Author:
Joan Hall
Date Of Creation:
2 July 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- Steps
- Part 1 of 4: Determining the Systolic Pressure from the Pulse
- Part 2 of 4: Using Pressure Applications
- Part 3 of 4: Interpreting Pressure Measurements
- Part 4 of 4: How to Improve Your Blood Pressure Readings
Blood pressure is the force with which the blood passing through the vessels presses against their walls. This is an important indicator that helps to determine the state of a person's health. There is a special device for measuring blood pressure - a tonometer, but it is not always at hand. In order to approximately estimate your systolic pressure (the pressure at the time of contraction of the heart muscle), you can simply measure the pulse. Diastolic pressure (at the time of relaxation of the heart muscle) can only be measured with a tonometer.
Steps
Part 1 of 4: Determining the Systolic Pressure from the Pulse
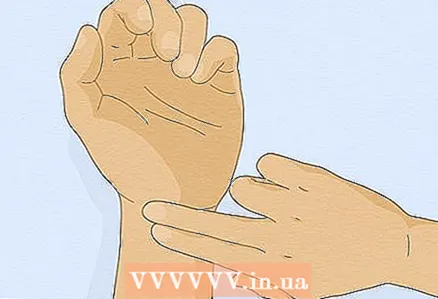 1 Press your fingers to the inside of your wrist. The first thing to do to determine the systolic ("upper") pressure is to feel your pulse. The pulse can be used to determine if your systolic pressure is within the normal range. Please note that the result will be very approximate: it can only help you understand if your systolic pressure is too low. Increased pressure cannot be detected in this way.
1 Press your fingers to the inside of your wrist. The first thing to do to determine the systolic ("upper") pressure is to feel your pulse. The pulse can be used to determine if your systolic pressure is within the normal range. Please note that the result will be very approximate: it can only help you understand if your systolic pressure is too low. Increased pressure cannot be detected in this way. - Place two fingers, preferably your index and middle fingers, on the thumb side of your wrist.
- The thumb is not used to determine the heart rate, as it has a rather strong own heart rate, which makes it difficult to find the pulse on the wrist.
 2 Feel for your pulse. Putting two fingers to your wrist, try to feel for a pulse - the waves of blood that your heart, contracting, pushes through the vessels. If you manage to find a pulse, this means that your systolic pressure is above 80 mm Hg, that is, within normal limits. However, high blood pressure cannot be detected in this way. If you cannot feel your pulse on your wrist, then your systolic pressure is most likely below 80 mmHg, which is also a normal variation.
2 Feel for your pulse. Putting two fingers to your wrist, try to feel for a pulse - the waves of blood that your heart, contracting, pushes through the vessels. If you manage to find a pulse, this means that your systolic pressure is above 80 mm Hg, that is, within normal limits. However, high blood pressure cannot be detected in this way. If you cannot feel your pulse on your wrist, then your systolic pressure is most likely below 80 mmHg, which is also a normal variation. - Why does wrist pulse mean systolic pressure is above 80 mmHg? The fact is that the radial artery, which is located on the wrist, is a rather small blood vessel, and in order for it to fill with blood when the heart muscle contracts, blood pressure must be at least 80 mmHg.
- If you have not been able to feel the pulse on your wrist, this does not mean that you have health problems.
- Without a tonometer, the diastolic ("lower") pressure cannot be determined.
- Some studies have questioned the effectiveness of measuring systolic pressure from the pulse.
 3 Re-measure your heart rate after a little physical activity. After a while, measure your heart rate again to check how fast it increases after exercise. This will help you more accurately determine if your blood pressure is high, normal, or low.
3 Re-measure your heart rate after a little physical activity. After a while, measure your heart rate again to check how fast it increases after exercise. This will help you more accurately determine if your blood pressure is high, normal, or low. - If you were unable to find your pulse after moderate exercise, then your blood pressure is most likely low.
- If you think your blood pressure is abnormal, see your doctor.
Part 2 of 4: Using Pressure Applications
 1 Please be aware that blood pressure applications are highly error-prone. Such applications are convenient to use, but, unfortunately, they cannot replace a real medical blood pressure monitor. Pressure applications are not medical devices; rather, they are classified as entertainment applications. When using these applications, please be aware that the data you receive from them is not accurate.
1 Please be aware that blood pressure applications are highly error-prone. Such applications are convenient to use, but, unfortunately, they cannot replace a real medical blood pressure monitor. Pressure applications are not medical devices; rather, they are classified as entertainment applications. When using these applications, please be aware that the data you receive from them is not accurate. - New technology is currently being developed that will allow clinicians to measure blood pressure without using a cuff. However, this technology has not yet been implemented.
 2 Open the app store on your smartphone. In the health category, you will find a range of applications that measure blood pressure, among others. Choose the app store that matches your operating system.
2 Open the app store on your smartphone. In the health category, you will find a range of applications that measure blood pressure, among others. Choose the app store that matches your operating system. - Enter the phrase "pressure measurement" in the search box.
- You will see a list of blood pressure apps.
- When choosing an app, don't forget to read user reviews. In reviews, pay attention to the app's overall rating and ease of use. If the app has a three-star rating or lower, please select another app.
 3 Install the app on your smartphone. After you have reviewed several applications and read reviews, select one of the applications and download it to your smartphone. To download the app:
3 Install the app on your smartphone. After you have reviewed several applications and read reviews, select one of the applications and download it to your smartphone. To download the app: - Click the download button on your smartphone. The button may look different depending on the operating system.
- Wait for the app to load.
- The download speed depends on the speed of your internet connection. To increase the download speed, connect your smartphone to a Wi-Fi network. Besides the faster speed, you don't have to pay for internet traffic when downloading over Wi-Fi.
 4 Measure your blood pressure using the app. After you have installed the application on your smartphone, click on the application icon to open it. Measure pressure using the app.
4 Measure your blood pressure using the app. After you have installed the application on your smartphone, click on the application icon to open it. Measure pressure using the app. - If the app has other diagnostic functions besides blood pressure measurement, select the "measure blood pressure" option.
- Read the instructions.
- Place your index finger on the camera on the back of your smartphone. Blood pressure apps use the effect of photoplethysmography, which means they use a built-in camera and flash to calculate the speed of the pulse wave during heartbeats. This technology allows you to analyze your pulse, heart rate and other data.
- Keep your finger on the camera until the app informs you that the measurement is over.
- Write down the results.
Part 3 of 4: Interpreting Pressure Measurements
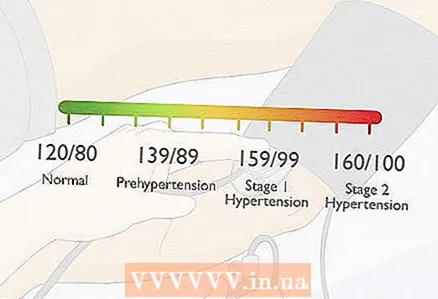 1 Check out the guidelines for blood pressure. When measuring pressure, the most important thing is to understand if it is within the normal range. If you have nothing to compare your blood pressure readings with, they won't tell you anything.
1 Check out the guidelines for blood pressure. When measuring pressure, the most important thing is to understand if it is within the normal range. If you have nothing to compare your blood pressure readings with, they won't tell you anything. - For most people, a blood pressure of 120/80 or lower is normal.
- Indicators 120-139 / 80-89 are considered prehypertension. If your blood pressure reading falls within this range, it is worth considering a healthier lifestyle.
- Indicators 140-159 / 90-99 are hypertension of the 1st degree, in which it is necessary to consult a doctor. Your doctor may recommend medications to lower your blood pressure.
- Indicators 160/100 or higher - this is hypertension of the 2nd degree, which without fail requires taking medications that lower blood pressure.
 2 Measure the pressure with a tonometer. Since other methods of measuring pressure are not yet perfect enough, it is necessary to accurately measure your blood pressure in order to use these indicators as basic in the future.
2 Measure the pressure with a tonometer. Since other methods of measuring pressure are not yet perfect enough, it is necessary to accurately measure your blood pressure in order to use these indicators as basic in the future. - The pressure can be measured in the clinic during the prophylactic medical examination.
- Some pharmacies have a free blood pressure measurement service.
- Compare any home blood pressure readings to your baseline.
- Keep a log of how your blood pressure is monitored to see how it changes over time.
Part 4 of 4: How to Improve Your Blood Pressure Readings
 1 Consult your doctor. If you are concerned about your blood pressure level, see your physician or general practitioner. Your doctor will advise you on how to improve your blood pressure readings.
1 Consult your doctor. If you are concerned about your blood pressure level, see your physician or general practitioner. Your doctor will advise you on how to improve your blood pressure readings. - If you have high blood pressure, you are likely to be prescribed drugs to lower your blood pressure.
- Your doctor may also recommend diet and exercise.
 2 Regular exercise can help lower blood pressure. One of the best ways to normalize blood pressure is through regular physical activity. Sports activities train the heart muscle and improve the condition of the cardiovascular system in general.
2 Regular exercise can help lower blood pressure. One of the best ways to normalize blood pressure is through regular physical activity. Sports activities train the heart muscle and improve the condition of the cardiovascular system in general. - Give preference to aerobic activity (cardio) such as running, cycling, swimming, or brisk walking.
- Don't drive yourself to the point of exhaustion.
- Talk to your doctor before embarking on a vigorous training regimen, especially if you have had blood pressure problems.
 3 Change your diet to reduce blood pressure. If you suffer from high blood pressure, it is recommended that you make certain dietary changes.
3 Change your diet to reduce blood pressure. If you suffer from high blood pressure, it is recommended that you make certain dietary changes. - Eat less salt. Limit salt intake to 2,300 mg per day.
- Eat six to seven servings of whole grains daily. Whole grains are high in fiber, which helps lower blood pressure.
- To reduce blood pressure, eat 4-5 servings of fruits and vegetables a day.
- Eliminate fatty meats and limit your intake of dairy products.
- In case of hypertension, it is worth reducing the consumption of sweets to 5 servings per week.
 4 If you have low blood pressure, you need to make other dietary changes. Change your diet to increase your blood pressure.
4 If you have low blood pressure, you need to make other dietary changes. Change your diet to increase your blood pressure. - If you have low blood pressure, consume at least 2,000 mg of salt per day.
- Drink plenty of water for hypotension.