Author:
Peter Berry
Date Of Creation:
12 February 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
Cross multiplication is the way to solve an equation whose variables are in two equal fractions. The variable represents an unknown value, and cross-multiplication reduces the rule of three to a simple equation, allowing you to solve the problem to find the variable. The cross-multiplication method is especially useful if you want to calculate the ratio. Here's how to do it:
Steps
Method 1 of 2: With the equation with one variable
Multiply the fraction on the left with the sample of the fraction on the right. For example, we have equations 2 / x = 10/13. Proceed to multiply 2 by 13. We have 2 * 13 = 26.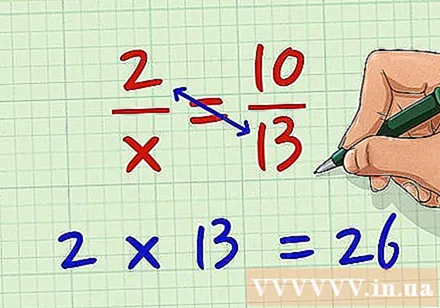
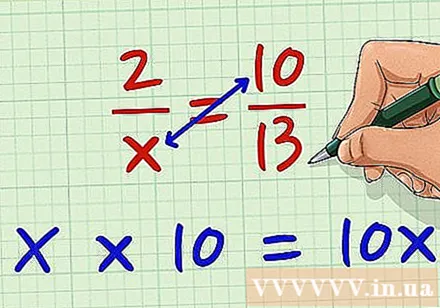
Multiply the fraction on the right with the sample of the fraction on the left. Performing multiplication with variables, we multiply x by 10. x * 10 = 10x. You multiply it in any direction first, as long as both the numerator and the denominator of the two fractions are multiplied diagonally.
Put two results in the equation. 26 would be equal to 10x. We have 26 = 10x. The order of the two sides is not important; Since they are equal, you can swap out both sides of the equation at the same time without any effect.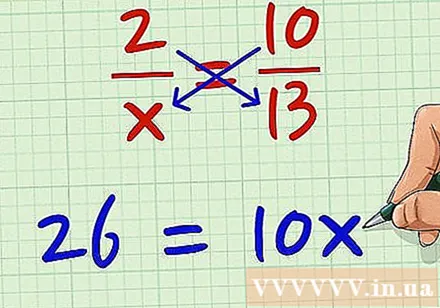
- So, to solve the equation 2 / x = 10/13 and find x, we have 2 * 13 = x * 10, which is equivalent to 26 = 10x.
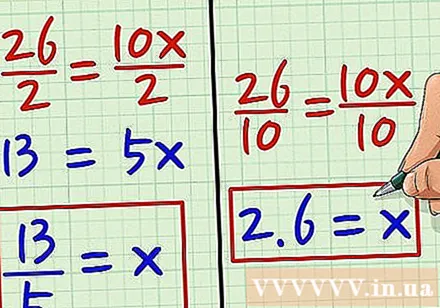
Find x. With 26 = 10x, you can divide both 26 and 10 by the common denominator of both numbers. Since both are even numbers, they can be divisible by 2; 26/2 = 13 and 10/2 = 5. The remaining equation will be 13 = 5x. So, you need to divide both sides of the equation by 5 to find x. We have 13/5 = 5/5, which is equivalent to 13/5 = x. If you want the answer to be a decimal number, you can divide the sides by 10 to get 26/10 = 10/10, deducing x = 2.6. advertisement
Method 2 of 2: With equation having two identical variables
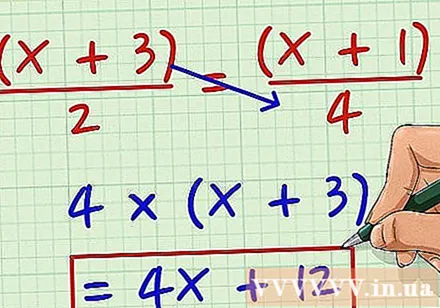
Multiply the fraction on the left with the sample of the fraction on the right. For example, the problem asks to find x in the equation: (x + 3) / 2 = (x + 1) / 4. For starters, you take (x + 3) * 4 = 4 (x +3) = 4x + 12.
Multiply the fraction on the right with the sample of the fraction on the left. Do the same as before, we have (x +1) x 2 = 2 (x +1) = 2x + 2.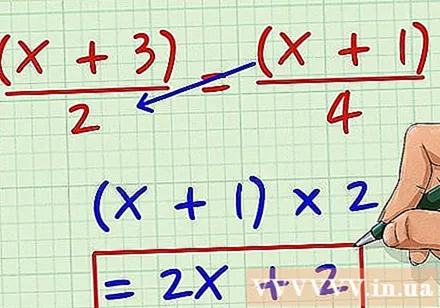
Put two equal sides and combine the same terms. Now we have 4x + 12 = 2x + 2. Please put the terms contained x to one side and the term remains constant on the other side of the equation.
- Combined 4x and 2x by giving 2x to the left side and change the term sign. When you move 2x to the left, only the right side remains 2. On the left, we have 4x - 2x = 2x, so it remains 2x.
- Do the same with 12 and 2 by giving 12 from left hand side to right side and change term sign. The left side will be 2-12 = -10.
- The remaining equation is 2x = -10.
Find x. Now you just need to divide both sides of the equation by 2. 2x / 2 = -10/2 => x = -5. After cross multiplication, we find x = -5. You can check by replacing x = -5 and calculating whether the two sides of the equation are equal or not. After replacing -5 again with the original equation, we have -1 = -1. advertisement
Advice
- You can test your assignment by replacing the answers you find with the original equation. If, after minimizing, the remaining equation is valid, such as 1 = 1, you have calculated it correctly. If the equation after minimization is not valid, for example 0 = 1 then you made a mistake. For example, if we replace 2.6 in the first equation, we get 2 / (2,6) = 10/13. Multiplying the left side by 5/5 gives 10/13 = 10/13, this equation is valid because after reduction it becomes 1 = 1. So 2.6 is the correct result.
- Note that when replacing another number (eg 5) with the same equation, you get 2/5 = 10/13. Even if you multiply the left hand side by 5/5 again, the result will be 10/25 = 10/13 and obviously not correct. If this is the case, it means you were wrong in performing cross multiplication.