Author:
Lewis Jackson
Date Of Creation:
6 May 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
The average mass atom is not a direct measure of the mass of an atom. Instead, this is the average mass per atom from a typical sample of the element. If you can measure the masses of billions of individual atoms, you can find this out by calculating their average. We have a more practical method, which is based on information about the different isotopes of the chemical element.
Steps
Part 1 of 2: Calculate the average mass atom
Understand isotopes and mass atoms. In nature, most elements exist in many forms or isotopes. The only difference between two isotopes of the same element is the number of neutrons in the atom, whose number of neutrons affects the mass atom. Calculating the average mass atom takes into account the effect of this difference, and tells you the average mass of each atom in a sample of those atoms.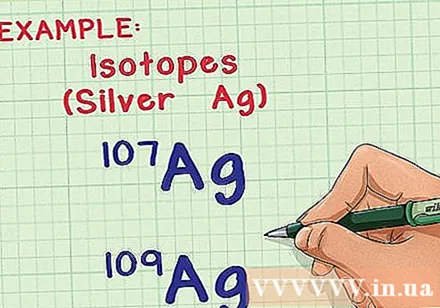
- For example, element silver (Ag) has two natural isotopes: Ag-107 and Ag-109 (or Ag and Ag). The isotope is named after the "mass number", or the sum of the number of protons and the number of neutrons in an atom. That means that Ag-109 has two more neutrons than Ag-107, so its atom is a bit heavier.
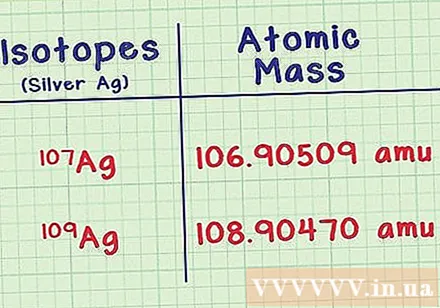
Find the mass of each isotope. You need two pieces of information for each isotope, you can look them up in reference books or look up online, for example webelements.com. The first is the mass atom or atomic mass of each isotope. Isotopes with more neutrons have more mass.- For example, the silver isotope Ag-107 has the mass atom 106,90509 amu (the unit of a cubic atom). The isotope Ag-109 is slightly heavier with mass of 108,90470.
- The pair of decimals at the end can be slightly different in the documents. Do not write any numbers in parentheses after the mass.

Write down the natural survival rate for each isotope. This ratio indicates the isotope's prevalence, as a percentage of the element's total atoms. You can find this information in the same document with a cubic atom on it. Natural survival of all isotopes should be 100% (although it may differ slightly due to the error of rounding).- Ag-107 isotope has the ratio of 51.86%. The isotope Ag-109 is less common at the rate of 48.14%. That means a normal silver sample has 51.86% Ag-107 and 48.14% Ag-109.
- Any isotopes that do not have this survival rate are ignored. These isotopes do not exist naturally on earth.
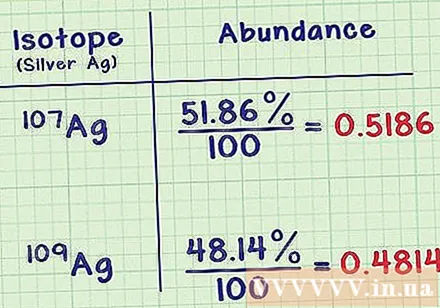
Convert the isotope percentage to a decimal number. Divide this ratio by 100 will yield the same value as a decimal.- In the silver sample above, the ratio of isotopes is 51.86 / 100 = 0,5186 and 48,14 / 100 = 0,4814.
Find the average cubic atom. The average mass atom of an element has n isotopes equal (Atomic BlockIsotope 1 * ratioIsotope 1) + (atomic massIsotope 2 * ratioIsotope 2) + ... + (atomic massisotopes n * ratioisotopes n. This is an example of an "average mass", meaning that the greater the survival rate of the isotope, the greater its effect on the result. How to apply this formula for silver is as follows:
- Medium mass atomAg = (cubic atomAg-107 * ratioAg-107) + (atomic massAg-109 * ratioAg-109)
=(106,90509 * 0,5186) + (108,90470 * 0,4814)
= 55,4410 + 52,4267
= 107.8677 amu. - Find that element on the periodic table to check the results. The average cubic atom is always written below the element's chemical symbol.
- Medium mass atomAg = (cubic atomAg-107 * ratioAg-107) + (atomic massAg-109 * ratioAg-109)
Part 2 of 2: Using results
Convert mass to atomic number. The average mass atom shows the relationship between mass and the number of atoms in a typical sample of that element. This is very useful in chemical laboratories because it is almost impossible to accurately count atoms, but masses are easy to determine. For example, you could weigh a sample of silver and know that there will be one silver atom for every 107,8677 amu.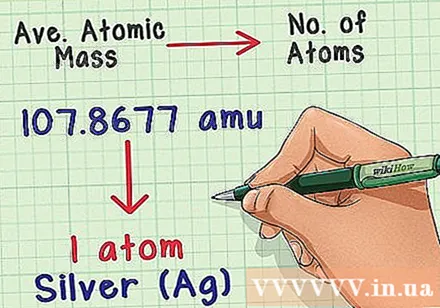
Convert to molar mass. The atomic mass unit is very small, so chemists often use the gram unit for mass. Luckily we have definitions of these concepts so the transformation should be easy. Just multiply the average mass atom by 1 g / mol (molar mass constant) to get a result in g / mol. For example, 107,8677 grams of silver contains one mole of silver atoms.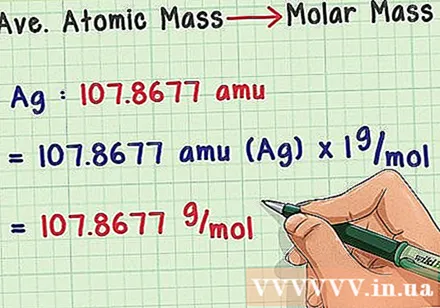
Find the average molecular mass. Since a molecule is a collection of atoms, you can add the mass of all atoms to find the molecular mass. If you were to use an average mass atom (instead of the mass of a particular isotope), the result would be the average molecular mass of a sample in nature. Here is an example: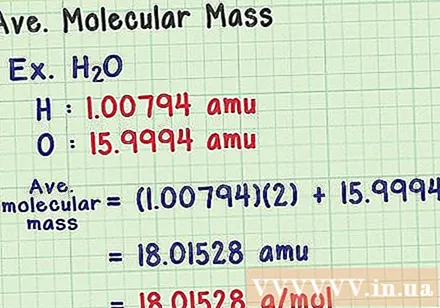
- A water molecule has the chemical formula H2O contains two hydrogen atoms (H) and one oxygen (O) atom.
- Hydrogen has an average mass atom of 1,00794 amu. Oxygen has an average atomic mass of 15,9994 amu.
- So the average molecular mass of H2O is equal to (1,00794) (2) + 15,9994 = 18,01528 amu, which is equivalent to 18,01528 g / mol.
Advice
- The concept of relative atomic mass is sometimes used synonymous with a medium mass atom. There is a slight difference because the atomic mass is relatively un unit; it is a measurement of the mass relative to a carbon-12 atom. As long as you use the atomic mass unit in the average cubic atom calculation, these two values are the same.
- The number in parentheses after the cubic atom tells us the error. For example, mass atom 1.0173 (4) means that the element's normal atom has a mass range of about 1.0173 ± 0.0004. You do not need to obtain this number if it is not requested.
- On the periodic table, the average cubic atom of the following element is larger than the one before it, with few exceptions. Here's a quick way to check your results.
- 1 atomic mass unit is 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
- Isotope survival rates are calculated according to typical naturally occurring samples on the earth. Non-naturally occurring substances such as meteorites or one produced in a laboratory can have different isotope ratios, so the average mass atom is also different.
Warning
- Mass atoms are always written in atomic mass units (amu or u), sometimes called daltons (Da). Never write another unit of mass (such as a kilogram) after this number without changing it.
What you need
- Pencil
- Paper
- Laptop
- Data on isotope survival rate in nature.
- Mass atomic unit data for isotopes.