Author:
William Ramirez
Date Of Creation:
15 September 2021
Update Date:
21 June 2024

Content
- Steps
- Method 1 of 3: Measuring Distance with a Linear Scale
- Method 2 of 3: Numerical Distance Measurement
- Method 3 of 3: Further Measurements
- Warnings
- What do you need
- Additional articles
A topographic map is a two-dimensional map that depicts three-dimensional terrain, with the elevation of the earth's surface indicated using contour lines. As with any map, the distance between two points on a topographic map is measured along a straight line connecting them, as if a bird were flying between these points. This is done first, and only then the surface relief and other terrain features that may affect the overall length of the route are taken into account. Learn how to measure distance along a straight line.
Steps
Method 1 of 3: Measuring Distance with a Linear Scale
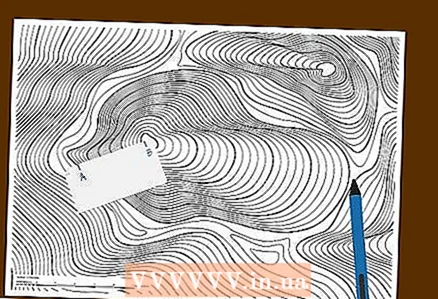 1 Place a strip of paper on the map and mark the dots on it. Place a strip of paper with a straight edge on the card.Align this edge at the same time with the first (“point A”) and second (“point B”) points, the distance between which you want to measure, and mark on the paper the location of these points.
1 Place a strip of paper on the map and mark the dots on it. Place a strip of paper with a straight edge on the card.Align this edge at the same time with the first (“point A”) and second (“point B”) points, the distance between which you want to measure, and mark on the paper the location of these points. - Take a strip of paper long enough to cover the distance between the points of interest. Note that this method is better suited for measuring relatively short linear distances.
- Press a strip of paper against the map and try to mark the location of the two dots on it as accurately as possible.
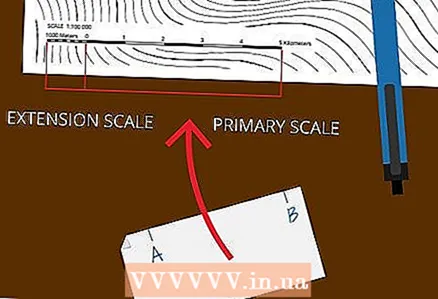 2 Attach a strip of paper to a linear scale. Look for a linear scale on a topographic map - usually located in the lower left corner of the map. Place a strip of paper with two marks on it to determine the distance between them. Use this method to measure small distances that fit on a linear scale.
2 Attach a strip of paper to a linear scale. Look for a linear scale on a topographic map - usually located in the lower left corner of the map. Place a strip of paper with two marks on it to determine the distance between them. Use this method to measure small distances that fit on a linear scale. - First of all, pay attention to the proportion shown on a linear scale. It indicates what real distance corresponds to the unit of length on the map. For example, topographic maps often have a scale of 1: 100000, which means that one centimeter on the map corresponds to one kilometer on the ground; if the scale is 1: 50,000, then one centimeter contains 500 meters, and so on.
- On a linear scale, the main scale is usually given. This scale is divided into equal segments, which are called the base of the scale. They are counted from left to right from the zero value, and the corresponding integer values are indicated next to them. In addition, an additional, more detailed scale is shown from right to left, on which the base of the scale is divided into smaller segments.
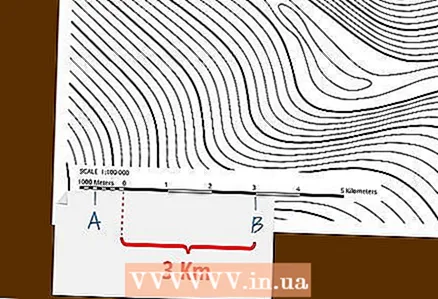 3 Determine bOmost of the distance on the main scale. Place a strip of paper on the scale so that the right mark aligns with a whole number on the scale. In this case, the left mark should be on the additional scale.
3 Determine bOmost of the distance on the main scale. Place a strip of paper on the scale so that the right mark aligns with a whole number on the scale. In this case, the left mark should be on the additional scale. - The point of the main scale, in which the right mark will be, is determined by the condition that the left mark must fall on the additional scale. In this case, it is necessary to combine the right label with an integer on the main scale.
- The integer corresponding to the right mark on the main scale indicates that the measured distance is at least so many meters or kilometers. The remainder of the distance can be more accurately determined using an additional scale.
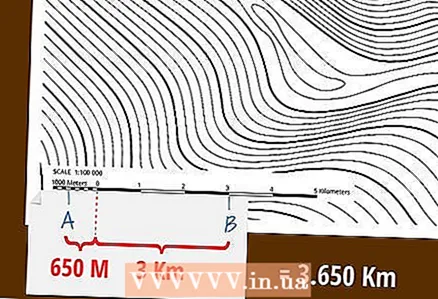 4 Go to the additional scale on which the base of the scale is divided into parts. Determine the length of the smaller part of the distance using the additional scale. The left mark will coincide with a whole number on the secondary scale - this number should be divided by ten and added to the distance determined on the primary scale.
4 Go to the additional scale on which the base of the scale is divided into parts. Determine the length of the smaller part of the distance using the additional scale. The left mark will coincide with a whole number on the secondary scale - this number should be divided by ten and added to the distance determined on the primary scale. - As a rule, individual segments on the additional scale are small rectangles, which for convenience are colored alternately in dark and light colors. You can even estimate smaller fractions of the distance - for this, you should mentally divide a short segment of the scale into ten parts and determine how many such parts are cut off by the left mark.
- Suppose one centimeter on a linear scale corresponds to 1000 meters: then if the right mark coincides with the number 3, the distance between the points is at least 3000 meters, or 3 kilometers. If at the same time the left mark falls on the left scale on the segment corresponding to the distance of 900 meters, these 900 meters should be added to 3 kilometers. If the left mark is exactly in the middle of this segment, this adds another 50 meters (since the length of the whole segment is 100 meters), which should be added to the total distance. As a result, the distance between the points will be 3950 meters.
Method 2 of 3: Numerical Distance Measurement
 1 Mark the distance on the strip of paper. Place a strip of paper with a straight edge on the card and align that edge with the points you want to measure between. Mark on the paper “point A” and “point B”.
1 Mark the distance on the strip of paper. Place a strip of paper with a straight edge on the card and align that edge with the points you want to measure between. Mark on the paper “point A” and “point B”. - Press the strip of paper against the card and do not bend it for the most accurate results possible.
- If you wish, you can use a ruler or measuring tape instead of paper. In this case, write down the measured distance between the points in millimeters.
 2 Measure the distance with a ruler. Place a ruler or measuring tape on the paper and measure the distance between the two marks. Use this method to measure large distances that are outside the linear scale, or if you want to calculate the distance as accurately as possible.
2 Measure the distance with a ruler. Place a ruler or measuring tape on the paper and measure the distance between the two marks. Use this method to measure large distances that are outside the linear scale, or if you want to calculate the distance as accurately as possible. - Try to determine the distance to the nearest millimeter.
- Find the scale at the bottom of the map. Here the ratio of lengths should be given, as well as a segment (linear scale) with centimeters laid out on it. As a rule, for convenience, the scale is chosen in whole numbers, for example, 1 centimeter = 1 kilometer.
 3 Calculate the distance along a straight line. To do this, use the distance measured on the map in millimeters and the numerical scale, which is the ratio of the lengths. Multiply the measured distance by the denominator of the scale.
3 Calculate the distance along a straight line. To do this, use the distance measured on the map in millimeters and the numerical scale, which is the ratio of the lengths. Multiply the measured distance by the denominator of the scale. - Suppose the map shows a scale of 1: 10000. If the distance measured on the map between points A and B is 10 centimeters, multiply 10 by 10,000. As a result, the distance in a straight line between points A and B will be 100,000 centimeters.
- You can convert the resulting distance into more convenient units. In our example, 100,000 centimeters is 1 kilometer.
Method 3 of 3: Further Measurements
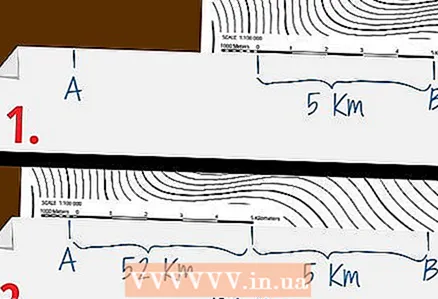 1 Measure a distance that is too far for a linear scale. The distance between points can exceed the length of the linear scale shown on the map. In this case, you can split the distance into several shorter segments, or use a ruler or measuring tape.
1 Measure a distance that is too far for a linear scale. The distance between points can exceed the length of the linear scale shown on the map. In this case, you can split the distance into several shorter segments, or use a ruler or measuring tape. - To use the linear scale for long distance measurements, align the right hand mark with the rightmost point of the linear scale. Then mark the left edge of the linear scale on a strip of paper and note the distance between this point and the right mark. Then use the new point as the right mark and measure the distance between it and the left mark using a linear scale. Add this distance to the previous value, and you get the desired distance between the points.
- If the distance between the points is too great and you are missing a ruler, try using a measuring tape.
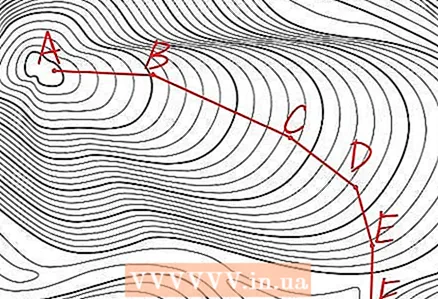 2 To measure the distance along a curved line, break it into straight segments. If you need to measure the distance between several points that do not lie on one straight line, it is enough to determine the distances between adjacent points and add them. If you want to measure the distance along a smooth curved line, break it into straight lines and add up their lengths as well.
2 To measure the distance along a curved line, break it into straight segments. If you need to measure the distance between several points that do not lie on one straight line, it is enough to determine the distances between adjacent points and add them. If you want to measure the distance along a smooth curved line, break it into straight lines and add up their lengths as well. - As with other things, use a strip of paper with a straight edge to measure. Instead of measuring the distance between two points A and B, measure the lengths of straight line segments along a curved line and add them together. You can also sequentially apply a strip of paper to these segments so that the end point of the previous segment coincides with the starting point of the next one, and thus plot the lengths of all segments on paper, and then use a linear scale to measure the distance between the start and end points.
- For greater accuracy, break the curved line into more straight lines.
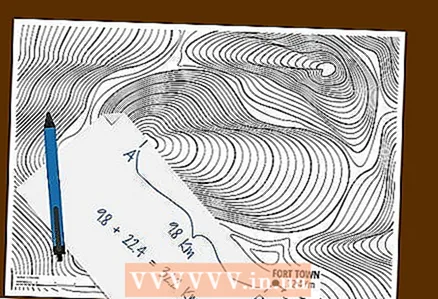 3 Find the distance to a point that lies outside the map. Many topographic maps show the distance from the edge of the map to an object that is not shown on the map - cities, highways, traffic intersections, and so on. Measure the distance from the point of interest to the edge of the map and add the indicated distance to the object to it.
3 Find the distance to a point that lies outside the map. Many topographic maps show the distance from the edge of the map to an object that is not shown on the map - cities, highways, traffic intersections, and so on. Measure the distance from the point of interest to the edge of the map and add the indicated distance to the object to it. - First, measure the distance from point A to the edge of the card using a piece of paper or a ruler as described above.After that, add to it the distance to the object of interest, which is indicated on the fields of the map. As a result, you will find the distance from point A to this object.
- Before adding the distances, make sure they are expressed in the same units.
Warnings
- Generally, straight line distance is not good for route planning because it does not take into account terrain and other terrain features. In fact, the distance is almost always greater than that which is measured on the map along a straight line.
What do you need
- Topographic map
- A strip of paper with a straight edge
- Pencil or pen
- Ruler or measuring tape (optional)
- Calculator (optional)
Additional articles
How to use the compass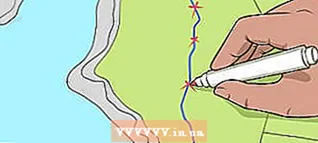 How to read the card
How to read the card  How to find directions without a compass
How to find directions without a compass  How to find latitude and longitude
How to find latitude and longitude  How to read coordinates in UTM system
How to read coordinates in UTM system  How to calculate the distance traveled using steps
How to calculate the distance traveled using steps  How to use the card
How to use the card  How to fry marshmallows
How to fry marshmallows  How to survive a wolf attack
How to survive a wolf attack  How to survive a fall from a great height
How to survive a fall from a great height  How to keep hornets away from your home How to light a match
How to keep hornets away from your home How to light a match  How to assemble a tent
How to assemble a tent  How to survive in the forest
How to survive in the forest