Author:
Virginia Floyd
Date Of Creation:
14 August 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- Steps
- Method 1 of 5: Find the number of vertices in a polyhedron
- Method 2 of 5: Finding the vertex of the domain of a system of linear inequalities
- Method 3 of 5: Finding the vertex of a parabola through the axis of symmetry
- Method 4 of 5: Finding the vertex of a parabola by completing a square
- Method 5 of 5: Find the vertex of a parabola using a simple formula
- What do you need
In mathematics, there are a number of problems in which you need to find the top. For example, a vertex of a polyhedron, a vertex or several vertices of a domain of a system of inequalities, a vertex of a parabola or quadratic equation. This article will show you how to find the top in different problems.
Steps
Method 1 of 5: Find the number of vertices in a polyhedron
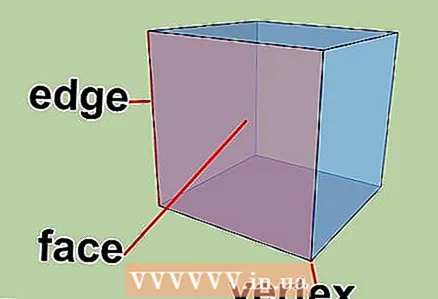 1 Euler's theorem. The theorem states that in any polyhedron, the number of its vertices plus the number of its faces minus the number of its edges is always two.
1 Euler's theorem. The theorem states that in any polyhedron, the number of its vertices plus the number of its faces minus the number of its edges is always two. - Formula describing Euler's theorem: F + V - E = 2
- F is the number of faces.
- V is the number of vertices.
- E is the number of ribs.
- Formula describing Euler's theorem: F + V - E = 2
 2 Rewrite the formula to find the number of vertices. Given the number of faces and the number of edges of a polyhedron, you can quickly find the number of vertices using Euler's formula.
2 Rewrite the formula to find the number of vertices. Given the number of faces and the number of edges of a polyhedron, you can quickly find the number of vertices using Euler's formula. - V = 2 - F + E
 3 Plug the values you give into this formula. This gives you the number of vertices in the polyhedron.
3 Plug the values you give into this formula. This gives you the number of vertices in the polyhedron. - Example: Find the number of vertices of a polyhedron that has 6 faces and 12 edges.
- V = 2 - F + E
- V = 2 - 6 + 12
- V = -4 + 12
- V = 8
- Example: Find the number of vertices of a polyhedron that has 6 faces and 12 edges.
Method 2 of 5: Finding the vertex of the domain of a system of linear inequalities
 1 Plot the solution (area) of a system of linear inequalities. In certain cases, you can see some or all of the vertices of the area of the system of linear inequalities on the graph. Otherwise, you have to find the vertex algebraically.
1 Plot the solution (area) of a system of linear inequalities. In certain cases, you can see some or all of the vertices of the area of the system of linear inequalities on the graph. Otherwise, you have to find the vertex algebraically. - When using a graphing calculator, you can view the entire graph and find the coordinates of the vertices.
 2 Convert inequalities to equations. In order to solve the system of inequalities (that is, find "x" and "y"), you need to put an "equal" sign instead of the inequality signs.
2 Convert inequalities to equations. In order to solve the system of inequalities (that is, find "x" and "y"), you need to put an "equal" sign instead of the inequality signs. - Example: given a system of inequalities:
- y x
- y> - x + 4
- Convert inequalities to equations:
- y = x
- y = - x + 4
- Example: given a system of inequalities:
 3 Now express any variable in one equation and plug it into another equation. In our example, plug the y value from the first equation into the second equation.
3 Now express any variable in one equation and plug it into another equation. In our example, plug the y value from the first equation into the second equation. - Example:
- y = x
- y = - x + 4
- Substitute y = x in y = - x + 4:
- x = - x + 4
- Example:
 4 Find one of the variables. Now you have an equation with only one variable, x, which is easy to find.
4 Find one of the variables. Now you have an equation with only one variable, x, which is easy to find. - Example: x = - x + 4
- x + x = 4
- 2x = 4
- 2x / 2 = 4/2
- x = 2
- Example: x = - x + 4
 5 Find another variable. Substitute the found value "x" in any of the equations and find the value "y".
5 Find another variable. Substitute the found value "x" in any of the equations and find the value "y". - Example: y = x
- y = 2
- Example: y = x
 6 Find the top. The vertex has coordinates equal to the found values "x" and "y".
6 Find the top. The vertex has coordinates equal to the found values "x" and "y". - Example: the vertex of the region of the given system of inequalities is the point O (2,2).
Method 3 of 5: Finding the vertex of a parabola through the axis of symmetry
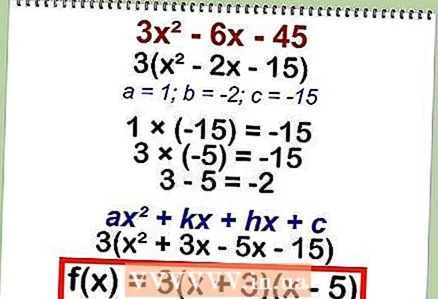 1 Factor the equation. There are several ways to factor a quadratic equation. As a result of the expansion, you get two binomials, which, when multiplied, will lead to the original equation.
1 Factor the equation. There are several ways to factor a quadratic equation. As a result of the expansion, you get two binomials, which, when multiplied, will lead to the original equation. - Example: given a quadratic equation
- 3x2 - 6x - 45
- First, bracket the common factor: 3 (x2 - 2x - 15)
- Multiply the coefficients "a" and "c": 1 * (-15) = -15.
- Find two numbers, the multiplication of which is -15, and their sum is equal to the coefficient "b" (b = -2): 3 * (-5) = -15; 3 - 5 = -2.
- Plug the found values into the equation ax2 + kx + hx + c: 3 (x2 + 3x - 5x - 15).
- Expand the original equation: f (x) = 3 * (x + 3) * (x - 5)
- Example: given a quadratic equation
 2 Find the point (s) at which the graph of the function (in this case, the parabola) crosses the abscissa. The graph crosses the X-axis at f (x) = 0.
2 Find the point (s) at which the graph of the function (in this case, the parabola) crosses the abscissa. The graph crosses the X-axis at f (x) = 0. - Example: 3 * (x + 3) * (x - 5) = 0
- x +3 = 0
- x - 5 = 0
- x = -3; x = 5
- Thus, the roots of the equation (or points of intersection with the X-axis): A (-3, 0) and B (5, 0)
- Example: 3 * (x + 3) * (x - 5) = 0
 3 Find the axis of symmetry. The axis of symmetry of the function passes through a point that lies in the middle between the two roots. In this case, the vertex lies on the axis of symmetry.
3 Find the axis of symmetry. The axis of symmetry of the function passes through a point that lies in the middle between the two roots. In this case, the vertex lies on the axis of symmetry. - Example: x = 1; this value lies in the middle between -3 and +5.
 4 Plug in the x value into the original equation and find the y value. These "x" and "y" values are the coordinates of the vertex of the parabola.
4 Plug in the x value into the original equation and find the y value. These "x" and "y" values are the coordinates of the vertex of the parabola. - Example: y = 3x2 - 6x - 45 = 3 (1) 2 - 6 (1) - 45 = -48
 5 Write down your answer.
5 Write down your answer.- Example: the vertex of a given quadratic equation is the point O (1, -48)
Method 4 of 5: Finding the vertex of a parabola by completing a square
 1 Rewrite the original equation as: y = a (x - h) ^ 2 + k, while the vertex lies at the point with coordinates (h, k). To do this, you need to supplement the original quadratic equation to a complete square.
1 Rewrite the original equation as: y = a (x - h) ^ 2 + k, while the vertex lies at the point with coordinates (h, k). To do this, you need to supplement the original quadratic equation to a complete square. - Example: given a quadratic function y = - x ^ 2 - 8x - 15.
 2 Consider the first two terms. Factor out the coefficient of the first term (the intercept is ignored).
2 Consider the first two terms. Factor out the coefficient of the first term (the intercept is ignored). - Example: -1 (x ^ 2 + 8x) - 15.
 3 Expand the free term (-15) into two numbers so that one of them completes the expression in parentheses to a complete square. One of the numbers must be equal to the square of half the coefficient of the second term (from the expression in parentheses).
3 Expand the free term (-15) into two numbers so that one of them completes the expression in parentheses to a complete square. One of the numbers must be equal to the square of half the coefficient of the second term (from the expression in parentheses). - Example: 8/2 = 4; 4 * 4 = 16; so
- -1 (x ^ 2 + 8x + 16)
- -15 = -16 + 1
- y = -1 (x ^ 2 + 8x + 16) + 1
- Example: 8/2 = 4; 4 * 4 = 16; so
 4 Simplify the equation. Since the expression in brackets is a complete square, you can rewrite this equation in the following form (if necessary, perform addition or subtraction operations outside the brackets):
4 Simplify the equation. Since the expression in brackets is a complete square, you can rewrite this equation in the following form (if necessary, perform addition or subtraction operations outside the brackets): - Example: y = -1 (x + 4) ^ 2 + 1
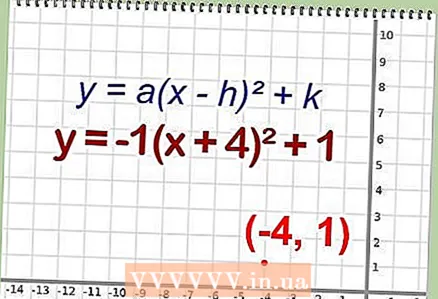 5 Find the coordinates of the vertex. Recall that the coordinates of the vertex of a function of the form y = a (x - h) ^ 2 + k are (h, k).
5 Find the coordinates of the vertex. Recall that the coordinates of the vertex of a function of the form y = a (x - h) ^ 2 + k are (h, k). - k = 1
- h = -4
- Thus, the vertex of the original function is the point O (-4,1).
Method 5 of 5: Find the vertex of a parabola using a simple formula
 1 Find the "x" coordinate using the formula: x = -b / 2a (for a function of the form y = ax ^ 2 + bx + c). Plug in the "a" and "b" values into the formula and find the "x" coordinate.
1 Find the "x" coordinate using the formula: x = -b / 2a (for a function of the form y = ax ^ 2 + bx + c). Plug in the "a" and "b" values into the formula and find the "x" coordinate. - Example: given a quadratic function y = - x ^ 2 - 8x - 15.
- x = -b / 2a = - (- 8) / (2 * (- 1)) = 8 / (- 2) = -4
- x = -4
 2 Plug in the x value you find into the original equation. Thus, you will find "y". These "x" and "y" values are the coordinates of the vertex of the parabola.
2 Plug in the x value you find into the original equation. Thus, you will find "y". These "x" and "y" values are the coordinates of the vertex of the parabola. - Example: y = - x ^ 2 - 8x - 15 = - (- 4) ^ 2 - 8 (-4) - 15 = - (16) - (- 32) - 15 = -16 + 32 - 15 = 1
- y = 1
- Example: y = - x ^ 2 - 8x - 15 = - (- 4) ^ 2 - 8 (-4) - 15 = - (16) - (- 32) - 15 = -16 + 32 - 15 = 1
 3 Write down your answer.
3 Write down your answer.- Example: the vertex of the original function is the point O (-4,1).
What do you need
- Calculator
- Pencil
- Paper