Author:
Marcus Baldwin
Date Of Creation:
19 June 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024
Content
- Steps
- Method 1 of 4: Learn the basics of trigonometry
- Method 2 of 4: Using trigonometry
- Method 3 of 4: Study the material ahead of time
- Method 4 of 4: Take notes
- Tips
- Warnings
Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics that studies trigonometric functions and their use in geometry. Trigonometric functions are used to describe the properties of various angles, triangles, and periodic functions. Learning trigonometry will help you understand these properties. Classes at school and independent work will help you master the basics of trigonometry and understand many of the periodic processes.
Steps
Method 1 of 4: Learn the basics of trigonometry
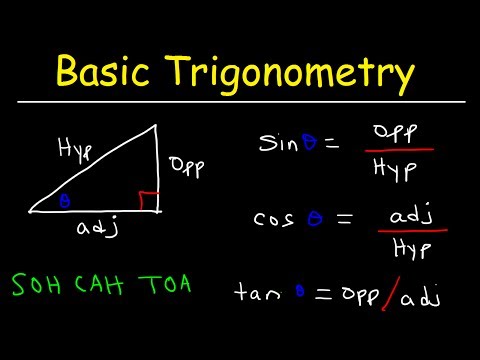
 1 Become familiar with the concept of a triangle. Basically, trigonometry deals with the study of various relationships in triangles. A triangle has three sides and three corners. The angles of any triangle add up to 180 degrees. When learning trigonometry, you need to be familiar with triangles and related concepts, such as:
1 Become familiar with the concept of a triangle. Basically, trigonometry deals with the study of various relationships in triangles. A triangle has three sides and three corners. The angles of any triangle add up to 180 degrees. When learning trigonometry, you need to be familiar with triangles and related concepts, such as: - hypotenuse - the longest side of a right triangle;
- obtuse angle - an angle of more than 90 degrees;
- acute angle - angle less than 90 degrees.
 2 Learn to draw a unit circle. The unit circle makes it possible to construct any right-angled triangle so that the hypotenuse is equal to one. This is useful when working with trigonometric functions such as sine and cosine. Having mastered the unit circle, you can easily find the values of trigonometric functions for certain angles and solve problems in which triangles with these angles appear.
2 Learn to draw a unit circle. The unit circle makes it possible to construct any right-angled triangle so that the hypotenuse is equal to one. This is useful when working with trigonometric functions such as sine and cosine. Having mastered the unit circle, you can easily find the values of trigonometric functions for certain angles and solve problems in which triangles with these angles appear. - Example 1. The sine of an angle of 30 degrees is 0.50.This means that the length of the leg opposite to this angle is half the length of the hypotenuse.
- Example 2. Using this ratio, you can calculate the length of the hypotenuse of a triangle in which there is an angle of 30 degrees, and the length of the leg opposite to this angle is 7 centimeters. In this case, the length of the hypotenuse will be 14 centimeters.
 3 Check out trigonometric functions. There are six basic trigonometric functions that you need to know when learning trigonometry. These functions represent the relationship between the different sides of a right triangle and help you understand the properties of any triangle. These six functions are:
3 Check out trigonometric functions. There are six basic trigonometric functions that you need to know when learning trigonometry. These functions represent the relationship between the different sides of a right triangle and help you understand the properties of any triangle. These six functions are: - sine (sin);
- cosine (cos);
- tangent (tg);
- secant (sec);
- cosecant (cosec);
- cotangent (ctg).
 4 Remember the relationships between functions. When learning trigonometry, it is extremely important to understand that all trigonometric functions are related. Although sine, cosine, tangent and other functions are used in different ways, they are widely used due to the fact that there are certain relationships between them. These relationships are easy to understand using the unit circle. Learn to use the unit circle, and with the help of the relationships it describes, you can solve many problems.
4 Remember the relationships between functions. When learning trigonometry, it is extremely important to understand that all trigonometric functions are related. Although sine, cosine, tangent and other functions are used in different ways, they are widely used due to the fact that there are certain relationships between them. These relationships are easy to understand using the unit circle. Learn to use the unit circle, and with the help of the relationships it describes, you can solve many problems.
Method 2 of 4: Using trigonometry
 1 Learn about the main areas of science that use trigonometry. Trigonometry is useful in many areas of mathematics and other exact sciences. With the help of trigonometry, you can find the values of angles and straight line segments. In addition, trigonometric functions can describe any cyclic process.
1 Learn about the main areas of science that use trigonometry. Trigonometry is useful in many areas of mathematics and other exact sciences. With the help of trigonometry, you can find the values of angles and straight line segments. In addition, trigonometric functions can describe any cyclic process. - For example, the oscillation of a spring can be described as a sinusoidal function.
 2 Think about batch processes. Sometimes the abstract concepts of mathematics and other exact sciences are difficult to understand. However, they are present in the world around them, and this can make them easier to understand. Take a closer look at the periodic phenomena around you and try to connect them to trigonometry.
2 Think about batch processes. Sometimes the abstract concepts of mathematics and other exact sciences are difficult to understand. However, they are present in the world around them, and this can make them easier to understand. Take a closer look at the periodic phenomena around you and try to connect them to trigonometry. - The moon has a predictable cycle that lasts about 29.5 days.
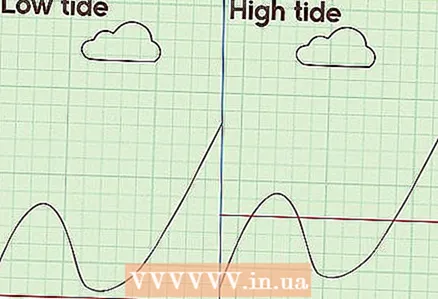 3 Imagine how you can study natural cycles. When you understand that there are many periodic processes in nature, think about how you can study them. Imagine how the image of such processes looks on the graph. Using the graph, you can write an equation that describes the observed phenomenon. This is where trigonometric functions come in handy.
3 Imagine how you can study natural cycles. When you understand that there are many periodic processes in nature, think about how you can study them. Imagine how the image of such processes looks on the graph. Using the graph, you can write an equation that describes the observed phenomenon. This is where trigonometric functions come in handy. - Imagine the ebb and flow of the seaside. When the tide is high, the water rises to a certain level, and then the tide comes and the water level drops. After ebb tide, the tide follows again, and the water level rises. This cyclical process can continue indefinitely. It can be described by a trigonometric function such as cosine.
Method 3 of 4: Study the material ahead of time
 1 Read the appropriate section. Some people find it difficult to grasp the ideas of trigonometry the first time. If you read the relevant material before class, you’ll be better off assimilating it. Try to repeat the subject more often - this way you will discover more relationships between different concepts and concepts of trigonometry.
1 Read the appropriate section. Some people find it difficult to grasp the ideas of trigonometry the first time. If you read the relevant material before class, you’ll be better off assimilating it. Try to repeat the subject more often - this way you will discover more relationships between different concepts and concepts of trigonometry. - It also allows you to identify unclear points in advance.
 2 Take notes. While a cursory glance at a textbook is better than nothing, slow, thoughtful reading is essential when learning trigonometry. Take detailed notes as you study a section. Remember that knowledge of trigonometry builds up gradually, and new material builds on what was previously learned, so writing down what you have already covered will help you move further.
2 Take notes. While a cursory glance at a textbook is better than nothing, slow, thoughtful reading is essential when learning trigonometry. Take detailed notes as you study a section. Remember that knowledge of trigonometry builds up gradually, and new material builds on what was previously learned, so writing down what you have already covered will help you move further. - Among other things, write down any questions you have so that you can ask your teacher later.
 3 Solve the tasks in the tutorial. Even if trigonometry is easy for you, you need to solve problems. To make sure that you really understand what you have learned, try to solve several problems before class.If you have any problems with this, you will determine what exactly you need to find out during the class.
3 Solve the tasks in the tutorial. Even if trigonometry is easy for you, you need to solve problems. To make sure that you really understand what you have learned, try to solve several problems before class.If you have any problems with this, you will determine what exactly you need to find out during the class. - Many textbooks have answers to problems at the end. With their help, you can check if you have solved the problems correctly.
 4 Take everything you need to class. Do not forget your notebooks with notes and problem solutions. These materials at hand will help you to refresh your memory of what you have already passed and move further in the study of the material. Also clarify any questions that have arisen during the preliminary reading of the textbook.
4 Take everything you need to class. Do not forget your notebooks with notes and problem solutions. These materials at hand will help you to refresh your memory of what you have already passed and move further in the study of the material. Also clarify any questions that have arisen during the preliminary reading of the textbook.
Method 4 of 4: Take notes
 1 Write everything down in one notebook. The various sections of trigonometry are closely related. It is best to write everything down in one place so that you can refresh your memory at any time. Set aside a separate notebook or folder for your notes.
1 Write everything down in one notebook. The various sections of trigonometry are closely related. It is best to write everything down in one place so that you can refresh your memory at any time. Set aside a separate notebook or folder for your notes. - Problem solutions can also be recorded there.
 2 Be attentive during class. Don't be distracted by chatting with friends or doing homework on another subject. Give all your attention to the subject and tasks being presented. Write down any important information and what the teacher writes on the board.
2 Be attentive during class. Don't be distracted by chatting with friends or doing homework on another subject. Give all your attention to the subject and tasks being presented. Write down any important information and what the teacher writes on the board.  3 Take the initiative. Call on the board to solve problems and answer the questions that the teacher asks. Ask questions yourself if anything is unclear to you. Discuss the study material with the teacher and classmates (within the limits of what is permitted). This will make the learning process easier and more enjoyable.
3 Take the initiative. Call on the board to solve problems and answer the questions that the teacher asks. Ask questions yourself if anything is unclear to you. Discuss the study material with the teacher and classmates (within the limits of what is permitted). This will make the learning process easier and more enjoyable. - If the teacher prefers not to be interrupted, you can ask questions after class. Don't be shy: the teacher's job is to help you learn trigonometry.
 4 Try to solve more problems. Do all your homework. Homework helps to better assimilate the material covered. Check if everything is clear to you. If the teacher did not ask anything at home, open the textbook and solve the problems on the last completed topic.
4 Try to solve more problems. Do all your homework. Homework helps to better assimilate the material covered. Check if everything is clear to you. If the teacher did not ask anything at home, open the textbook and solve the problems on the last completed topic.
Tips
- Remember that learning math is about learning a certain way of thinking, not just memorizing formulas.
- Before learning trigonometry, brush up on the basics of algebra and geometry.
Warnings
- Trigonometry cannot be learned by automatic memorization. You need to understand the basic ideas and methods.
- Simple cramming is ineffective in learning trigonometry.