Author:
Peter Berry
Date Of Creation:
20 February 2021
Update Date:
28 June 2024

Content
Margin is key information that shows whether the business is generating income and if so, how much it is. You need to track profit margins to be able to build a good business plan, track costs, adjust prices and measure the profitability of your business over time. Margin is expressed as a percentage: the higher the percentage, the greater the profit.
Steps
Part 1 of 2: Calculating the profit margin
Know the difference between gross profit, gross profit margin and net profit. Gross profit is equal to the total revenue earned from the product or service minus the cost of producing or supplying goods or services (COGS - Cost of Goods or Services). This calculation does not include expenses such as wages, rental charges or other utilities. It only considers costs that are directly attributable to creating the product or providing a service. Gross profit margin is equal to gross profit divided by revenue.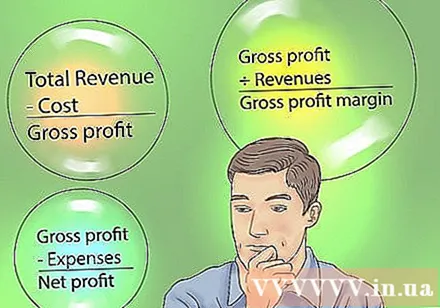
- Net profit considers the full cost of the business and is calculated by subtracting administrative costs and other related expenses from gross profit. These include the usual operating costs (wages, rental costs, etc.) and one-time costs (taxes, bills of service, etc.). You must also include any additional income, such as return on investments.
- Net profit is more complete, detailing the health of the business and in general, is often used in corporate management. Below are detailed steps to find net profit.
- Net profit is also known as the "last line".

Determine the period to be calculated. To find the profit margin of a business, you need to select the time period you want to analyze. Usually, the month, quarter or year is used in the calculation of the profit margin.- Consider why you want your margins to be calculated. If you want to file a loan or attract investment, information about how your business has been doing in just one month is not enough. However, if you compare profit margins between months just for your own sake, you can still use shorter intervals.

Calculate the total revenue from business activities in the period to be calculated. Profits are everything a business brings through sales, service provision or interest income.- If your business only supplies merchandise, such as a restaurant or retail store, your total revenue equals all sales during the selected period minus any discounts or sales. exchange, return goods. If this number is not available, multiply the total number of line items sold by the corresponding price and adjust the discounts and returns.
- Likewise, if the business provides a service, such as lawn mowing, your total revenue is all the proceeds from providing the service during that period.
- Finally, if the business is engaged in investing, you should include interest and dividend income from this source in your revenue calculation.

Subtract any expenses to figure your net income. Cost is the opposite of revenue. They are any future payables or payments for the things you do or / or use during the calculation period. These include the operating costs as well as the costs required to sustain the investment.- Commonly include labor costs, rental costs, electricity, equipment, necessities, banking costs, interest expenses. In general, if you run a small business, you can simply add up any payments for the period.
- For example, if in the period, the business earns 2 billion VND and in order to have that revenue, you need to spend 1.4 billion VND on rental expenses, necessities, equipment, taxes, interest, take 2 billion collected minus 1.4 billion expense. The remaining revenue after expenses will be 600 million VND.
Divide your net income by your total sales. The percentage earned is your profit margin: it is the percentage of sales you can keep as you earn.
- In the above example, our brand name is 600 million VND. 600,000,000 VND ÷ 2,000,000,000 VND = 0.3 (30%)
- Going deeper, assuming you sell paint, the margins show, on average, when someone buys a bucket of paint from you, out of the proceeds, what your profit is.
Part 2 of 2: Understanding the meaning of profit margins
Evaluate whether the profit margin meets your business requirements. If you're planning to rely solely on earnings from your business, consider the profit margins and revenue that can be earned over a year. You should also reinvest part of your income to grow your business. When you get rid of that capital investment, is the remaining return enough to meet your needs?
- Let's review the example above. Your business earns 600 million dong of net profit when revenue is 2 billion dong. If you use 300 million dong of profit to reinvest in the business (and pay off debts, if any), you have 300 million dong left.
Compare with similar business. Comparing with similar firms is very helpful in understanding marginal cost, which in turn helps you to position yourself. If you are filing a loan, your bank will more likely tell you the desired profit margin for the size or type of your business. If the company is bigger than the competition, you can research these companies, find their margins and compare them.
- Assume that Company 1 has a revenue of VND 1 billion and a total cost of VND 460 million. The profit margin is 54%.
- Assume that Company 2 has a revenue of VND 2 billion and a total cost of VND 1.16 billion. The profit margin of company 2 is 42%.
- Firm 1 has a better profit margin even though Firm 2 has double the revenue and higher profit margin.
Guaranteed equivalence when comparing profit margins. The margins of companies vary widely, depending on size and industry. Ideally, compare two or more companies in the same industry and have similar revenue to get the best effect from this comparison.
- For example, on average, the profit margin of the airline industry is only about 3%. Meanwhile, for engineering and software companies, this figure is in the 20% range.
- When comparing, don't forget to consider the size of the company so that the comparison makes sense.
Adjust profit margins if needed. You can change the percentage of profit margins by generating a lot of revenue (such as raising prices or boosting sales) or lowering the cost of the business. At the same time, even if the profit margin remains the same, if the total revenue and expenses are increased, the net income will still increase. Consider your business, competition, and risk appetite when trying to increase prices or cut costs.
- In general, you should start with small changes and gradually expand to prevent the risk of a sudden decline in business or anger from customers. Remember, there is always a price to pay for boosting margins, and doing too aggressively can have the opposite effect, causing the business to plunge quickly.
- Don't confuse margins with price-setting rates. The pricing ratio is the difference between the cost of production and the selling price of a good or service.