Author:
Helen Garcia
Date Of Creation:
18 April 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- Steps
- Method 1 of 4: Preparing for the examination
- Method 2 of 4: Discussing Your Health
- Method 3 of 4: Getting a physical examination
- Method 4 of 4: Next Steps
- Tips
Taking care of your reproductive health is of great importance for a woman's life. It's natural to feel anxious and anxious before a pelvic exam, especially for the first time. Knowing what to expect and preparing ahead of time can help reduce your anxiety. Prepare a list of questions in advance about any problems you have and your options for preventing unwanted pregnancies. Remember that your conversation with your doctor is confidential, so you can rest easy and discuss any concerns you have.
Steps
Method 1 of 4: Preparing for the examination
 1 Make an appointment. Regular check-ups should be scheduled between the last and the next period. Otherwise, the doctor will not be able to conduct a complete examination.
1 Make an appointment. Regular check-ups should be scheduled between the last and the next period. Otherwise, the doctor will not be able to conduct a complete examination. - If you have urgent matters, be sure to inform your doctor. Make an appointment at a convenient time for you.
- If this is your first pelvic check-up, notify the person making your appointment. Based on your medical history, you may be scheduled for an examination at a different time, and personal wishes will be taken into account during the examination.
- The first visit to the gynecologist should be planned at the age of twenty or within three years from the date of the onset of sexual activity (it all depends on which comes first). This recommendation is not universal and depends on where you live. Discuss this with your family doctor.
- Any young woman or adolescent who is sexually active, has menstrual problems, or if the menstrual cycle has not started after age 16, should be checked regularly by a gynecologist.
 2 Take a bath or shower as usual. You need to take a bath or shower within 24 hours of the appointment date of the examination, you should not use hygiene products that you have not used before.
2 Take a bath or shower as usual. You need to take a bath or shower within 24 hours of the appointment date of the examination, you should not use hygiene products that you have not used before. - You should not have sexual intercourse in the 24 hours before the examination, as this can negatively affect the test results.
- No procedures should be performed prior to examination. Do not douche, use any creams, deodorants or sprays 24 hours before the examination.
- Choose the right clothing. Remember to undress. Try not to wear clothes that are difficult to remove.
 3 Take your companion with you. If this makes you more comfortable, take a family member with you, such as your mother, older sister, or friend.
3 Take your companion with you. If this makes you more comfortable, take a family member with you, such as your mother, older sister, or friend. - Your relative or friend can wait in the waiting room or walk with you into the examination room.
 4 Prepare your questions in advance. You will be given the opportunity to ask a question about your reproductive or sexual health. These may include questions about different contraceptive methods, safe sex, sexually transmitted diseases, physiological changes in your body, and possible future problems.
4 Prepare your questions in advance. You will be given the opportunity to ask a question about your reproductive or sexual health. These may include questions about different contraceptive methods, safe sex, sexually transmitted diseases, physiological changes in your body, and possible future problems.
Method 2 of 4: Discussing Your Health
 1 Be prepared for questions about your health in general and must be answered honestly and frankly. Your doctor should have as much information about you as possible so that he can effectively cure all existing problems and prevent possible complications in the future.
1 Be prepared for questions about your health in general and must be answered honestly and frankly. Your doctor should have as much information about you as possible so that he can effectively cure all existing problems and prevent possible complications in the future. - In some clinics you will need to write your medical history, in others you may be asked specific questions about your health.
- Also, be prepared to report your sexual activity; your doctor needs to know if you are sexually active.
- Your doctor may ask you questions about your breasts, abdomen, or vagina, sexual problems that bother you, and whether you have been sexually assaulted.
- Your doctor will also ask you if you are currently or previously using contraception.
- Other questions may include your list of medications you have been prescribed, other medications including vitamins and supplements you are currently taking, and questions about your bad habits such as smoking and drinking.
 2 Be prepared for questions about your menstrual cycle. You must tell the nurse or doctor the date of your first period and your age. You may also be asked at what age your breasts began to form.
2 Be prepared for questions about your menstrual cycle. You must tell the nurse or doctor the date of your first period and your age. You may also be asked at what age your breasts began to form. - You will be asked about how many days your regular cycle lasts, for example 28 days, how long it lasts, and whether there are additional, possibly painful, symptoms.
- You also need to answer whether you have spotting or bleeding in between periods of your cycle. You may also be asked about the amount of discharge during critical days. You should be prepared to tell you how many pads or tampons you usually use, especially in the first 48 hours after your period starts.
 3 Be sure to provide information on any current issues. This can include strange vaginal discharge, foul odor, itching in the groin area, unusual pain or discomfort in the abdomen, soreness during sex, breast problems, and other symptoms.
3 Be sure to provide information on any current issues. This can include strange vaginal discharge, foul odor, itching in the groin area, unusual pain or discomfort in the abdomen, soreness during sex, breast problems, and other symptoms. - Your doctor may ask you to get tested for STIs. A urine test can detect trichomoniasis, chlamydia, and gonorrhea, and a blood test can detect HIV, herpes, and syphilis.
- It is not worth worrying about - the tests are painless; if any infection is detected in them, there are currently effective methods of treating such diseases. Early detection of STIs eliminates the risk of further complications. For example, early treatment of chlamydia and gonorrhea can prevent pelvic inflammatory disease; If the above infections are not treated promptly, it can lead to complications in the form of fertility problems and the development of chronic pelvic pain.
 4 If you suspect pregnancy, be sure to tell your doctor. A laboratory urine test will be done to confirm the result. If the pregnancy is confirmed, you will be assigned an extra appointment time.
4 If you suspect pregnancy, be sure to tell your doctor. A laboratory urine test will be done to confirm the result. If the pregnancy is confirmed, you will be assigned an extra appointment time. - You may need to get an ultrasound scan if you are unsure of the exact date or if you have cramps or bleeding.
- Lab tests include tests to determine your blood type, hemoglobin levels, and screening tests for antibodies such as rubella or chickenpox. Other tests can check for signs of hepatitis, HIV, cystic fibrosis, sickle cell disease, and tuberculosis.
- You may be asked additional questions about your medical history. This may include information about previous pregnancies, miscarriages, abortions, and contraceptive use during pregnancy.
- Your doctor will help you set up a routine for the entire pregnancy. He will tell you about prenatal vitamins, diet, nutrition, exercise, possible weight gain, travel restrictions, pets, dental services, and drug options.
Method 3 of 4: Getting a physical examination
 1 Ask your doctor about the steps in this procedure. During some of them, you may feel uncomfortable. In this case, talking with your doctor directly during the examination can help you. Ask your doctor to explain to you what exactly and how he does it.
1 Ask your doctor about the steps in this procedure. During some of them, you may feel uncomfortable. In this case, talking with your doctor directly during the examination can help you. Ask your doctor to explain to you what exactly and how he does it. - If the examination is performed by a man, a female nurse will also be in the room during the examination. If she is not there, ask her to be present.
- The outside of the groin will be examined first, then the inside. The outer areas include the clitoris, labia minora, vaginal opening, and rectum.
- An internal examination is done using a gynecological speculum to check the vaginal canal, cervix, smear, and other tissue samples as needed. An ultrasound is performed to examine the uterus and ovaries. However, internal examination is not always necessary, especially if you are not yet sexually active. Tell your doctor if you are uncomfortable with this exam. If you have been sexually assaulted, it probably won't take a single visit before you can have an internal examination. Talk to your doctor about any issues that concern you - do not be silent about them.
- A complete inspection usually takes a few minutes.
 2 Take off your clothes. After a series of routine questions and medical procedures, you will be given a special shirt and asked to undress.Remove all clothing, including underwear, unless specifically instructed by the nurse.
2 Take off your clothes. After a series of routine questions and medical procedures, you will be given a special shirt and asked to undress.Remove all clothing, including underwear, unless specifically instructed by the nurse. 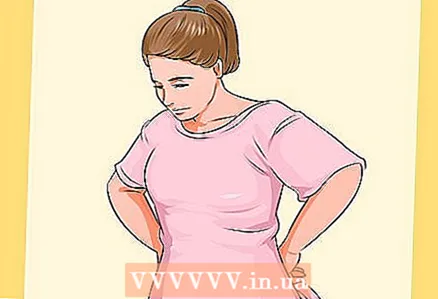 3 Put on your shirt. Gynecological examination clothing is open at the front so that your doctor can examine your breasts.
3 Put on your shirt. Gynecological examination clothing is open at the front so that your doctor can examine your breasts. - These shirts are made from a special paper material. Additional paper cover can cover the area below the knees.
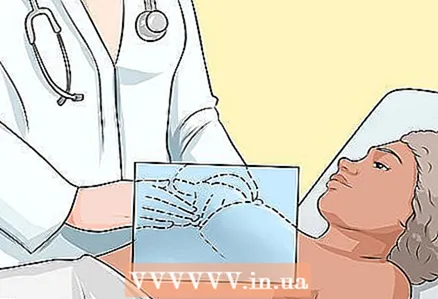 4 First of all, an examination of the mammary glands is carried out. The doctor will feel your chest in a circular motion.
4 First of all, an examination of the mammary glands is carried out. The doctor will feel your chest in a circular motion. - The doctor will check the breast tissue, including the underarm areas, as well as the nipples for possible abnormalities.
- A breast exam is done to check for lumps or other abnormalities. If you feel any discomfort during the examination, inform your doctor.
 5 Sit in a special chair. You need to position yourself so that your feet are on special supports.
5 Sit in a special chair. You need to position yourself so that your feet are on special supports. - Your legs should remain in such a position that the doctor can proceed to the next stage of the examination. Try to relax your leg muscles.
 6 Visual inspection. During this procedure, the doctor examines the vaginal area and urethra for signs of irritation, infection, or tissue changes. With the help of the urethra (urethra), urine is drawn out of the bladder.
6 Visual inspection. During this procedure, the doctor examines the vaginal area and urethra for signs of irritation, infection, or tissue changes. With the help of the urethra (urethra), urine is drawn out of the bladder. - The doctor will examine these areas, then may feel the tissue for more detailed examination. For example, if the labia are inflamed, the doctor may examine them in more detail in order to identify possible abnormalities.
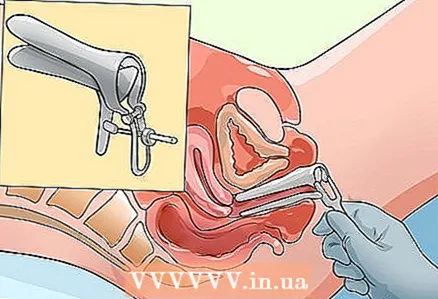 7 Prepare for the insertion of the dilator. Next, the doctor will introduce a special instrument, a gynecological speculum. It can be plastic or metal. During the insertion of the metal dilator, you will feel cold when the instrument touches the skin.
7 Prepare for the insertion of the dilator. Next, the doctor will introduce a special instrument, a gynecological speculum. It can be plastic or metal. During the insertion of the metal dilator, you will feel cold when the instrument touches the skin. - The instrument will slide into the vagina and then open wider so the doctor can examine the vaginal and cervical area.
- The speculum is applying some pressure, but you shouldn't feel pain. If you feel pain, tell your doctor. Metal dilators come in a variety of sizes, so you can use a different tool if this one provokes pain.
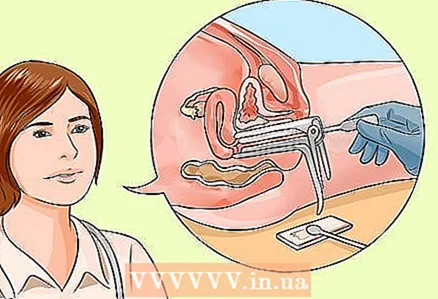 8 Learn what a PAP test is. After the doctor examines the vagina and cervix, he will insert a small swab or brush through the opening in the dilator to take a few swabs from the cervical area for analysis. This test is called a Pap smear and is not recommended until age 21.
8 Learn what a PAP test is. After the doctor examines the vagina and cervix, he will insert a small swab or brush through the opening in the dilator to take a few swabs from the cervical area for analysis. This test is called a Pap smear and is not recommended until age 21. - The sample taken will be sent to a laboratory where it will be examined in detail for the presence of abnormal or cancerous cells. For most young girls, the test gives good results.
- You will know the results of the PAP test within 10-14 days.
- If you have any problems, the doctor will take additional tissue samples for transfer to the laboratory.
 9 Palpation examination. At the next stage of the examination, the doctor will insert one or two fingers into the vagina while pressing on the abdominal area.
9 Palpation examination. At the next stage of the examination, the doctor will insert one or two fingers into the vagina while pressing on the abdominal area. - In this way, the doctor will be able to detect the possible presence of tumors and other abnormalities in the ovaries, uterus and cervix, fallopian tubes and other organs.
 10 At the end of the examination, consult your doctor again. After completing the inspection, you will be able to take off your shirt and change into your clothes. The nurse will take you to the doctor's office or waiting room, or the doctor will tell you about the results of the examination in the same room.
10 At the end of the examination, consult your doctor again. After completing the inspection, you will be able to take off your shirt and change into your clothes. The nurse will take you to the doctor's office or waiting room, or the doctor will tell you about the results of the examination in the same room. - The doctor will study the results of the examination in detail in your presence and answer your questions. He will also give you a prescription for a drug if needed, such as birth control pills.
Method 4 of 4: Next Steps
 1 Ask your doctor about your next appointment. Tests such as a Pap smear are usually done every two years. However, if this is your first time, it is recommended that you take a Pap test every year to make sure you are in good health.
1 Ask your doctor about your next appointment. Tests such as a Pap smear are usually done every two years. However, if this is your first time, it is recommended that you take a Pap test every year to make sure you are in good health. - If there are any abnormalities in the Pap smear test results (or in any other tests), the doctor will ask you to come back to the appointment to prescribe treatment or issue a referral for other tests.
 2 See your doctor if you have any concerns. Symptoms such as abdominal pain, vaginal discharge, burning sensation, foul odor, severe pain during menstruation, or spotting between cycles are a reason to see a gynecologist.
2 See your doctor if you have any concerns. Symptoms such as abdominal pain, vaginal discharge, burning sensation, foul odor, severe pain during menstruation, or spotting between cycles are a reason to see a gynecologist. - You can ask your gynecologist questions about reproductive health, contraceptive options, safe sex, and pregnancy.
- After you start to have a sex life, the gynecologist will select the most suitable method of protection for you. This may be a prescription for a drug that your doctor will prescribe for you.
- The most common methods of contraception are oral contraceptives or birth control pills, patches, injections, condoms, diaphragms, intrauterine devices, or coils.
- Remember, it is the gynecologist's job to inform women about all sorts of reproductive health issues. Don't be afraid to see your doctor, even if you are concerned about sex-related issues.
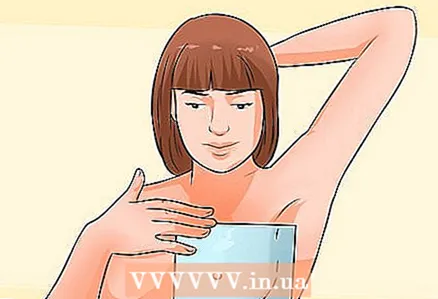 3 Conduct a self-examination of the mammary glands. Your doctor will show you how to properly examine your breasts for possible tumors. You should do this regularly and tell your doctor right away if you find a lump or lump in your breast tissue.
3 Conduct a self-examination of the mammary glands. Your doctor will show you how to properly examine your breasts for possible tumors. You should do this regularly and tell your doctor right away if you find a lump or lump in your breast tissue.
Tips
- Be honest with your doctor, even if you feel uncomfortable. Knowing what hurts or worries you, including your sex life, will help your gynecologist find the best treatment for you.
- As a rule, gynecological examinations are carried out by qualified specialists. However, nurse practitioners, physician assistants and obstetricians can also perform routine examinations.
- You can bring a family member or girlfriend with you as support. Try to honestly answer questions about your sex life, smoking habit and possibly drugs.
- During the examination, try to breathe deeply to help you relax. Inhale slowly and deeply through your nose and exhale through your mouth.
- You should understand that a man may turn out to be a gynecologist, but for them this is a very common examination procedure. A female nurse will be with you during the examination. If you do not want a man to do the examination, please let us know before making an appointment.
- In addition to the pelvic examination, a standard mammogram may also be included. It is now recommended to have an annual mammogram if you are over 50, as the risk of breast cancer increases with age.
- If this is your first pelvic exam and you don't want your parents to know about it, get tested at a specialized family planning center or your local adolescent clinic. These facilities have specialized, trained staff who respect your privacy rights, although different countries have different privacy policies for adolescent health. Your doctor will be able to explain everything to you in detail.
- Don't be afraid to ask questions. Overcome feelings of embarrassment and shame and ask about anything that interests you.