Author:
Sara Rhodes
Date Of Creation:
17 February 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- Steps
- Method 1 of 7: Square, rectangle, parallelogram
- Method 2 of 7: Trapezoid
- Method 3 of 7: Circle
- Method 4 of 7: Sector
- Method 5 of 7: Ellipse
- Method 6 of 7: Triangle
- Method 7 of 7: Complex Shapes
- Tips
- Warnings
There are many different geometric shapes and many reasons for finding their area. Read this article if you are doing your geometry homework or if you just want to figure out the amount of paint to renovate a room.
Steps
Method 1 of 7: Square, rectangle, parallelogram
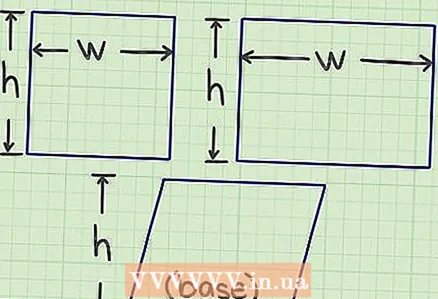 1 Measure the length and width of the shape. In other words, find the values of the two adjacent sides of the shape.
1 Measure the length and width of the shape. In other words, find the values of the two adjacent sides of the shape. - In a parallelogram, measure the height and the side to which the height is lowered.
- In a geometric problem, the values of the sides are usually given. In everyday life, the sides need to be measured.
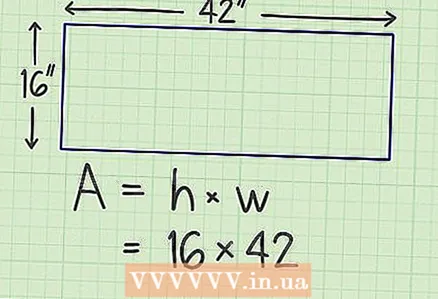 2 Multiply the sides and you will find the area. For example, to find the area of a rectangle with sides of 16 cm and 42 cm, you need to multiply 16 by 42.
2 Multiply the sides and you will find the area. For example, to find the area of a rectangle with sides of 16 cm and 42 cm, you need to multiply 16 by 42. - In a parallelogram, multiply the height and the side to which the height is lowered.
- To calculate the area of a square, you can square one of its sides. To do this, you can use the calculator: to do this, first press the desired number, and then the key responsible for squaring the number (on many calculators this is x).
 3 Write down your answer with units. Area is measured in square centimeters (meters, kilometers, etc.). Thus, the area of the rectangle is 672 square centimeters.
3 Write down your answer with units. Area is measured in square centimeters (meters, kilometers, etc.). Thus, the area of the rectangle is 672 square centimeters. - Often in problems, the square of a number is given as follows: x.
Method 2 of 7: Trapezoid
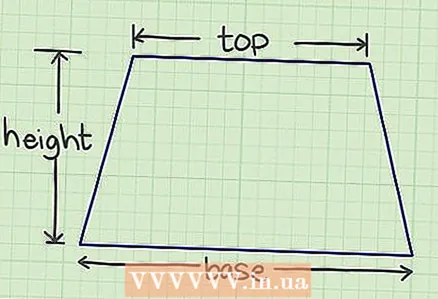 1 Find the values of the upper and lower bases of the trapezoid, as well as its height. Bases - two parallel sides of the trapezoid; height - a segment located perpendicular to the bases of the trapezoid.
1 Find the values of the upper and lower bases of the trapezoid, as well as its height. Bases - two parallel sides of the trapezoid; height - a segment located perpendicular to the bases of the trapezoid. - In a geometric problem, the values of the sides are usually given. In everyday life, the sides need to be measured.
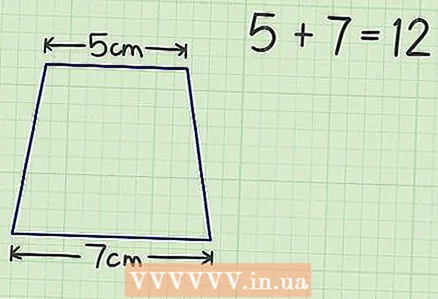 2 Fold up the top and bottom bases. For example, a trapezoid is given with bases 5 cm and 7 cm and a height of 6 cm.The sum of the bases is 12 cm.
2 Fold up the top and bottom bases. For example, a trapezoid is given with bases 5 cm and 7 cm and a height of 6 cm.The sum of the bases is 12 cm. 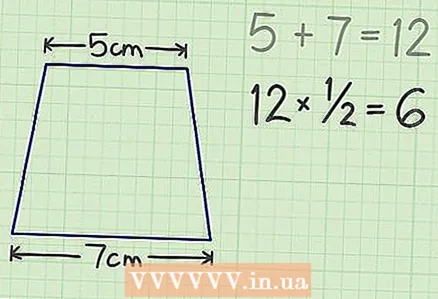 3 Multiply the result by 1/2. In our example, you will get 6.
3 Multiply the result by 1/2. In our example, you will get 6. 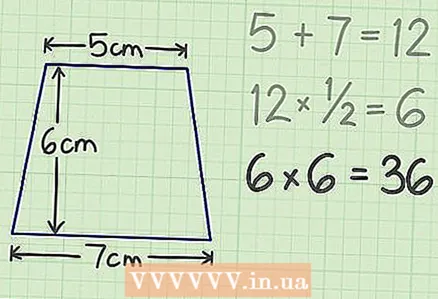 4 Multiply the result by the height. In our example, you get 36 - this is the area of the trapezoid.
4 Multiply the result by the height. In our example, you get 36 - this is the area of the trapezoid. 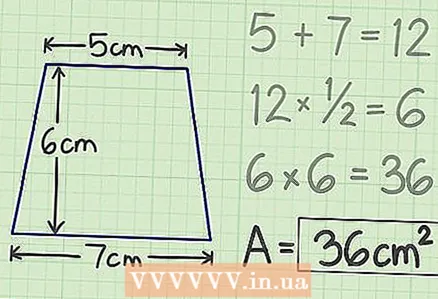 5 Write down your answer. The area of the trapezoid is 36 square meters. cm.
5 Write down your answer. The area of the trapezoid is 36 square meters. cm.
Method 3 of 7: Circle
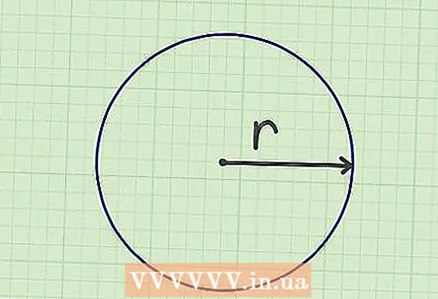 1 Find the radius of the circle. It is a line segment connecting the center of the circle and any point on the circle. You can also find the radius by dividing the diameter of the circle in half.
1 Find the radius of the circle. It is a line segment connecting the center of the circle and any point on the circle. You can also find the radius by dividing the diameter of the circle in half. - In a geometric problem, the value of the radius or diameter is usually given. They need to be measured in everyday life.
 2 Square the radius (multiply by yourself). For example, the radius is 8 cm. Then the square of the radius is 64.
2 Square the radius (multiply by yourself). For example, the radius is 8 cm. Then the square of the radius is 64.  3 Multiply the result by pi. Pi (π) is a constant equal to 3.14159. In our example, we get 201.06176 - this is the area of the circle.
3 Multiply the result by pi. Pi (π) is a constant equal to 3.14159. In our example, we get 201.06176 - this is the area of the circle.  4 Write down your answer. The area of the circle is 201.06176 sq. cm.
4 Write down your answer. The area of the circle is 201.06176 sq. cm.
Method 4 of 7: Sector
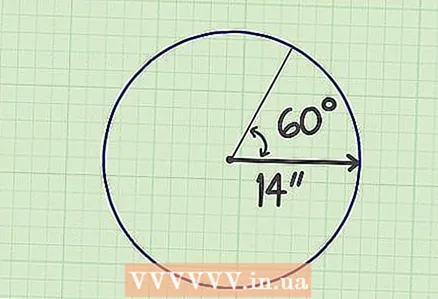 1 Use these tasks. A sector is the part of a circle bounded by two radii and an arc. To calculate its area, you need to know the radius of the circle and the central angle. For example: the radius is 14 cm and the angle is 60 °.
1 Use these tasks. A sector is the part of a circle bounded by two radii and an arc. To calculate its area, you need to know the radius of the circle and the central angle. For example: the radius is 14 cm and the angle is 60 °. - In a geometric problem, the initial data is usually given. They need to be measured in everyday life.
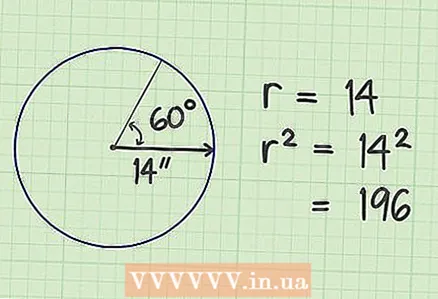 2 Square the radius (multiply by yourself). In our example, the square of the radius is 196 (14x14).
2 Square the radius (multiply by yourself). In our example, the square of the radius is 196 (14x14).  3 Multiply the result by pi. Pi (π) is a constant equal to 3.14159. In our example, we get 615.75164.
3 Multiply the result by pi. Pi (π) is a constant equal to 3.14159. In our example, we get 615.75164. 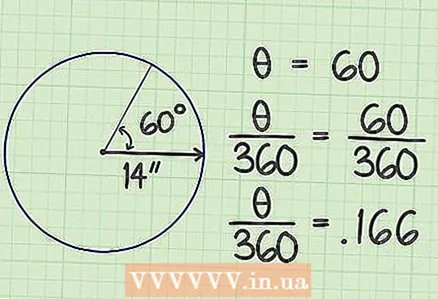 4 Divide the center angle by 360. In our example, the center angle is 60 degrees, resulting in 0.166.
4 Divide the center angle by 360. In our example, the center angle is 60 degrees, resulting in 0.166.  5 Multiply this result (dividing the angle by 360) by the previous result (pi times the square of the radius). In our example, you get 102.214 - this is the area of the sector.
5 Multiply this result (dividing the angle by 360) by the previous result (pi times the square of the radius). In our example, you get 102.214 - this is the area of the sector. 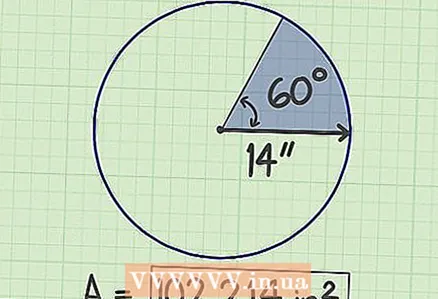 6 Write down your answer. The area of the sector is 102.214 sq. cm.
6 Write down your answer. The area of the sector is 102.214 sq. cm.
Method 5 of 7: Ellipse
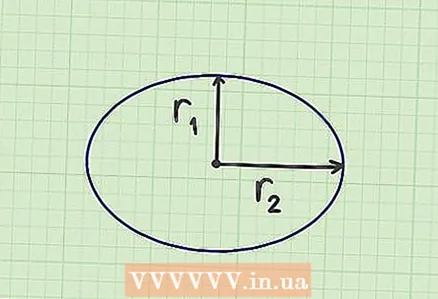 1 Use initial data. To calculate the area of an ellipse, you need to know the semi-major axis and the semi-minor axis of the ellipse (that is, half the axes of the ellipse). Semi-axes are segments drawn from the center of the ellipse to its vertices on the major and minor axes. The semiaxes form a right angle.
1 Use initial data. To calculate the area of an ellipse, you need to know the semi-major axis and the semi-minor axis of the ellipse (that is, half the axes of the ellipse). Semi-axes are segments drawn from the center of the ellipse to its vertices on the major and minor axes. The semiaxes form a right angle. - In a geometric problem, the initial data is usually given.They need to be measured in everyday life.
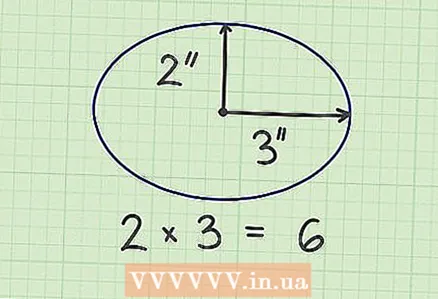 2 Multiply the semiaxes. For example, the axes of the ellipse are 6 cm and 4 cm. Thus, the semi-axes of the ellipse are 3 cm and 2 cm. Multiply the semi-axes and get 6.
2 Multiply the semiaxes. For example, the axes of the ellipse are 6 cm and 4 cm. Thus, the semi-axes of the ellipse are 3 cm and 2 cm. Multiply the semi-axes and get 6.  3 Multiply the result by pi. Pi (π) is a constant equal to 3.14159. In our example, we get 18.84954 - this is the area of the ellipse.
3 Multiply the result by pi. Pi (π) is a constant equal to 3.14159. In our example, we get 18.84954 - this is the area of the ellipse.  4 Write down your answer. The area of the ellipse is 18.84954 sq. cm.
4 Write down your answer. The area of the ellipse is 18.84954 sq. cm.
Method 6 of 7: Triangle
 1 Find the values for the height of the triangle and the side to which this height is lowered. For example, the height of a triangle is 1 m, and the side to which the height is dropped is 3 m.
1 Find the values for the height of the triangle and the side to which this height is lowered. For example, the height of a triangle is 1 m, and the side to which the height is dropped is 3 m. - In a geometric problem, the initial data is usually given. They need to be measured in everyday life.
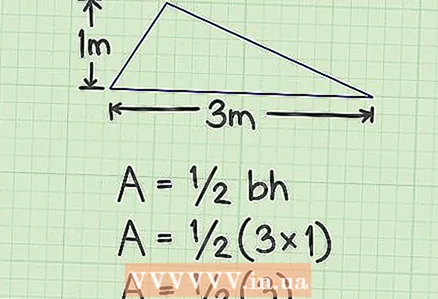 2 Multiply the height and side. In our example, you will get 3.
2 Multiply the height and side. In our example, you will get 3. 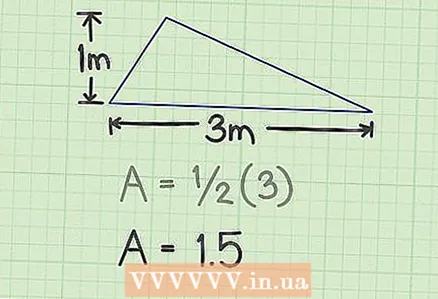 3 Multiply the result by 1/2. In our example, you get 1.5 - this is the area of the triangle.
3 Multiply the result by 1/2. In our example, you get 1.5 - this is the area of the triangle. 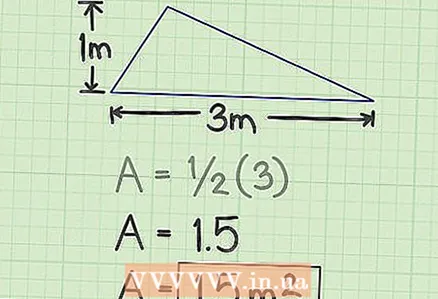 4 Write down your answer. The area of the triangle is 1.5 square meters. m.
4 Write down your answer. The area of the triangle is 1.5 square meters. m.
Method 7 of 7: Complex Shapes
 1 To calculate the area of a complex shape, divide it into several standard shapes, calculate the area of each of them, and add the results. In a geometric problem, this is easy to do, but in everyday life, you will most likely have to break a complex shape into many standard shapes.
1 To calculate the area of a complex shape, divide it into several standard shapes, calculate the area of each of them, and add the results. In a geometric problem, this is easy to do, but in everyday life, you will most likely have to break a complex shape into many standard shapes. - Start by looking for right angles and parallel lines. These will serve as the basis for the standard shapes.
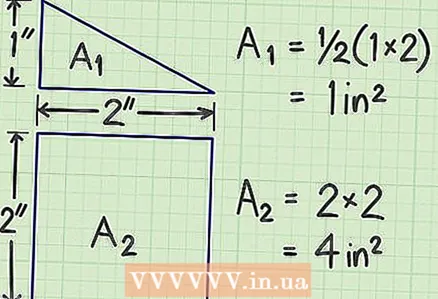 2 Calculate the area of each standard shape using the methods described above.
2 Calculate the area of each standard shape using the methods described above.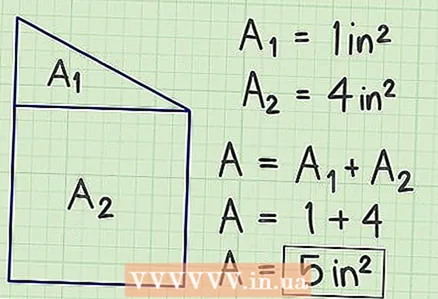 3 Add up the areas found. This will calculate the area of a complex shape.
3 Add up the areas found. This will calculate the area of a complex shape.  4 Use alternative methods. For example, add an “imaginary” shape to a complex shape that will turn the complex shape into a standard shape. Find the area of such a standard shape, and then subtract the area of the "imaginary" shape from it. You will find the area of a complex shape.
4 Use alternative methods. For example, add an “imaginary” shape to a complex shape that will turn the complex shape into a standard shape. Find the area of such a standard shape, and then subtract the area of the "imaginary" shape from it. You will find the area of a complex shape.
Tips
- Use this area calculator if you need help or want to look at the calculation process.
- If you need help, ask someone with a knowledge of geometry for it.
Warnings
- Make sure that the calculations involve quantities measured in the same units (for example, only in centimeters, or only in meters, and so on).
- Always check the answer!



