Author:
Peter Berry
Date Of Creation:
17 February 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
Unfortunately, biting your tongue while chewing food, talking or being confused is a common occurrence. This wikiHow article will show you how to heal an injured tongue. Consult your general practitioner or your dentist if you are often injured by accidentally biting your tongue.
Steps
Method 1 of 4: Give first aid
Wash your hands. Before you touch the inside of your mouth, take a minute to wash your hands with hot water and soap. If you don't have soap and water available, you can use a hand sanitizer. The goal is to prevent the germs from the hands from spreading to the open tongue wound causing infection.
- Resistant viruses can also cause infection if they come into contact with bleeding wounds.
Use pressure. When you bite your tongue, you will probably bleed at first because the tongue is a concentrated place for many blood vessels. The pressure on the affected area slows the bleeding and helps the blood clot. It is important to act immediately after an injury.- When the tip of your tongue is injured, push your tongue to the palate and hold it for 5 seconds. You can also use your tongue to press against the inside of your cheeks.
- If you reach the wound, place an ice cube on the affected tongue. You can also use the jaw to hold the stone and hold it against your tongue if it is not too painful. Move the ice cube until it melts. You can also place a clean cloth or medical gauze over the affected area and gently press it.
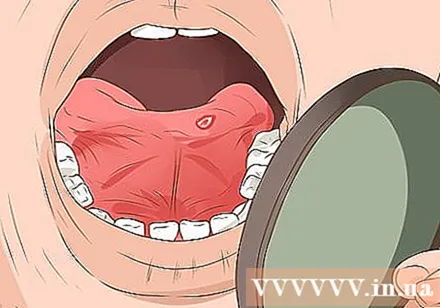
Check the wound. Open your mouth wide and use the mirror to see your tongue. If the bleeding has stopped and the wound looks shallow, you can continue with home treatment. If the bleeding continues and the cut looks deep, call your dentist and ask if the wound needs stitches.- If the bleeding is severe, call emergency services.
Check for other injuries. A tongue bite is usually caused by a sports injury or an accident. Check the rest of your mouth for damage or looseness, or bleeding gums from a broken tooth. Move your jaw up and down to see if it hurts. If one of the above injuries occurs, you should contact your doctor or dentist immediately.
Use a cold compress. The tongue will swell soon after being injured, so it will be easy to bite again. Place a cold object like a clean cloth on the wound. Hold for 1 minute until numbness occurs, then remove. You can do this multiple times over a few days.
- If the injured person was a child, they would probably prefer a frozen fruit stick to numb the wound.
Take a pain reliever. Choose an anti-inflammatory that you tolerate well, such as Advil, and take the recommended dosage as soon as possible. Medications can help reduce swelling while fighting pain that often occurs soon after an injury.
Gargle with mouthwash. If a mouthwash is available, rinse your mouth immediately.This will help clean the wound and prevent infection, especially if you bite your tongue while eating. Spit it out and rinse it again if there is bleeding. advertisement
Method 2 of 4: Wash and heal the wound by rinsing your mouth
Make a salt gargle. Take 250 ml of tap water. Add 1 teaspoon (5 g) of salt and stir. Gargle for 15-20 seconds, do it 3 times a day until it heals. Especially effective if you rinse your mouth right after a meal.
- Salt kills harmful bacteria in the mouth. The salt water rinse helps to clean the wound and reduces the risk of infection. Salt also has healing properties, which will help the wound heal faster.
Gargle hydrogen peroxide and water. Mix half part hydrogen peroxide (3%) and half water. Rinse your mouth with this solution for 15-20 seconds and spit it out. Be careful not to swallow. You can rinse your mouth up to four times a day.
- Hydrogen peroxide is a powerful antiseptic that inhibits bacteria activity in the wound. It also acts as a cleaning agent by removing debris from cuts and providing an amount of oxygen to the cells, which can help stop bleeding.
- Hydrogen peroxide is also gel-like, and you can apply it directly to the cut with a cotton ball.
Gargle with antacid / antihistamine. Partially mix diphenhydramine (as antiallergic solution Benadryl) with one part antacid (such as magnesia milk). Gargle with this mixture for a minute and spit it out. You can do this once or twice a day.
- Antacids control the level of acid in the mouth, helping to speed up the healing process. Antihistamines help reduce inflammation. These two drugs when combined together will form a type of solution that some people call "magic mouthwash".
- If you don't like rinsing your mouth with this mixture, you can make a thicker formulation and apply it as a paste.
Use a traditional mouthwash. Benzydamine hydrochloride, 0.12% chlorhexidine gluconate, or standard mouthwash are also good options. Rinse the recommended dosage for 15-30 seconds, then spit it out. Especially, rinsing after eating will clean food debris from the wound, helping the wound heal by preventing infection. advertisement
Method 3 of 4: Cure and relieve pain
Continue using an ice pack or cold compress. Put some ice in a plastic bag and place it on your tongue until the pain subsides. You can also wrap the ice pack in a damp handkerchief for added comfort. Sucking on ice cream or drinking cold water can also help relieve pain, but make sure you don't drink acidic ones.
- This will help stop bleeding if the cut is left open and relieve pain during the healing process.
Apply aloe. You can buy aloe vera gel from pharmacies. Or, you can cut off a branch of aloe and apply the gel inside the leaf to the wound, up to 3 times per day. For best results, apply it after rinsing your mouth and at night before bed.
- Aloe vera is an herbal remedy that has been shown to improve blood circulation. It is also effective against certain types of harmful bacteria. However, be careful not to swallow aloe vera directly.
- You can also add aloe vera gel to a sterile gauze and apply it to the wound. This will last longer by preventing the saliva from dissolving the gel.
Use mouth gel. Buy an anesthetic and antiseptic gel from pharmacies. Orajel, for example, comes in a small tube that is easy to apply. Just squeeze a little gel onto a clean cotton ball and apply it to the wound. Repeat each day 2-4 times until it heals.
Try a mouth cream. This cream works similarly to an oral gel. Apply some cream over the cotton ball and apply it to the wound. Repeat this therapy up to 4 times a day until it heals. You can also apply it directly to the wound with your finger.
Use baking soda. Mix 1 teaspoon of baking soda with water until it becomes a smooth paste. Dip a cotton ball in the mixture and apply it to the wound. Baking soda reduces the secretion of acids and bacteria, and also helps reduce swelling, inflammation and pain.
Eat honey. Take a teaspoon of honey and either lick any honey off the spoon or drip honey on the wound. Repeat twice a day. Honey will coat the oral mucosa and prevent the accumulation of harmful bacteria. For best results, you can add turmeric to honey. Turmeric has an antibacterial effect, helping to speed up the healing process when combined with propolis.
Apply magnesia milk to the wound. Dip a cotton ball in a magnesia milk bottle and apply it to the wound. You can do this 3 to 4 times a day. This therapy is even more effective if applied after rinsing the mouth. Magnesia milk is an active antacid that creates a favorable environment for beneficial bacteria. advertisement
Method 4 of 4: Take preventive measures
Go to the dentist. You should visit the dentist at least twice a year for routine dental care. If you need extra care due to a problem of bites, you will need to visit the dentist more often. Some people are especially at high risk of injury in the mouth, such as those with sharp teeth or having many holes in their teeth, resulting in teeth prone to fracture and leaving sharp edges. The dentist will recommend curing solutions.
- For example, if your teeth are not aligned, you may find yourself biting your tongue. The dentist and molar doctor will come up with preventive measures.
Check for teeth and gums for tightness. Make sure your teeth fit snugly against your gums and don't wobble too much. Sharp teeth are also not good. You should see your dentist for a tight fit if you are injured by biting.
Avoid irritation from oral tools. If you are wearing oral tools, make sure they fit snugly in your mouth without too much movement. Ask your molar doctor about how much movement you should pay attention to. This will help you tune in and avoid biting your tongue.
Wear protective gear. If you are playing sports with a risk to your teeth, you will need to wear a mouth guard and / or a helmet. These tools will help stabilize the jaw in the event of a collision and reduce the chance of biting the tongue or other injuries.
Take safety measures for epilepsy. If you have epilepsy, you should give guidance to those around you. Putting something in the mouth during a seizure is more harmful than gums and can lead to bite injuries. Instead, they should call an ambulance and roll you on your side until medical help is available. advertisement
Advice
- Contact your dentist or doctor promptly if you have no pain relief or no improvement after 1 week, if the wound worsens and smells strange or if you have a fever.
- Keep oral hygiene. Continue brushing 3 times a day with a soft brush. Be careful not to touch the wound.
Warning
- Chew food slowly, do not drink alcohol, and do not use tobacco products (such as smoking or chewing) as these will irritate and slow the healing process.
- Avoid spicy, spicy foods and acidic drinks as they irritate the wound and make you uncomfortable.