Author:
Peter Berry
Date Of Creation:
18 February 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
Knowing your computer's specifications will help you to make informed choices about your hardware and software. Knowing the exact range of all hardware will also help you reduce technical problems. With any operating system, you can quickly find the specification of a machine.
Steps
Method 1 of 4: Windows
Opens the Run dialog box. You can find it in the Start menu or by pressing a key combination ⊞ Win+R.

Type.msinfo32and press↵ Enter. The System Information window will open.- It may take a few minutes to open this window.
- There are many ways to check your system specs on Windows. In particular, with System Information, you will be provided with the most complete report in one place.

Go through the System Summary and find your basic information. There are a few notable items on the System Summary screen - the default screen when the System Information window is opened, including:- OS Name (Operating System Name) - This is the version of Windows you are using.
- System Manufacturer / Model (Series / System Manufacturer) - This is the manufacturer of the computer and the model of the machine.
- System Type (System Type) - This shows whether you are using a 32-bit (x86) or 64-bit (x64) version of Windows.
- Processor (Processor) - This shows the model and speed of the processor. The speed stated here is the advertising speed. If the processor has multiple cores, this will be demonstrated as well. Note that if the processor is overclocked to increase speed, it is likely that the new specification will not be updated. Click here for more information on measuring processor speed.
- Installed Physical Memory (RAM) (Temporary Data Memory) - This is the amount of RAM installed in your computer.
- Baseboard Manufacturer / Model (Motherboard Manufacturer / Series) - This is the motherboard manufacturer and model information. The motherboard model is not always properly reported.
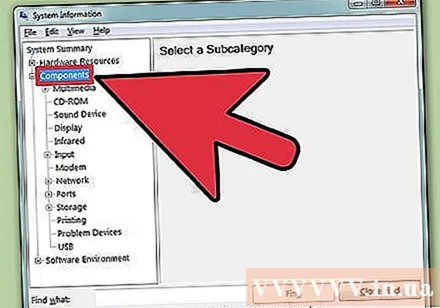
Expand the "Components" section. This section provides detailed information about the graphics card and hard drive.
Select "Display". The graphics card you have installed will be shown here. If the motherboard features integrated graphics and you also add a separate card, two different sets of specifications are presented.
- When looking for graphics card specifications, the most common information you need to know is Name (Name) and RAM adapter (Graphics Card Memory). Here, the RAM Adapter is displayed in bytes. However, in system specifications it is usually expressed in gigabytes (GB). A gigabyte contains about 1 billion bytes (Windows will report the same figure as the manufacturer).
Expand the "Storage" section and select "Drives". The available space and the total size of all the hard drives and partitions in your computer will be displayed.
- Select the "Disks" option to read the physical drive specifications and the different partitions contained in each drive.
Explore other parts. The above information helps you to determine specifications related to system requirements for hardware and software. However, they are just basic information. You can find a lot of detailed information for each of the above.
- The "Software Environment" section shows all of your drivers, running processes, and startup programs.
Export file for computer repair. If they are looking to a technician to solve problems with your computer, they may want to see the documentation of your computer's specifications. You can export your system specifications by clicking the "File" menu and selecting "Export". Give it a name and the file will be saved as text. advertisement
Method 2 of 4: Mac
Click the Apple menu and select "About This Mac". The window showing the OS X version and system properties summary will appear. It includes the speed of the processor, memory (RAM), and graphics card (if installed).
Use the tabs at the top of the window (Yosemite). The latest version of OS X has tabs along the top part of the About This Mac window, allowing you to quickly switch between different hardware groups. If you are using Mavericks (OS X 10.9) or earlier, move down to the next step.
- The Overview tab gives you a brief report on the most common searches for the specification. This page should have enough information for you to determine whether or not your computer can run a program.
- The Displays tab shows all of your connected displays.
- The Storage tab lists the hard drive and capacity of each drive.
Click.More Info (More info - Mavericks and earlier). A new window with detailed information about the hardware will open. Use the navigation tree on the left to navigate to the hardware you want to explore.
- The Hardware section displays detailed information about all of your hardware components. When "Hardware" is selected, information about the central processing unit (CPU) will be displayed in the right pane. If the CPU has more than one core, they will also be listed here.
- Note: The processor speed shown here is the advertised speed from the manufacturer, and it is completely free to use it to determine whether the computer meets the technical requirements to run the chapter. program or not. However, it will not show the fruits of the overclocking, the speed increases. Click here for more information on how to find the actual processor speed.
Method 3 of 4: Linux
Open the emulator. You can use the lightweight hardware listing program found in many Linux distributions. If not, the installation is pretty easy. You can quickly open emulators in most distributions by pressing a combination of keys Ctrl+Alt+T.
Setting lshw (necessary). Many Linux distributions, including Ubuntu and Mint, do lshw. Use one of the following commands to install it lshw. If you already have it on your computer, you will be notified that the program is installed.
- Debian distributions - sudo apt-get install lshw
- Red Hat / Fedora Distributions - sudo yum install lshw
Run lshw to read information about your computer's hardware. Use the following command to trim most of the miscellaneous content and display the most frequently searched items:
- sudo lshw -short.
Find the item you are looking for. Use the "Class" column to find. You can find the processor, memory (RAM), graphics card ("display"), and drives.
Create a text file of your hardware specifications. It can be useful when getting someone else to fix it or selling a computer.
- Type sudo lshw -short> specs.txt. You can rename the file as you like. You will find this text file in your / home directory.
- You can also type sudo lshw -html> specs.html, create HTML file. This volume may be easier to read when opened in the browser.
GUI (Graphical User Interface) installation. This interface allows you to view hardware information on the graphics window and navigate within it. As such, it may be more comfortable for those who are used to Windows or OS X.
- Type commands sudo apt-get install lshw-gtk (Debian) or sudo yum install lshw-gui (RH / Fedora).
- Type commands sudo lshw -X to open the GUI for lshw. The GUI uses a "3-frame" design. When you expand something in the left frame, the subsection will appear in the frame to the right. Expand the different groups to find your specifications.
Method 4 of 4: Android
Download emulator simulation application. While you can use the Settings menu to find basic information about your phone, you will not be able to see any detailed information about the processor or memory. With an emulator emulator application, you will be able to execute a Linux command to display the system parameters.
- If you have access to the Dev Tools on your device (Settings → Developer Tools), you can open the Terminal Emulator from there. If you don't have access to these tools you can download an emulator emulator application. The most popular free terminal emulator is "Terminal Emulator for Android". You can download it from the Google App Store. This method does not require root access - it allows access and adjustment of the entire file system in the operating system.
Open Terminal Emulator. You will be redirected to the emulator prompt in Linux style.
Type commands.cat / proc / cpuinfoand press Enter. The mobile processor information on your Android device will be displayed.
Type commands.cat / proc / meminfoand press Enter. Memory (RAM) information on your device, including information about the total and how much space is being used, is displayed. advertisement