Author:
Helen Garcia
Date Of Creation:
22 April 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- Steps
- Method 1 of 5: Calculating Pi by Measuring a Circumference
- Method 2 of 5: Calculate Pi with an Infinite Number Series
- Method 3 of 5: Calculating Pi with the Buffon Needle Method
- Method 4 of 5: Calculating Pi Using a Limit
- Method 5 of 5: Arcsine function
- Tips
Pi (π) is one of the most important and intriguing numbers in mathematics. This constant, approximately 3.14, is used to calculate the circumference of a circle based on its radius. It is also an irrational number, meaning it can be calculated to an infinite number of decimal places. It's not easy to do, but it's still possible.
Steps
Method 1 of 5: Calculating Pi by Measuring a Circumference
 1 Make sure you are using a perfect circle. This method does not work with ellipses, ovals or anything else, this method is only suitable for a perfect circle. A circle is defined as the collection of all points on a plane that lie at the same distance from one center point. A jar lid is the perfect item for this method. If you want to make the most accurate calculations, use a pencil with a very thin lead.
1 Make sure you are using a perfect circle. This method does not work with ellipses, ovals or anything else, this method is only suitable for a perfect circle. A circle is defined as the collection of all points on a plane that lie at the same distance from one center point. A jar lid is the perfect item for this method. If you want to make the most accurate calculations, use a pencil with a very thin lead. 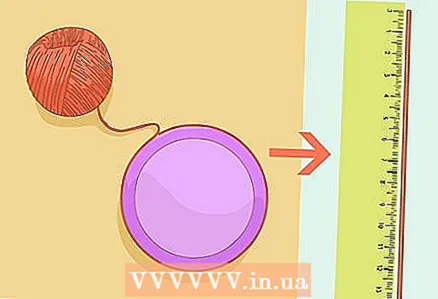 2 Measure the circumference as accurately as possible. This is not an easy task (which is why Pi is so important).
2 Measure the circumference as accurately as possible. This is not an easy task (which is why Pi is so important). - Wrap the thread around the lid as tightly as possible.Mark the point where the start and end coincide, and then measure the length of the thread with a ruler.
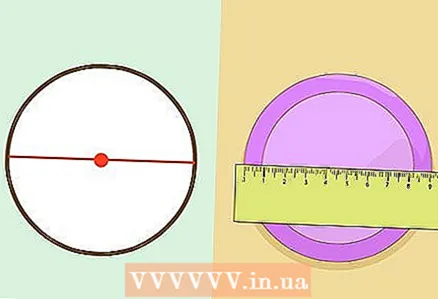 3 Measure the diameter of the circle. Diameter - the length of the line segment passing through the center of the circle and any two points lying on the circle.
3 Measure the diameter of the circle. Diameter - the length of the line segment passing through the center of the circle and any two points lying on the circle. 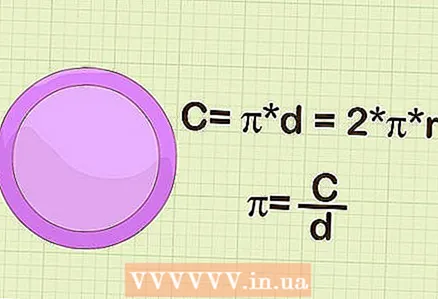 4 Use a formula. The circumference is calculated by the formula C = π * d = 2 * π * r... Thus, pi is equal to the circumference divided by its diameter. Calculate pi (with your values) on the calculator. The result should be approximately 3.14.
4 Use a formula. The circumference is calculated by the formula C = π * d = 2 * π * r... Thus, pi is equal to the circumference divided by its diameter. Calculate pi (with your values) on the calculator. The result should be approximately 3.14.  5 To refine your calculations, repeat this procedure with several different circles and then average the results. Your measurements will not be perfect for one circle taken, but given multiple circles, they should be averaged to the exact pi value.
5 To refine your calculations, repeat this procedure with several different circles and then average the results. Your measurements will not be perfect for one circle taken, but given multiple circles, they should be averaged to the exact pi value.
Method 2 of 5: Calculate Pi with an Infinite Number Series
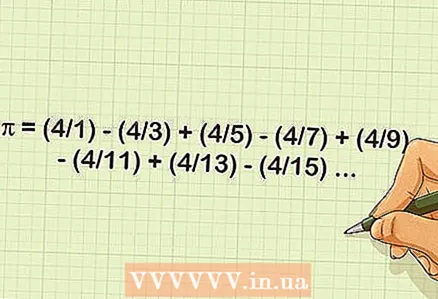 1 Use the Leibniz series. Mathematicians have found several different infinite series that allow you to accurately calculate pi to a large number of decimal places. Some are so complex that supercomputers are required to process. However, one of the simplest series is the Leibniz series. Although not the most efficient, it will give a more accurate pi value with each iteration; after 500,000 iterations, the Leibniz series will give the exact pi value with ten decimal places. Here is the formula to apply.
1 Use the Leibniz series. Mathematicians have found several different infinite series that allow you to accurately calculate pi to a large number of decimal places. Some are so complex that supercomputers are required to process. However, one of the simplest series is the Leibniz series. Although not the most efficient, it will give a more accurate pi value with each iteration; after 500,000 iterations, the Leibniz series will give the exact pi value with ten decimal places. Here is the formula to apply. - π = (4/1) - (4/3) + (4/5) - (4/7) + (4/9) - (4/11) + (4/13) - (4/15) ...
- Take 4/1 and subtract 4/3. Then add 4/5. Then subtract 4/7. Continue by alternating addition and subtraction of fractions with 4 in the numerator and every odd number in the denominator. The more times you do this, the more accurate Pi you will get.
 2 Try the Nilakant series. This is another infinite pi series that is fairly easy to understand. This series is more complex than the Leibniz series, but it gives the exact pi much faster.
2 Try the Nilakant series. This is another infinite pi series that is fairly easy to understand. This series is more complex than the Leibniz series, but it gives the exact pi much faster. - π = 3 + 4/(2*3*4) - 4/(4*5*6) + 4/(6*7*8) - 4/(8*9*10) + 4/(10*11*12) - (4/(12*13*14) ...
- For this series, write down the number 3 and alternate the addition and subtraction of fractions with the number 4 in the numerator and the product of three consecutive integers, which increase with each new iteration, in the denominator. Each subsequent piece begins with the largest number used in the previous piece. Do this just a few times and you will get a fairly accurate pi value.
Method 3 of 5: Calculating Pi with the Buffon Needle Method
 1 Spend experiment. It turns out Pi can be found by conducting an interesting experiment called the Buffon needle method, which seeks to determine the probability that accidentally thrown needles will land either between drawn equidistant parallel lines or intersect exactly one straight line. If the distance between the lines is equal to the length of the needle, then the ratio of the number of throws when the needle crosses the line to the total number of throws tends to 2 / Pi. You can also try the hot dog experiment (follow the link at the beginning of the step).
1 Spend experiment. It turns out Pi can be found by conducting an interesting experiment called the Buffon needle method, which seeks to determine the probability that accidentally thrown needles will land either between drawn equidistant parallel lines or intersect exactly one straight line. If the distance between the lines is equal to the length of the needle, then the ratio of the number of throws when the needle crosses the line to the total number of throws tends to 2 / Pi. You can also try the hot dog experiment (follow the link at the beginning of the step). - Scientists and mathematicians cannot determine the exact way to calculate pi, since they cannot find a subject so subtle that the calculations are accurate.
- Scientists and mathematicians cannot determine the exact way to calculate pi, since they cannot find a subject so subtle that the calculations are accurate.
Method 4 of 5: Calculating Pi Using a Limit
 1 Choose a large number first. The higher the number, the more accurate the result will be.
1 Choose a large number first. The higher the number, the more accurate the result will be.  2 Then plug that number (let's call it x) into the formula for pi:x * sin (180 / x) ’... For this method to work, the calculator must be turned on in Degrees mode. We say that this method uses a limit, since the result is limited to pi (that is, pi is the maximum possible value). The larger the x value, the more accurate pi will be calculated.
2 Then plug that number (let's call it x) into the formula for pi:x * sin (180 / x) ’... For this method to work, the calculator must be turned on in Degrees mode. We say that this method uses a limit, since the result is limited to pi (that is, pi is the maximum possible value). The larger the x value, the more accurate pi will be calculated.
Method 5 of 5: Arcsine function
 1 Choose any number between -1 and 1. The function y = arcsin (x) does not have x values greater than 1 or less than -1 that can be associated with any value of y (it does not matter if it is infinite or not). This means that the function y = arcsin (x) is defined only on the interval from x = -1 to x = 1, inclusive, and is not defined for any other x.
1 Choose any number between -1 and 1. The function y = arcsin (x) does not have x values greater than 1 or less than -1 that can be associated with any value of y (it does not matter if it is infinite or not). This means that the function y = arcsin (x) is defined only on the interval from x = -1 to x = 1, inclusive, and is not defined for any other x.  2 Plug your number into the following formula and you can calculate pi.
2 Plug your number into the following formula and you can calculate pi.- Pi = 2 * (Arcsin (SQRT (1 - x ^ 2))) + ABS (Arcsin (x)).
- The arcsine value will be presented in radians.
- Sqrt is the square root.
- Abs is the absolute value of a number
- x ^ 2 - in this case it is x squared.
- Pi = 2 * (Arcsin (SQRT (1 - x ^ 2))) + ABS (Arcsin (x)).
Tips
- Calculating pi is fun and interesting, but calculating many decimal places doesn't make much sense. Astrophysicists claim that pi with 39 decimal places is sufficient for cosmological calculations, which are carried out accurate to the size of an atom.