Author:
Bobbie Johnson
Date Of Creation:
5 April 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- Steps
- Method 1 of 3: Identify and Avoid Pollinosis Triggers
- Method 2 of 3: See an allergist to identify triggers for hay fever
- Method 3 of 3: Take your hay fever medication
- Tips
Pollinosis, also known as hay fever or seasonal allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, is a type of allergy that is caused by allergens (outdoors or indoors) such as dust, mold, animal hair, or pollen. Allergy symptoms resemble the common cold and include a runny nose, itchy eyes, sneezing, sinus pressure, and nasal congestion. Hay fever is not caused by viruses and is not contagious. Although there is no cure for hay fever, certain methods can help relieve symptoms and improve your condition.
Attention:the information in this article is for informational purposes only. Before using any methods, consult your doctor.
Steps
Method 1 of 3: Identify and Avoid Pollinosis Triggers
 1 Monitor your pollen levels. Pollen is one of the main causes of allergic reactions in hay fever, so you need to monitor its level on a daily basis, especially during the flowering season. Try to stay at home when pollen levels are high. The pollen content in the air can be monitored daily on numerous websites.
1 Monitor your pollen levels. Pollen is one of the main causes of allergic reactions in hay fever, so you need to monitor its level on a daily basis, especially during the flowering season. Try to stay at home when pollen levels are high. The pollen content in the air can be monitored daily on numerous websites. - Some television weather forecasts also report pollen levels. This level is usually said to be low, moderate, medium, or high. Try not to leave your home when pollen levels are high.
- If you are very sensitive to pollen and it is causing you a severe allergic reaction, consider staying at home even at a moderate level.
- You can check with your doctor about your susceptibility to pollen.
 2 Wear a pollen mask. Always wear a face shield, such as an N95 respirator, when working in your garden. This includes activities such as mowing the lawn, raking leaves, or gardening. Respirators can be ordered online or purchased from a pharmacy.
2 Wear a pollen mask. Always wear a face shield, such as an N95 respirator, when working in your garden. This includes activities such as mowing the lawn, raking leaves, or gardening. Respirators can be ordered online or purchased from a pharmacy. - If you can't find an N95 respirator, you can use a regular medical mask or handkerchief. Although they are less effective at filtering air than an N95 respirator, they will filter out some of the pollen and keep it out of your nose.
- If you have severe allergies, consider asking someone to cut the grass in front of your house.
- You can also wear glasses (such as sunglasses) to protect your eyes from allergens. Glasses or sunglasses will suffice, although you can purchase special safety glasses from a hardware store or online.
- When you return home from the street, take a shower and wash your clothes. If you cannot do this immediately, wash and change, then shower and wash your clothes as soon as possible.
 3 Flush your sinuses. A relatively cheap way to relieve hay fever symptoms is to clear the nasal passages with a neti pot or saline spray. It is easier to rinse your nose with a saline spray: just inject it into each nostril. In addition, for neti pot, you need to prepare the saline solution yourself.
3 Flush your sinuses. A relatively cheap way to relieve hay fever symptoms is to clear the nasal passages with a neti pot or saline spray. It is easier to rinse your nose with a saline spray: just inject it into each nostril. In addition, for neti pot, you need to prepare the saline solution yourself. - You can make your own saline solution by mixing 3 teaspoons (about 20 grams) of iodine-free salt and 1 teaspoon (7 grams) of baking soda. Dissolve 1 teaspoon (7 grams) of this mixture in 1 cup (240 milliliters) lukewarm distilled or bottled water. Do not use unboiled tap water.
- After each use, wash the irrigator with distilled or bottled water and air dry. This will help prevent bacterial growth.
 4 Reduce the number of allergens in your home. If you do not want allergens to enter your home from the street, you need to close the windows and turn on the air conditioning in your home and car, especially when pollen levels are high. Keep the filters in your air conditioner clean and purchase suitable HEPA filters.
4 Reduce the number of allergens in your home. If you do not want allergens to enter your home from the street, you need to close the windows and turn on the air conditioning in your home and car, especially when pollen levels are high. Keep the filters in your air conditioner clean and purchase suitable HEPA filters. - Check the manufacturer's instructions or ask the seller to find out which filter is best to use.
- Also use vacuum cleaners with HEPA filters if available. The vacuum cleaner draws in air and dust particles, while the HEPA filter traps allergens. Check the attached instructions for how often the filter should be changed - usually it is changed after a few times.
 5 Maintain humidity at 30-50 percent. Make sure the humidity level in your home is between 30 and 50% to help prevent mold. Purchase a hygrometer to measure humidity in all rooms. Just place the device in the room and it will show the humidity level just like a thermometer shows the temperature.
5 Maintain humidity at 30-50 percent. Make sure the humidity level in your home is between 30 and 50% to help prevent mold. Purchase a hygrometer to measure humidity in all rooms. Just place the device in the room and it will show the humidity level just like a thermometer shows the temperature. - A hygrometer can be purchased at a store or ordered online. Read the instructions first to know how to use the appliance correctly.
 6 Purchase tick protectors. To reduce allergens in fabrics and furniture, buy anti-mite covers for pillows, mattresses, quilts, and duvets. This will help protect tissues from mites and allergens and prevent hay fever.
6 Purchase tick protectors. To reduce allergens in fabrics and furniture, buy anti-mite covers for pillows, mattresses, quilts, and duvets. This will help protect tissues from mites and allergens and prevent hay fever. - Bed linen and bedspreads should be washed frequently in hot water.
- It may be worth cutting back on pillows, blankets, or stuffed animals in your room or your baby's room.
 7 Do not use some window treatments. There are certain window treatments that can attract pollen and mold, and collect dust.Heavyweight curtains that can only be dry cleaned collect more dust and allergens than lightweight curtains that can be vacuumed or machine washed. You can also use synthetic blinds, which are easy to wipe and clean.
7 Do not use some window treatments. There are certain window treatments that can attract pollen and mold, and collect dust.Heavyweight curtains that can only be dry cleaned collect more dust and allergens than lightweight curtains that can be vacuumed or machine washed. You can also use synthetic blinds, which are easy to wipe and clean. - Do not dry your clothes outside, otherwise allergens may build up on them.
 8 Clean your bathroom and kitchen often. Another major trigger for hay fever is mold. To prevent mold from forming in your home, you need to clean your bathroom and kitchen more often. In this case, you can use cleaning solutions with chlorine bleach - it destroys mold and other allergens.
8 Clean your bathroom and kitchen often. Another major trigger for hay fever is mold. To prevent mold from forming in your home, you need to clean your bathroom and kitchen more often. In this case, you can use cleaning solutions with chlorine bleach - it destroys mold and other allergens. - You can also make your own cleaning solution: dilute 1/2 cup (120 ml) of chlorine bleach with 4 liters of water.
 9 Give preference to wet cleaning. When cleaning your home, use a damp product to collect most of the allergens and dust particles. Moisten a cloth, mop, and broom with water.
9 Give preference to wet cleaning. When cleaning your home, use a damp product to collect most of the allergens and dust particles. Moisten a cloth, mop, and broom with water. - This way you can collect dust much more efficiently than dry cleaning.
 10 Don't keep houseplants and flowers. Since pollen causes hay fever, live plants in the house should be discarded. Instead, get fake flowers or non-flowering plants to spice up the interior. This way you will beautify your home and avoid pollen at the same time.
10 Don't keep houseplants and flowers. Since pollen causes hay fever, live plants in the house should be discarded. Instead, get fake flowers or non-flowering plants to spice up the interior. This way you will beautify your home and avoid pollen at the same time. - While some artificial plants do not look like real plants, others look quite natural. Try to find artificial plants that are difficult to distinguish from real ones.
 11 Avoid pet triggers. There are many ways to do this. If you know that certain animals are causing you allergies, do not keep them at home. If the allergic reaction is caused by the fur of any pets, keep them outside, not inside the house. If this is not possible, try to keep animals out of the bedroom to avoid breathing in fur at night. You should also purchase an air purifier with a HEPA filter and place it where your pet spends most of its time.
11 Avoid pet triggers. There are many ways to do this. If you know that certain animals are causing you allergies, do not keep them at home. If the allergic reaction is caused by the fur of any pets, keep them outside, not inside the house. If this is not possible, try to keep animals out of the bedroom to avoid breathing in fur at night. You should also purchase an air purifier with a HEPA filter and place it where your pet spends most of its time. - After contact with an animal, wash your hands to remove hair.
- If possible, remove the carpet as it collects animal hair. If this is not possible, vacuum it frequently to collect the fur. Many vacuum cleaners have special attachments or filters to collect pet hair.
- You should brush and bathe your pets at least once a week so that they leave less hair around. It is better to ask someone else to do this so that you do not have an allergic reaction to the coat.
- Some dogs and cats are considered “hypoallergenic,” meaning they are less likely to cause allergies. This can be a good choice if you really want to have a pet.
Method 2 of 3: See an allergist to identify triggers for hay fever
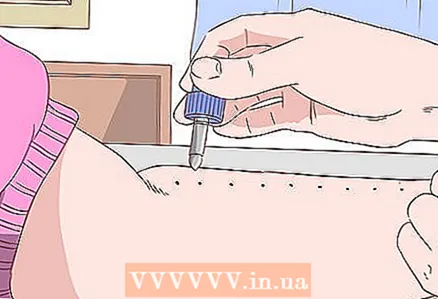 1 Make a scarification test. If you have tried to eliminate all allergy triggers (pollen, mold, dust), but still have problems, you should see an allergist. He will be able to carry out tests and identify the cause of the hay fever. One of the most common tests is the scarification test, or prick test. This test lasts 10–20 minutes and involves applying tiny drops of possible allergens to the punctured or scratched skin. After that, the doctor monitors the reaction of the skin.
1 Make a scarification test. If you have tried to eliminate all allergy triggers (pollen, mold, dust), but still have problems, you should see an allergist. He will be able to carry out tests and identify the cause of the hay fever. One of the most common tests is the scarification test, or prick test. This test lasts 10–20 minutes and involves applying tiny drops of possible allergens to the punctured or scratched skin. After that, the doctor monitors the reaction of the skin. - Sometimes the reaction is immediate. In an allergic reaction, the skin that has been exposed to the allergen swells and looks like a mosquito bite.
- The doctor will note the reaction and measure its intensity, and then interpret the results.
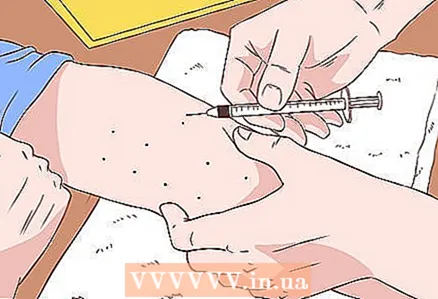 2 Get an intradermal test. An allergist may also order a so-called intradermal test. In this case, allergens are not applied to punctures or scratches, but are injected into the skin through a thin needle. This test is generally more accurate than the scarification test.
2 Get an intradermal test. An allergist may also order a so-called intradermal test. In this case, allergens are not applied to punctures or scratches, but are injected into the skin through a thin needle. This test is generally more accurate than the scarification test. - This test takes about 20 minutes.
 3 Get a blood test. To confirm the results of a skin test, an allergist may order a blood test called a radioallergosorbent test (RAST). This test measures the concentration of the allergy-causing antibodies in the blood - immunoglobulin E (IgE). Based on the results of the analysis (the amount of split antibodies in the blood), the doctor will be able to judge which allergens the body reacts to.
3 Get a blood test. To confirm the results of a skin test, an allergist may order a blood test called a radioallergosorbent test (RAST). This test measures the concentration of the allergy-causing antibodies in the blood - immunoglobulin E (IgE). Based on the results of the analysis (the amount of split antibodies in the blood), the doctor will be able to judge which allergens the body reacts to. - The results of this test are usually obtained after a few days, as the blood sample is sent to the laboratory.
Method 3 of 3: Take your hay fever medication
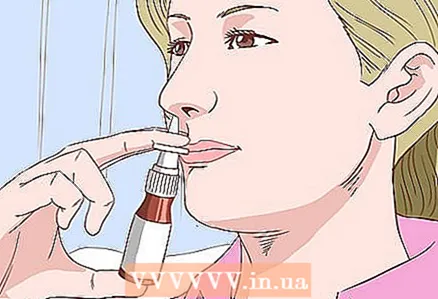 1 Take nasal corticosteroids. If you can't avoid the triggers of hay fever, try to relieve your symptoms. For this, nasal corticosteroids can be used. These drugs prevent and treat inflammation of the nasal mucosa, itching and runny nose caused by hay fever. Generally, most people can safely take them for extended periods of time. Side effects (although rare) include unpleasant smell and taste, and nasal irritation.
1 Take nasal corticosteroids. If you can't avoid the triggers of hay fever, try to relieve your symptoms. For this, nasal corticosteroids can be used. These drugs prevent and treat inflammation of the nasal mucosa, itching and runny nose caused by hay fever. Generally, most people can safely take them for extended periods of time. Side effects (although rare) include unpleasant smell and taste, and nasal irritation. - Some of these drugs are available with a prescription; others do not need one to buy. It is generally best to use them every day, at least during the flowering season or when you usually experience allergy symptoms. Check with your doctor or pharmacist to determine which drug is best for you.
- Common drugs include Fliksonase, Nazarel, Nazonex, Pulmicort.
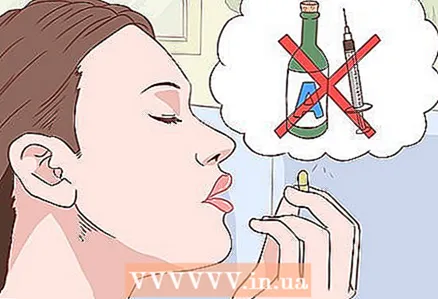 2 Take antihistamines. Antihistamines can also help manage the symptoms of hay fever. These drugs are available as oral tablets, liquid solutions, chewable tablets, lozenges, nasal sprays, and eye drops. They help with itching, sneezing and runny nose by blocking histamine, which is secreted by the immune system and causes symptoms of hay fever. Tablets and nasal sprays help relieve nasal symptoms, and eye drops relieve itchy and irritated eyes caused by hay fever.
2 Take antihistamines. Antihistamines can also help manage the symptoms of hay fever. These drugs are available as oral tablets, liquid solutions, chewable tablets, lozenges, nasal sprays, and eye drops. They help with itching, sneezing and runny nose by blocking histamine, which is secreted by the immune system and causes symptoms of hay fever. Tablets and nasal sprays help relieve nasal symptoms, and eye drops relieve itchy and irritated eyes caused by hay fever. - Antihistamines include such drugs as Claritin, Zyrtec, Allegra, Omaron, Diphenhydramine (the last two drugs are available by prescription). Nasal antihistamines also include Allergodil, Nosephrin, and Mometasone sprays (the latter two are available by prescription).
- When using antihistamines, do not drink alcohol or take tranquilizers.
- Do not use multiple antihistamines at the same time, unless advised by your doctor or allergist.
- When taking antihistamines, do not operate heavy machinery and be careful while driving. Do not use sedative antihistamines if you are driving. Most people can drive safely if they are taking non-sedating or mildly sedating antihistamines such as Zyrtec, Allegra, or Claritin.
 3 Try decongestants. OTC decongestants are commercially available, such as Stopussin or Ambroxol. You can also ask your doctor for a prescription for a decongestant solution, tablet, or nasal spray. There are many different decongestants available at pharmacies, but be aware that they can increase blood pressure, insomnia, irritation and headaches.
3 Try decongestants. OTC decongestants are commercially available, such as Stopussin or Ambroxol. You can also ask your doctor for a prescription for a decongestant solution, tablet, or nasal spray. There are many different decongestants available at pharmacies, but be aware that they can increase blood pressure, insomnia, irritation and headaches. - Decongestants should be used temporarily and not every day.
- Decongestant nasal sprays include drugs such as Nazol and Afrin. They should not be used for more than 2–3 days in a row, or the congestion may worsen.
 4 Ask your allergist about leukotriene receptor blockers. Leukotriene receptor blockers (antagonists) include Singular, which should be taken before any symptoms appear. Among other things, it relieves asthma symptoms. Headache is a common side effect.In rare cases, the drug can cause psychological reactions such as agitation, aggression, hallucinations, depression, or suicidal thoughts.
4 Ask your allergist about leukotriene receptor blockers. Leukotriene receptor blockers (antagonists) include Singular, which should be taken before any symptoms appear. Among other things, it relieves asthma symptoms. Headache is a common side effect.In rare cases, the drug can cause psychological reactions such as agitation, aggression, hallucinations, depression, or suicidal thoughts. - This drug is available in pill form.
- If, while taking the drug, you notice unusual mental phenomena, you should immediately consult a doctor.
 5 Try using Atrovent. This medication contains ipratropium bromide and is a prescription nasal spray that can relieve severe rhinitis. Possible side effects include dry nose, nosebleeds, and sore throat. In rare cases, side effects such as blurred vision, dizziness, and difficulty urinating may occur.
5 Try using Atrovent. This medication contains ipratropium bromide and is a prescription nasal spray that can relieve severe rhinitis. Possible side effects include dry nose, nosebleeds, and sore throat. In rare cases, side effects such as blurred vision, dizziness, and difficulty urinating may occur. - This drug should not be taken if you have glaucoma or an enlarged prostate.
 6 Take oral corticosteroids. Prednisolone is sometimes used to relieve severe allergy symptoms. However, you should be careful, as long-term use of this drug can lead to serious side effects such as cataracts, osteoporosis, muscle weakness.
6 Take oral corticosteroids. Prednisolone is sometimes used to relieve severe allergy symptoms. However, you should be careful, as long-term use of this drug can lead to serious side effects such as cataracts, osteoporosis, muscle weakness. - This drug is prescribed only for a short time, often with a decreasing dosage.
 7 Get an allergy vaccine. If your allergic reaction has not been reduced by taking other drugs and you cannot avoid exposure to the allergens, your doctor may recommend an allergy vaccine (called immunotherapy). Instead of fighting the allergic reaction, the vaccine will alter the immune system so that it stops responding to allergens. When vaccinated, a diluted extract of the allergen is administered (often in increasing doses) until a dose is found that will help relieve the allergic reaction. Vaccinations are then given over longer periods of time. Vaccination can take 3-5 years.
7 Get an allergy vaccine. If your allergic reaction has not been reduced by taking other drugs and you cannot avoid exposure to the allergens, your doctor may recommend an allergy vaccine (called immunotherapy). Instead of fighting the allergic reaction, the vaccine will alter the immune system so that it stops responding to allergens. When vaccinated, a diluted extract of the allergen is administered (often in increasing doses) until a dose is found that will help relieve the allergic reaction. Vaccinations are then given over longer periods of time. Vaccination can take 3-5 years. - The goal of vaccination is to accustom the body to allergens that trigger an allergic reaction. As a result, the body stops responding to allergens.
- Allergy shots are safe and have very mild side effects. The most common side effects are redness and swelling at the injection site, which may appear immediately or within a few hours after the shot. They must pass within 24 hours. A mild allergic reaction, similar to the one you experience with hay fever, is also possible.
- In rare cases, after the first vaccination, there is a severe allergic reaction, which can be repeated with subsequent injections. When receiving allergy vaccinations, patients are always supervised. Symptoms of a severe reaction, or anaphylaxis, include shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, hives, swelling of the face and body, irregular or rapid heartbeat, tightness in the throat and chest, dizziness, loss of consciousness, and in very severe cases, even death.
- If you experience a severe allergic reaction that is accompanied by one or more of the symptoms listed above, call the emergency room 103 immediately.
Tips
- Keep medicines out of the reach of children.
- If you are pregnant or about to become pregnant, breastfeeding, have glaucoma or an enlarged prostate, have a cold or other health problem, are allergic to certain medications, or are already taking medications, tell your doctor before taking any medication ...
- Never take medicines prescribed for another person.
- If your eyes are itchy and swollen, apply a damp, cold cloth or washcloth to each eye. This will help relieve itching.
- Even with severe itching, do not scratch your eyes. This will only worsen the itching and irritation.
- If you are allergic, do not smoke and avoid secondhand smoke.