Author:
Gregory Harris
Date Of Creation:
16 August 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- Steps
- Method 1 of 6: Subtracting large integers through borrowing
- Method 2 of 6: Subtracting smaller integers
- Method 3 of 6: Subtracting decimal fractions
- Method 4 of 6: Subtracting fractions
- Method 5 of 6: Subtracting a Fraction from an Integer
- Method 6 of 6: Subtracting Variables
- Tips
- Warnings
Subtraction is the opposite of addition. It's easy to subtract whole numbers, but it's not so easy with fractions or decimal numbers. Once you learn how to subtract, you can move on to more advanced math concepts and can easily add, multiply, and divide numbers.
Steps
Method 1 of 6: Subtracting large integers through borrowing
 1 Write the larger number first. For example, let's calculate 32 - 17. First write 32.
1 Write the larger number first. For example, let's calculate 32 - 17. First write 32.  2 Write the smaller number directly below the larger number, placing units below the ones and tens below the tens (and so on). In our example, write 7 under 2 (ones) and 1 under 3 (tens).
2 Write the smaller number directly below the larger number, placing units below the ones and tens below the tens (and so on). In our example, write 7 under 2 (ones) and 1 under 3 (tens). 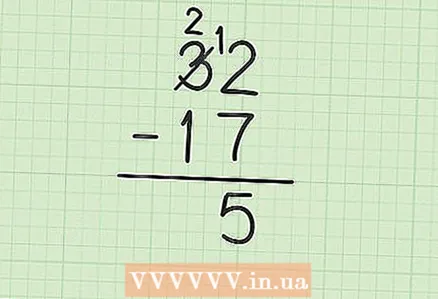 3 Subtract the bottom number from the top number. It can be a little tricky if the bottom number is larger than the top one. In our example, 7 is greater than 2. Here's what you need to do:
3 Subtract the bottom number from the top number. It can be a little tricky if the bottom number is larger than the top one. In our example, 7 is greater than 2. Here's what you need to do: - Borrow 1 from 3 (in 32) to turn 2 (in 32) into 12.
- In the number 32, cross out the number 3, and write the number 2 above it.
- Now subtract: 12 - 7 = 5. Write 5 under the digits to subtract (in the units column).
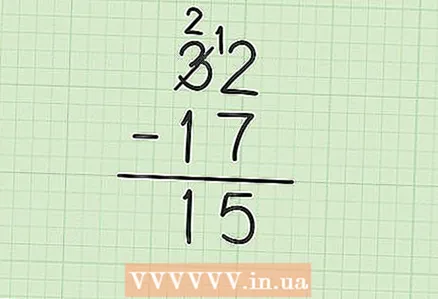 4 Subtract the numbers in the tens column. Remember that 3 has become 2. So subtract 1 (in 17) from 2 to get: 2-1 = 1. Write 1 below the digits to subtract (in the tens column to the left of 5). As a result, you get the number 15. This means that 32 - 17 = 15.
4 Subtract the numbers in the tens column. Remember that 3 has become 2. So subtract 1 (in 17) from 2 to get: 2-1 = 1. Write 1 below the digits to subtract (in the tens column to the left of 5). As a result, you get the number 15. This means that 32 - 17 = 15. 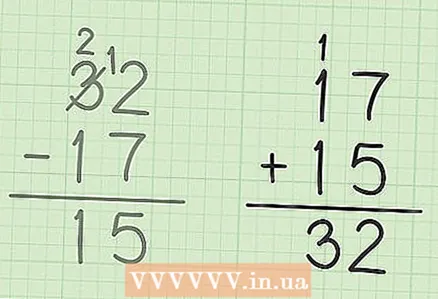 5 Check your answer. To do this, add the result and the lower number; you should get a larger number. In our example, add 15 and 17: 15 + 17 = 32. So the result is correct.
5 Check your answer. To do this, add the result and the lower number; you should get a larger number. In our example, add 15 and 17: 15 + 17 = 32. So the result is correct.
Method 2 of 6: Subtracting smaller integers
 1 Determine the larger number. Consider two examples: 15 - 9 and 2 - 30.
1 Determine the larger number. Consider two examples: 15 - 9 and 2 - 30. - In the first sample (15 - 9), the number 15 is greater than 9.
- In the second sample (2 - 30) 30 (second number) is greater than 2.
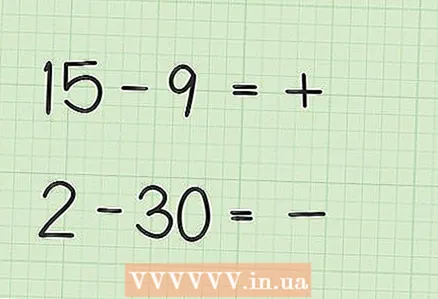 2 Determine the sign of the answer. If the first number is greater than the second, then the answer will be yes. If the second number is greater than the first, then the answer will be negative.
2 Determine the sign of the answer. If the first number is greater than the second, then the answer will be yes. If the second number is greater than the first, then the answer will be negative. - In the first problem (15 - 9), the answer will be yes, because the first number is greater than the second.
- In the second problem (2 - 30), the answer will be no, because the second number is greater than the first.
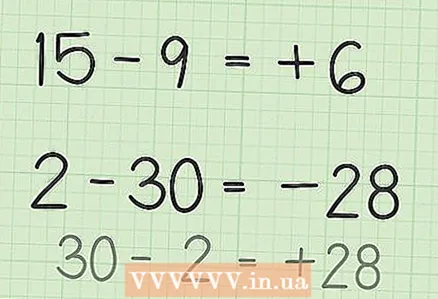 3 Find the difference between the two numbers. To do this, imagine the task as an illustrative example.
3 Find the difference between the two numbers. To do this, imagine the task as an illustrative example. - In the first problem (15 - 9), imagine that you have 15 chips. Remove 9 of them and you are left with 6 tokens. So 15 - 9 = 6. You can also represent 15 on the number line. Count 9 divisions to the left to stop at 6.
- In the second problem (2 - 30), swap the numbers, and then write a minus sign before the answer, that is, 30 - 2 = 28. Since in the problem the second number is greater than the first, the answer will be negative. So 2 - 30 = -28.
Method 3 of 6: Subtracting decimal fractions
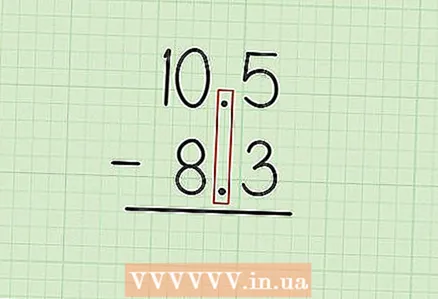 1 Write the smaller fraction directly below the larger one so that the decimal points are below each other. For example, consider Problem 10.5 - 8.3. Write 10.5 over 8.3; in this example, 3 is written under 5, and 8 under 0.
1 Write the smaller fraction directly below the larger one so that the decimal points are below each other. For example, consider Problem 10.5 - 8.3. Write 10.5 over 8.3; in this example, 3 is written under 5, and 8 under 0. - If you are given a problem in which decimal fractions have a different number of digits after the decimal point, add zeros to the fraction with fewer digits after the decimal point. For example, the given problem is 5.32 - 4.2. You can write it as 5.32 - 4.20. This does not change the initial value of the fraction to which zeros are assigned.
 2 Subtract decimals the way you do with whole numbers, but don't forget the decimal point. In our example, subtract 3 from 5: 5 - 3 = 2 and write 2 under 3 (in a fraction of 8.3).
2 Subtract decimals the way you do with whole numbers, but don't forget the decimal point. In our example, subtract 3 from 5: 5 - 3 = 2 and write 2 under 3 (in a fraction of 8.3). - In your answer, put the decimal point directly below the decimal points of the subtracted fractions.
 3 Continue to subtract the numbers from right to left. In our example, subtract 8 from 0 by borrowing 1 from the number on the left. So subtract 8 from 10 and get 2. Or, you can simply subtract 8 from 10, since there are no more digits in the second fraction (8.3) to the left of 8. Write the result of the subtraction under 8 to the left of the decimal point.
3 Continue to subtract the numbers from right to left. In our example, subtract 8 from 0 by borrowing 1 from the number on the left. So subtract 8 from 10 and get 2. Or, you can simply subtract 8 from 10, since there are no more digits in the second fraction (8.3) to the left of 8. Write the result of the subtraction under 8 to the left of the decimal point.  4 Write down your final answer. Your answer is 2.2.
4 Write down your final answer. Your answer is 2.2. 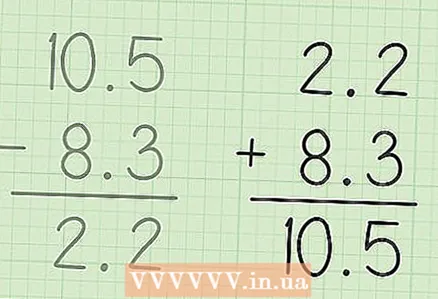 5 Check your answer. To do this, add the result and the smaller fraction; you should get a big fraction. In our example, add 2.2 and 8.3: 2.2 + 8.3 = 10.5. So the result is correct.
5 Check your answer. To do this, add the result and the smaller fraction; you should get a big fraction. In our example, add 2.2 and 8.3: 2.2 + 8.3 = 10.5. So the result is correct.
Method 4 of 6: Subtracting fractions
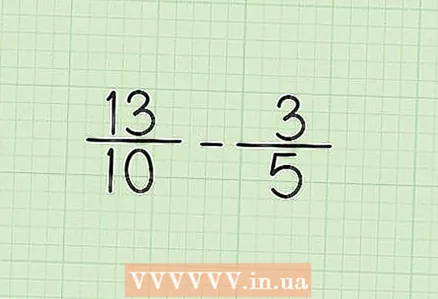 1 For example, given the problem 13/10 - 3/5. Write this problem down to match both numerators (13 and 3) and both denominators (10 and 5). Place a minus sign between the fractions.
1 For example, given the problem 13/10 - 3/5. Write this problem down to match both numerators (13 and 3) and both denominators (10 and 5). Place a minus sign between the fractions.  2 Find the lowest common denominator (LCN). The lowest common denominator is the smallest number that is divisible by both denominators. In our example, you need to find the NCD for the denominators of 10 and 5. In this case, NCD = 10, because 10 is divisible by both 5 and 10.
2 Find the lowest common denominator (LCN). The lowest common denominator is the smallest number that is divisible by both denominators. In our example, you need to find the NCD for the denominators of 10 and 5. In this case, NCD = 10, because 10 is divisible by both 5 and 10. - Please note that NOZ is not always equal to any of the denominators. For example, the lowest common denominator of 3 and 2 is 6 because it is the smallest number that can be divisible by 3 and 2.
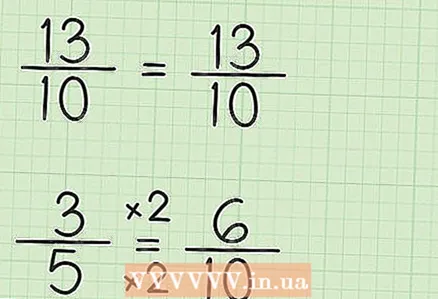 3 Bring the fractions to a common denominator. The fraction 13/10 does not need to be given, since its denominator is already equal to NOZ. To bring 3/5 to a common denominator, multiply its numerator and denominator by 2 (since 10/5 = 2). So 3/5 * 2/2 = 6/10. You do not change the value of the second fraction, but reducing it to a common denominator will allow you to subtract these fractions.
3 Bring the fractions to a common denominator. The fraction 13/10 does not need to be given, since its denominator is already equal to NOZ. To bring 3/5 to a common denominator, multiply its numerator and denominator by 2 (since 10/5 = 2). So 3/5 * 2/2 = 6/10. You do not change the value of the second fraction, but reducing it to a common denominator will allow you to subtract these fractions. - Write the problem down like this: 13/10 - 6/10.
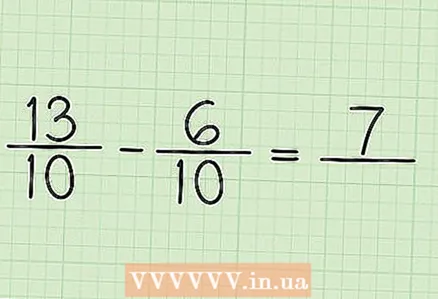 4 Subtract the numerators of the two fractions. In our example, 13 - 6 = 7. There is no need to subtract the denominators of the fractions (the denominator remains the same).
4 Subtract the numerators of the two fractions. In our example, 13 - 6 = 7. There is no need to subtract the denominators of the fractions (the denominator remains the same).  5 Write the result of subtracting the numerators over the previous denominator to get your final answer. Your new numerator is 7. Both fractions have a denominator of 10. So the final answer is 7/10.
5 Write the result of subtracting the numerators over the previous denominator to get your final answer. Your new numerator is 7. Both fractions have a denominator of 10. So the final answer is 7/10.  6 Check your answer. To do this, add the result and the smaller fraction; you should get a big fraction. In our example, add 7/10 and 6/10: 7/10 + 6/10 = 13/10. So the result is correct.
6 Check your answer. To do this, add the result and the smaller fraction; you should get a big fraction. In our example, add 7/10 and 6/10: 7/10 + 6/10 = 13/10. So the result is correct.
Method 5 of 6: Subtracting a Fraction from an Integer
 1 Write down the task. For example: 5 - 3/4.
1 Write down the task. For example: 5 - 3/4.  2 Convert an integer to a fraction with the denominator equal to the denominator of the fraction you want to subtract. In our example, convert 5 to a fraction with a denominator of 4. To get started, imagine 5 as a fraction 5/1. Then multiply the numerator and denominator of that fraction by 4 to get two fractions with a common denominator. So 5/1 * 4/4 = 20/4. This fraction is 5, but this way you can subtract a fraction from an integer.
2 Convert an integer to a fraction with the denominator equal to the denominator of the fraction you want to subtract. In our example, convert 5 to a fraction with a denominator of 4. To get started, imagine 5 as a fraction 5/1. Then multiply the numerator and denominator of that fraction by 4 to get two fractions with a common denominator. So 5/1 * 4/4 = 20/4. This fraction is 5, but this way you can subtract a fraction from an integer. 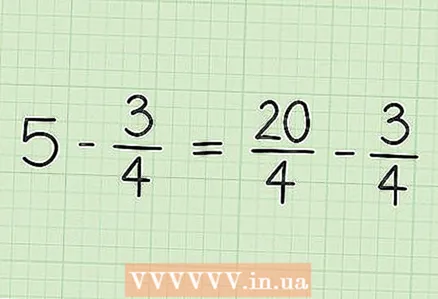 3 Rewrite the problem. In our example: 20/4 - 3/4.
3 Rewrite the problem. In our example: 20/4 - 3/4. 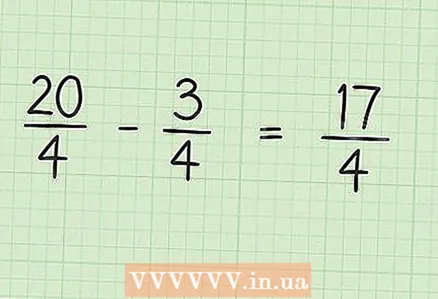 4 Subtract the numerators of the two fractions. In our example, 20 - 3 = 17. The denominators of the fractions do not need to be subtracted (the denominator remains the same).
4 Subtract the numerators of the two fractions. In our example, 20 - 3 = 17. The denominators of the fractions do not need to be subtracted (the denominator remains the same). 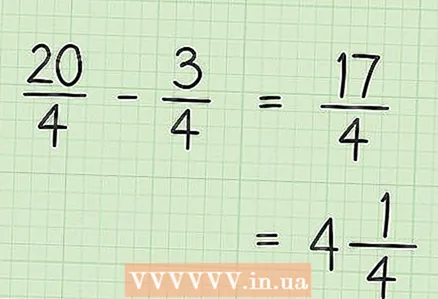 5 Write the result of subtracting the numerators over the previous denominator to get your final answer. Your new numerator is 17. Both fractions have a denominator of 4. So the final answer is 17/4. If you want to convert this improper fraction to a mixed number, divide the numerator by the denominator. Write the whole result of division as the whole part of the mixed number, write the remainder in the numerator of the fractional part of the mixed number, and write the denominator of the improper fraction in the denominator of the fractional part of the mixed number. In our example, 17/4 = 4 1/4.
5 Write the result of subtracting the numerators over the previous denominator to get your final answer. Your new numerator is 17. Both fractions have a denominator of 4. So the final answer is 17/4. If you want to convert this improper fraction to a mixed number, divide the numerator by the denominator. Write the whole result of division as the whole part of the mixed number, write the remainder in the numerator of the fractional part of the mixed number, and write the denominator of the improper fraction in the denominator of the fractional part of the mixed number. In our example, 17/4 = 4 1/4.
Method 6 of 6: Subtracting Variables
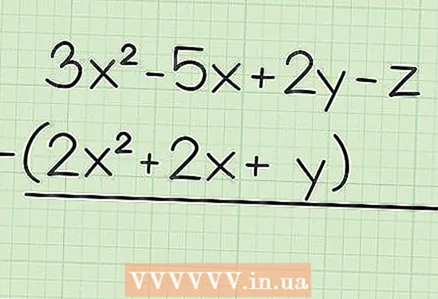 1 Write down the task. For example: 3x - 5x + 2y - z - (2x + 2x + y).
1 Write down the task. For example: 3x - 5x + 2y - z - (2x + 2x + y). 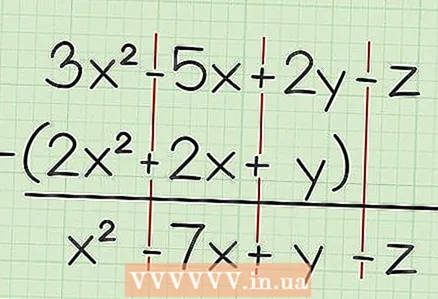 2 Subtract similar terms. These are members containing a variable with one exponent or the same variable.This means that you can subtract 4x from 7x, but you cannot subtract 4x from 4y. In our example:
2 Subtract similar terms. These are members containing a variable with one exponent or the same variable.This means that you can subtract 4x from 7x, but you cannot subtract 4x from 4y. In our example: - 3x - 2x = x
- -5x - 2x = -7x
- 2y - y = y
- -z - 0 = -z
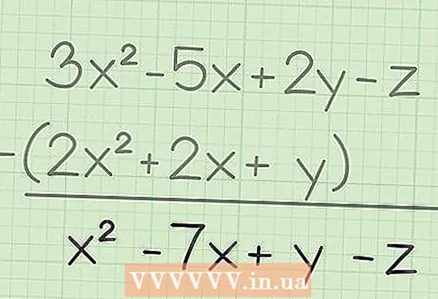 3 Write down your final answer. To do this, simply write down the results of calculating similar terms. In our example:
3 Write down your final answer. To do this, simply write down the results of calculating similar terms. In our example: - 3x - 5x + 2y - z - (2x + 2x + y) = x - 7x + y - z
Tips
- Break the larger number into smaller numbers. For example: 63 - 25. You don't need to subtract 25 at once. You can subtract 3 to get 60; then subtract 20 to get 40; then subtract the remaining number 2. Result: 38.
Warnings
- If the problem contains both positive and negative numbers, read this article.