Author:
Alice Brown
Date Of Creation:
25 May 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- Steps
- Method 1 of 2: Preventing Snake Bites in the Wild
- Method 2 of 2: Preventing Snake Bites at Home
- Tips
- Warnings
Typically, snakes avoid human contact and would rather hide than bite. However, if the snake is frightened or unable to escape, the ability to avoid its bite will come in handy. Knowing which snakes live in your area and where they like to hide, as well as protective clothing will help you in most cases to avoid snake bites.
Steps
Method 1 of 2: Preventing Snake Bites in the Wild
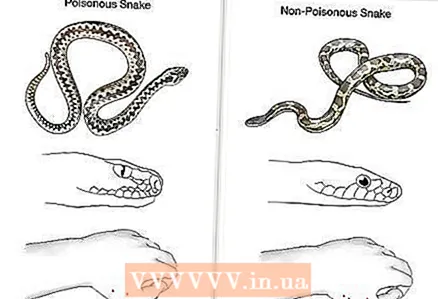 1 Find out which snakes live in your area. Whether you're out in the wild or just out on your backyard, knowing which snakes are typical for your region will come in handy.You must be able to recognize both venomous and non-venomous snakes, and know the differences between them. Before visiting an unfamiliar area, find out which snakes live there.
1 Find out which snakes live in your area. Whether you're out in the wild or just out on your backyard, knowing which snakes are typical for your region will come in handy.You must be able to recognize both venomous and non-venomous snakes, and know the differences between them. Before visiting an unfamiliar area, find out which snakes live there. - Remember: since you want to avoid a snakebite anyway, you should understand the differences and the level of danger of the two types of bites - venomous and non-venomous snake bites.
- Some snakes, such as the coral snake and the king snake, look very similar. They live in the same region, but only the coral snake is poisonous. You should be able to distinguish between similar snakes, especially if one of them is poisonous.
 2 Avoid areas with tall grass and dense bushes. Stick to paths and open spaces where you see where you step. If you have to go into tall grass or bushes, use a long stick to feel the place where you are going to step. Snakes hide from predators, heat and their prey in natural shelters such as tall grass and thickets of bushes. On the paths, they have nowhere to hide, so try not to turn into dense thickets.
2 Avoid areas with tall grass and dense bushes. Stick to paths and open spaces where you see where you step. If you have to go into tall grass or bushes, use a long stick to feel the place where you are going to step. Snakes hide from predators, heat and their prey in natural shelters such as tall grass and thickets of bushes. On the paths, they have nowhere to hide, so try not to turn into dense thickets.  3 Resist the temptation to stick your arm or leg into various crevices and holes. Snakes often hide in dark places such as holes in fallen trees or crevices between boulders. Be attentive and look around the place where you are going to stick your leg or arm. This is especially important when climbing or exploring caves. If you come across a crevice, it's best to walk past. If you do need to examine it, first poke it with a long stick to make sure it is empty.
3 Resist the temptation to stick your arm or leg into various crevices and holes. Snakes often hide in dark places such as holes in fallen trees or crevices between boulders. Be attentive and look around the place where you are going to stick your leg or arm. This is especially important when climbing or exploring caves. If you come across a crevice, it's best to walk past. If you do need to examine it, first poke it with a long stick to make sure it is empty. - Although snakes do not dig their own holes, they hide in holes dug by other animals. The snake can hide, for example, in the burrow of a chipmunk or a mole.
 4 Remember that snakes can climb trees. Be careful when walking under low hanging branches or climbing a tree, as the snake can easily be confused with a branch. Snakes can climb trees and hang down from them at the level of your head. Always be on the lookout and remember that snakes can lie in wait for you at every turn.
4 Remember that snakes can climb trees. Be careful when walking under low hanging branches or climbing a tree, as the snake can easily be confused with a branch. Snakes can climb trees and hang down from them at the level of your head. Always be on the lookout and remember that snakes can lie in wait for you at every turn.  5 Wear protective clothing when going outdoors. Be sure to wear long pants and high boots. Never walk barefoot or in sandals where you cannot see exactly where you are stepping.
5 Wear protective clothing when going outdoors. Be sure to wear long pants and high boots. Never walk barefoot or in sandals where you cannot see exactly where you are stepping. - When walking on tall grass, be sure to wear closed shoes to avoid being bitten. It is more difficult for snakes to bite through thick material, such as leather, than thinner materials such as canvas.
- It is better to wear long and loose trousers rather than tight-fitting trousers. If you do get bitten by a snake, loose-fitting trousers will reduce the likelihood of its fangs reaching your skin.
 6 Try not to camp in areas where snakes may be. Do not pitch your tent near rocks, tall grass, or overlying tree trunks. Most snakes are nocturnal, so you should be especially careful in the dark. Zip up your tent and sleep on a camp bed if possible, as it is more difficult for snakes to climb onto raised surfaces. If you need to go to the toilet, be sure to use a flashlight and check your shoes and the space in front of the tent.
6 Try not to camp in areas where snakes may be. Do not pitch your tent near rocks, tall grass, or overlying tree trunks. Most snakes are nocturnal, so you should be especially careful in the dark. Zip up your tent and sleep on a camp bed if possible, as it is more difficult for snakes to climb onto raised surfaces. If you need to go to the toilet, be sure to use a flashlight and check your shoes and the space in front of the tent. - Shake clothes, shoes, and sleeping bags before using them to make sure there is no snake lurking in there.
 7 Be careful when swimming, fishing or wading rivers or lakes, especially after heavy rains. Poisonous snakes live in the water, and in the event of a bite, you may need urgent medical attention. Water snakes are not found in all regions. After heavy rains, snakes are more common in the water due to the fact that the water floods their habitats. Water floods the nooks where snakes usually hide, and they have to get out into the open.
7 Be careful when swimming, fishing or wading rivers or lakes, especially after heavy rains. Poisonous snakes live in the water, and in the event of a bite, you may need urgent medical attention. Water snakes are not found in all regions. After heavy rains, snakes are more common in the water due to the fact that the water floods their habitats. Water floods the nooks where snakes usually hide, and they have to get out into the open. - Do not swim in muddy or overgrown water, as water snakes like to hide there.
Method 2 of 2: Preventing Snake Bites at Home
 1 Mow the grass in and around your garden plot. Prune branches and bushes to prevent snakes from settling near your home. As in the wild, snakes love to hide in tall grass and dense bushes. Cut the grass shortly to reduce the risk of a snake entering your area.
1 Mow the grass in and around your garden plot. Prune branches and bushes to prevent snakes from settling near your home. As in the wild, snakes love to hide in tall grass and dense bushes. Cut the grass shortly to reduce the risk of a snake entering your area.  2 Tell your children about snakes. Children should know that snakes are dangerous and should be avoided. If children live in your home, tell them about the different types of snakes that live in your area and the dangers of meeting them. Tell the children to never try to play with or catch the snake.
2 Tell your children about snakes. Children should know that snakes are dangerous and should be avoided. If children live in your home, tell them about the different types of snakes that live in your area and the dangers of meeting them. Tell the children to never try to play with or catch the snake. - Make sure that your children do not play in areas where snakes may be hiding. Do not let them play in wastelands overgrown with tall grass and bushes.
 3 Be careful when handling various materials in your area. Use your tools when grabbing logs from a pile of firewood, trimming bushes, or removing heaps of branches. Remember to wear boots and gloves as well. Snakes like to hide in cool, dark places like wood or under a canopy. Use a long stick to poke your hand into a place like this. This will scare away lurking snakes, and they are more likely to choose to hide.
3 Be careful when handling various materials in your area. Use your tools when grabbing logs from a pile of firewood, trimming bushes, or removing heaps of branches. Remember to wear boots and gloves as well. Snakes like to hide in cool, dark places like wood or under a canopy. Use a long stick to poke your hand into a place like this. This will scare away lurking snakes, and they are more likely to choose to hide. - Be especially careful in the summer, during the dry season. During this time, snakes can crawl to the garden hose, swimming pool and under the air conditioner in search of water.
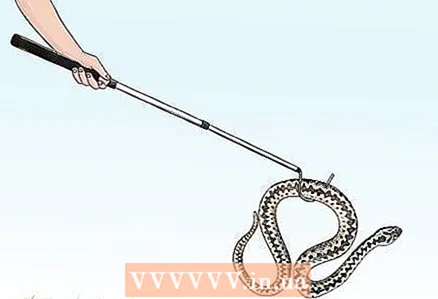 4 Take precautions if you have a snake in your home. If a snake lives as a pet in your house, you need to take it responsibly. Although venomous snakes are generally not kept as pets, bites should still be avoided. Try not to grab the snake with your hands and use a snake hook. In most cases, snakes bite while feeding, so you need to be especially careful during this time.
4 Take precautions if you have a snake in your home. If a snake lives as a pet in your house, you need to take it responsibly. Although venomous snakes are generally not kept as pets, bites should still be avoided. Try not to grab the snake with your hands and use a snake hook. In most cases, snakes bite while feeding, so you need to be especially careful during this time. - Choose an agreeable snake as your pet. For example, maize snake and king python are believed to rarely bite their hosts.
- Do not pick up the snake after touching its potential victims, such as mice, as the characteristic smell remains on your hands.
 5 Approach the snake with extreme caution. This also applies when you think the snake is dead. Snakes are able to reflexively move and even bite for some time after death. In addition, the snake may appear dead while simply basking in the sun. Never try to touch or hold the snake. Many experts believe that you should not try to kill a snake. If you see a snake on your territory, in no case try to catch it. Keep children and pets away from the snake and do not leave a dangerous guest unattended. Make sure the snake crawls out of your territory.
5 Approach the snake with extreme caution. This also applies when you think the snake is dead. Snakes are able to reflexively move and even bite for some time after death. In addition, the snake may appear dead while simply basking in the sun. Never try to touch or hold the snake. Many experts believe that you should not try to kill a snake. If you see a snake on your territory, in no case try to catch it. Keep children and pets away from the snake and do not leave a dangerous guest unattended. Make sure the snake crawls out of your territory. - Most snakes will try to escape and avoid human contact, even if you invade their territory. If you run into a snake, step back slowly without turning your back to it. Avoid sudden movements and loud noises, as the snake can perceive them as a threat, which increases the danger of being bitten.
Tips
- Rattlesnakes are widely known for their distinctive sound. However, the rattlesnake does not always make noise, even when you are very close to it. Stay alert even if there is no sound.
- Explain to the children that snakes are dangerous, so it is best to avoid them.
- In colder climates, many snakes hibernate. However, care should be taken at any time of the year.
- Almost 90% of snake bites occur in the ankle area, so always wear high boots when going outdoors.
- Snakes are more active during warmer months and at night. However, you can meet the snake at any other time.
Warnings
- If you do get bitten by a snake, seek medical attention as soon as possible.
- Never travel alone in remote and wild places.Travel to these areas with a companion who can help you in an emergency.