Author:
Helen Garcia
Date Of Creation:
21 April 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- Steps
- Method 1 of 2: Using Urea alone
- Method 2 of 2: Mixing Urea with Other Fertilizers
- Tips
- Warnings
Urea, or urea, is a stable organic fertilizer that helps improve soil quality, provides plants with nitrogen, and increases yields. Typically, urea is sold in dry, granular form. There are several benefits to using urea as a fertilizer, but it also has its drawbacks. Knowing how to properly fertilize the soil with urea and how it interacts with other types of fertilizers can help you avoid these disadvantages and get the most out of the fertilizer.
Steps
Method 1 of 2: Using Urea alone
 1 Minimize ammonia loss by adding urea on a cool day. Urea is best applied on a cold day, at temperatures between 0 and 15 ° C and in light winds. At lower temperatures, the ground freezes, which makes it more difficult to apply urea to the soil. At higher temperatures and strong winds, urea will break down faster than the soil can absorb it.
1 Minimize ammonia loss by adding urea on a cool day. Urea is best applied on a cold day, at temperatures between 0 and 15 ° C and in light winds. At lower temperatures, the ground freezes, which makes it more difficult to apply urea to the soil. At higher temperatures and strong winds, urea will break down faster than the soil can absorb it.  2 Use urea with urease inhibitor before planting. Urease is an enzyme that triggers a chemical reaction that converts urea into the nitrogen needed by plants. Fertilizing before planting results in a large amount of urea wasted before it can benefit the plants. A urease inhibitor will slow down the chemical reaction by trapping urea in the soil.
2 Use urea with urease inhibitor before planting. Urease is an enzyme that triggers a chemical reaction that converts urea into the nitrogen needed by plants. Fertilizing before planting results in a large amount of urea wasted before it can benefit the plants. A urease inhibitor will slow down the chemical reaction by trapping urea in the soil.  3 Spread the urea evenly over the ground. Urea is sold in packages in the form of small, hard granules. Apply urea with a fertilizer spreader or manually spread the granules evenly over the ground. Typically, urea should be applied near the roots of the plants or near where you will plant them.
3 Spread the urea evenly over the ground. Urea is sold in packages in the form of small, hard granules. Apply urea with a fertilizer spreader or manually spread the granules evenly over the ground. Typically, urea should be applied near the roots of the plants or near where you will plant them.  4 Wet the ground. Before the urea is converted to the nitrogen needed by plants, it first becomes ammonia gas. Since gases can easily leave the surface of the ground, apply fertilizer to wet soil so that the urea is absorbed into it even before the chemical reaction begins. This will leave more ammonia in the soil.
4 Wet the ground. Before the urea is converted to the nitrogen needed by plants, it first becomes ammonia gas. Since gases can easily leave the surface of the ground, apply fertilizer to wet soil so that the urea is absorbed into it even before the chemical reaction begins. This will leave more ammonia in the soil. - The top 1.3 cm of soil should be moist to retain as much ammonia as possible. Water the soil yourself, apply urea before the rain, or within 48 hours after the snow has completely melted in your garden.
 5 Dig up the soil to apply fertilizer. Plowing a vegetable garden or orchard is a great way to add urea to the soil before some of the ammonia wears off. Loosen or dig up the area to add urea to the topsoil.
5 Dig up the soil to apply fertilizer. Plowing a vegetable garden or orchard is a great way to add urea to the soil before some of the ammonia wears off. Loosen or dig up the area to add urea to the topsoil.  6 Control the amount of nitrogen that potatoes receive. Some potato varieties can handle high soil nitrogen levels, but not all. Be careful and fertilize all potatoes equally. Don't fertilize your potatoes with a lot of nitrogen.
6 Control the amount of nitrogen that potatoes receive. Some potato varieties can handle high soil nitrogen levels, but not all. Be careful and fertilize all potatoes equally. Don't fertilize your potatoes with a lot of nitrogen. - Urea can be applied directly to potato plants or mixed with another fertilizer, provided the nitrogen concentration does not exceed 30%.
- A solution with urea, the concentration of which is above 30%, can be applied to the ground only before planting potatoes.
 7 Fertilize your cereals on a cool day. Urea can be applied directly to most cereals, but do not apply at temperatures above 15 ° C. If fertilizer is applied on a warm day, the plant will begin to smell unpleasantly of ammonia.
7 Fertilize your cereals on a cool day. Urea can be applied directly to most cereals, but do not apply at temperatures above 15 ° C. If fertilizer is applied on a warm day, the plant will begin to smell unpleasantly of ammonia.  8 Fertilize corn only indirectly. To do this, sprinkle urea on the ground, at least 5 cm from the seeds. Direct exposure to urea can be toxic to the seeds and severely reduce the yield of corn.
8 Fertilize corn only indirectly. To do this, sprinkle urea on the ground, at least 5 cm from the seeds. Direct exposure to urea can be toxic to the seeds and severely reduce the yield of corn.
Method 2 of 2: Mixing Urea with Other Fertilizers
 1 Determine the ideal fertilizer ratio. The fertilizer ratio, or A-P-K numbers, is a series of three numbers that indicate how much nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium is in the fertilizer. If you've done a soil analysis, you should already know the ideal fertilizer ratio to help fill nutrient deficiencies in the soil.
1 Determine the ideal fertilizer ratio. The fertilizer ratio, or A-P-K numbers, is a series of three numbers that indicate how much nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium is in the fertilizer. If you've done a soil analysis, you should already know the ideal fertilizer ratio to help fill nutrient deficiencies in the soil. - Most hobby gardeners can find ready-made mixes at a nursery or gardening store.
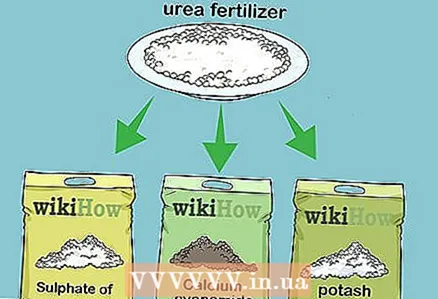 2 Mix urea with other fertilizers to create a stable mixture. Urea will supply nitrogen to plants, but other elements like phosphorus and potassium are also essential for plant health. Urea can be safely mixed and stored with fertilizers such as:
2 Mix urea with other fertilizers to create a stable mixture. Urea will supply nitrogen to plants, but other elements like phosphorus and potassium are also essential for plant health. Urea can be safely mixed and stored with fertilizers such as: - calcium cyanamide;
- potassium sulfate;
- potassium magnesium.
 3 Mix urea with a specific fertilizer to fertilize the plants immediately. Some types of fertilizers can be mixed with urea, but after 2-3 days they lose their properties. This is due to the reaction that occurs between the fertilizer chemicals. These fertilizers include:
3 Mix urea with a specific fertilizer to fertilize the plants immediately. Some types of fertilizers can be mixed with urea, but after 2-3 days they lose their properties. This is due to the reaction that occurs between the fertilizer chemicals. These fertilizers include: - Chilean saltpeter;
- ammonium sulfate;
- nitromanesia;
- ammonium hydrogen phosphate;
- tomoslag;
- phosphorite;
- potassium chloride.
 4 Prevent unwanted chemical reactions from harming your plants. Some fertilizers can react with urea, causing a volatile chemical reaction or making the fertilizer unusable. Never mix urea with the following fertilizers:
4 Prevent unwanted chemical reactions from harming your plants. Some fertilizers can react with urea, causing a volatile chemical reaction or making the fertilizer unusable. Never mix urea with the following fertilizers: - calcium nitrate;
- calcium ammonium nitrate;
- calcium ammonium nitrate
- ammonium sulfate nitrate;
- potassium nitrate;
- potassium ammonium nitrate;
- superphosphate;
- triple superphosphate.
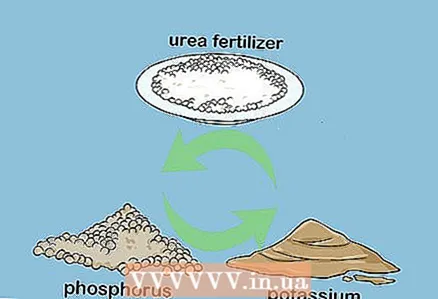 5 Mix urea with a fertilizer rich in phosphorus and potassium for a balanced fertilizer. Check the list of fertilizers that can and cannot be mixed with urea, and select fertilizers with phosphorus and potassium to add to the mixture. Many of these fertilizers can be purchased at a nursery or gardening store.
5 Mix urea with a fertilizer rich in phosphorus and potassium for a balanced fertilizer. Check the list of fertilizers that can and cannot be mixed with urea, and select fertilizers with phosphorus and potassium to add to the mixture. Many of these fertilizers can be purchased at a nursery or gardening store. - Mix fertilizers according to the weight indicated in the fertilizer ratio. Mix them thoroughly. This can be done in a large bucket, wheelbarrow, or power mixer.
 6 Spread the fertilizer with urea evenly over the ground. Apply fertilizer in the same way as urea, spreading it evenly over the ground. Then water and dig up the ground.
6 Spread the fertilizer with urea evenly over the ground. Apply fertilizer in the same way as urea, spreading it evenly over the ground. Then water and dig up the ground. - Urea is not as dense as other fertilizers. If you are spreading urea with a spreader and need to cover a large area of land, reduce the spreading distance to 15 m to spread the fertilizer more evenly.
Tips
- Apply in-store fertilizer according to the directions on the package.
- This article discusses fertilizer ratios. Do not confuse fertilizer ratio with fertilizer percentage. The fertilizer ratio determines how much of a particular fertilizer (by weight) needs to be added to the mix. The percentage of the components tells how much of each individual element is contained in the fertilizer. If you want to use the percentage of the ingredients to calculate the fertilizer ratio, divide each percentage by the smallest of the three numbers.
Warnings
- Excessive amounts of nitrogen can burn plants. Add urea to wet soil to prevent this.
- Always keep urea and ammonium nitrate separate from each other.