leg), "c" (hypotenuse). Then mark the angles of the triangle through "A" (opposite the leg "a"), "B" (opposite the leg "b"), "C" (opposite the hypotenuse).
4 Label the sides of the triangle with "a" (known leg), "b" (unknown leg), "c" (hypotenuse). Then mark the angles of the triangle through "A" (opposite the leg "a"), "B" (opposite the leg "b"), "C" (opposite the hypotenuse).  5 Find the third corner. If you are given one of the acute corners of a right-angled triangle (BUT or IN), and the second angle is always 90 degrees (C = 90), then the third angle is calculated by the formula 180 - (90 + A) = B (remember that the sum of the angles in any triangle is 180 degrees). If necessary, the equation can be changed like this: 180 - (90 + B) = A.
5 Find the third corner. If you are given one of the acute corners of a right-angled triangle (BUT or IN), and the second angle is always 90 degrees (C = 90), then the third angle is calculated by the formula 180 - (90 + A) = B (remember that the sum of the angles in any triangle is 180 degrees). If necessary, the equation can be changed like this: 180 - (90 + B) = A. - For example, if the angle A = 40 degrees, then B = 180 - (90 + 40) = 180 - 130 = 50 degrees.
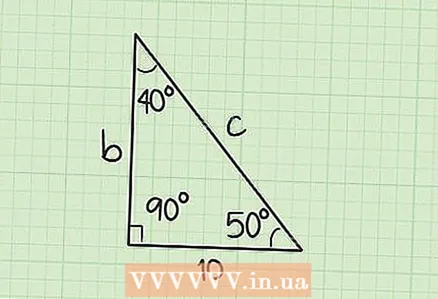 6 At this stage, you know the values of all three angles and the length of the leg "a". Now you can plug these values into the sine theorem formula to find the other two sides.
6 At this stage, you know the values of all three angles and the length of the leg "a". Now you can plug these values into the sine theorem formula to find the other two sides. - In our example, let's assume that the leg a = 10, and the angles are C = 90˚, A = 40˚, B = 50˚.
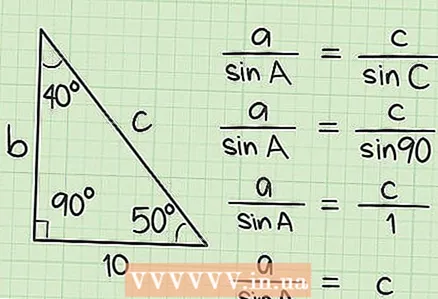 7 Plug the data and the found values into the sine theorem to find the hypotenuse:leg "a" / sine of angle "A" = hypotenuse "c" / sine of angle "C"... In this case, sin 90˚ = 1. Thus, the equation is simplified to: a / sinA = c / 1 or c = a / sinA.
7 Plug the data and the found values into the sine theorem to find the hypotenuse:leg "a" / sine of angle "A" = hypotenuse "c" / sine of angle "C"... In this case, sin 90˚ = 1. Thus, the equation is simplified to: a / sinA = c / 1 or c = a / sinA.  8 Divide the length of leg "a" by the sine of angle "A" to find the length of the hypotenuse. To do this, first find the sine of the angle and then divide. Or you can use the calculator by entering 10 / (sin40) or 10 / (40sin) (don't forget the parentheses).
8 Divide the length of leg "a" by the sine of angle "A" to find the length of the hypotenuse. To do this, first find the sine of the angle and then divide. Or you can use the calculator by entering 10 / (sin40) or 10 / (40sin) (don't forget the parentheses). - In our example, sin 40 = 0.64278761, and c = 10/0,64278761 = 15,6.