Author:
Lewis Jackson
Date Of Creation:
5 May 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
OpenDNS provides internet filtering services that can block website access. If OpenDNS keeps you from accessing the website you want, you can change the DNS settings on your computer to connect to another DNS server. These servers will compile website addresses so you can connect to them. If you can't change the DNS settings on your computer, you can use the Tor browser to access it.
Steps
Method 1 of 6: change DNS settings (Windows)
Click the Start menu and type.ncpa.cpl. Press ↵ Enter.
- OpenDNS changes the DNS settings on the router to redirect requests. When adjusting the DNS settings on the operating system, these changes will override any DNS settings on the router, so you can bypass OpenDNS. This doesn't work if the router is configured to block all DNS requests except for OpenDNS on port 53.

Right click on the active network. Select "Properties".- If you are unable to access because you do not have administrator rights, click here
Select "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP / IPv4)" (Internet Protocol Version 4) from the list. Click on Properties.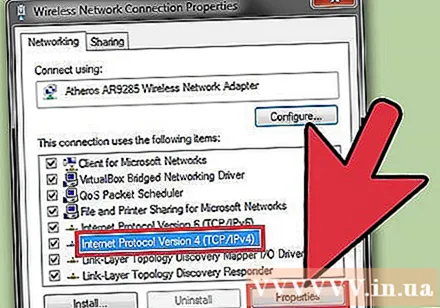

Select "Use the following DNS server addresses" (Use the following DNS host addresses). It allows you to set up an alternate DNS address, which is the server that compiles website addresses so you can connect in your browser. Usually, the DNS server is set up by your network service provider, but OpenDNS overwrites the router's DNS with its own server.
Enter the address of the public DNS server. There are many available DNS servers. If it is difficult to connect to this address, you can try a different one. Make sure to enter sufficient Primary and Secondary addresses.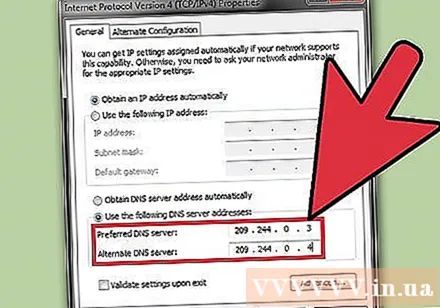

Try opening the website. After changing the DNS settings, you can connect to the blocked website. Changing DNS settings on Windows overrides the DNS settings on the router.- If you can't connect, try a different public DNS provider.
Method 2 of 6: change DNS settings (Mac)
Click the Apple menu and select "System Preferences". You are going to change DNS servers, which compile website addresses and allow you to connect to them.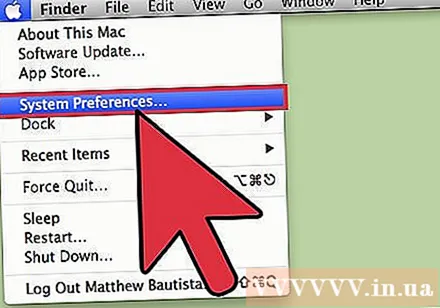
- OpenDNS changes the DNS settings on your router to redirect your request. When adjusting the DNS settings on the operating system, this change will override the router's DNS settings, allowing you to bypass OpenDNS. This doesn't work if your router is configured to block all DNS except OpenDNS on port 53.
Select "Network" in the "System Preferences" menu.
- If you can't access this option because you don't have administrator rights, click here
Click on active connection. The connection usually has a green dot next to it.
- Click the button.Advanced ''
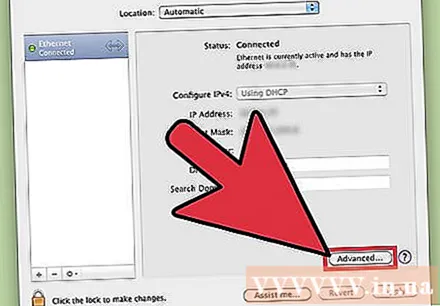
Click on the "DNS" tab.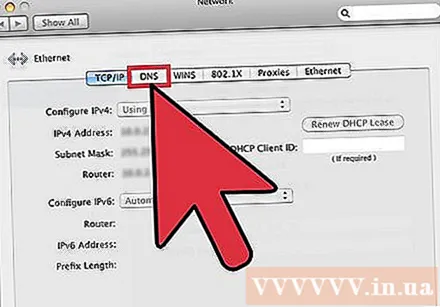
Click the "+" button. This button allows you to add new DNS servers. There are many public DNSs out there. If you can't connect using this DNS server, you can try another one. Remember to enter 2 Primary and Secondary addresses.
Get rid of the old DNS server. If there is a DNS server on the list, delete the old DNS so the computer can connect to the new DNS server first.
Try opening a website. After changing the DNS settings, you can connect to the blocked website. Changing the DNS settings on the Mac will override the DNS settings on the router.
- If you can't connect, try a different public DNS provider.
Method 3 of 6: editing Hosts file (server)
- Open the hosts file. The host file on your computer acts as your own private DNS, allowing you to manually assign an IP address with a domain name. It will override any settings on the router.
- Windows - The hosts file is usually located. Right-click the hosts file and select Open With, then click Notepad.
- Mac - Open Terminal and type sudo en / private / etc / hosts.
- Determine the IP address of the website you want to visit. To add a website to the hosts file, you need to know the website's IP address.
- Open Command Prompt (Windows) or Terminal (OS X).
- Type ping websiteaddress.com and press ↵ Enter. It will respond to the website's IP address.
- Add the IP address and hostname at the end of the hosts file. At the end of the file, you usually see it. Add the new IP address and hostname after this line. Write in line format, including IP address and hostname.
- It is recommended to write each hostname twice, yes and no www.. For example, to add Facebook, you write an IP address line withwww.facebook.com, on the other line write the IP address with facebook.com.
- Save and turn off the file. You may need to restart your computer for the changes to take effect. advertisement
Method 4 of 6: Use Google caching
- Open a web browser. You can access the cached version of the website as it loads through Google. The recent caching version is incomplete, but not too outdated either.
- Copy and paste the following address. Paste in the address bar of the web browser:
- webcache.googleusercontent.com/search?q=cache:http://example.com/
- Instead of, replace .http://example.com/website address you want to visit. For example, to access a cached version of Facebook, you type webcache.googleusercontent.com/search?q=cache:https://facebook.com/. advertisement
Method 5 of 6: Using Tor
Download the Tor browser. Tor is a browser that allows you to browse anonymously, bypassing most filters and blocking the internet. You can download the Tor browser for free from.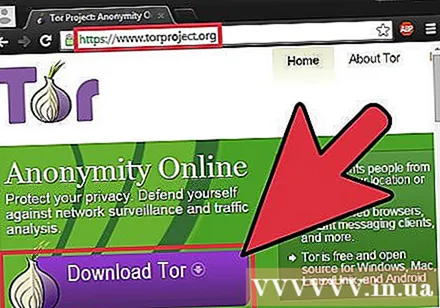
- If the Tor website is blocked on your computer, you can download it from another computer and install it on a USB flash drive.
Run the Tor installer. Follow the instructions to install the browser on your computer. If you want to install to USB, select USB as the installation location.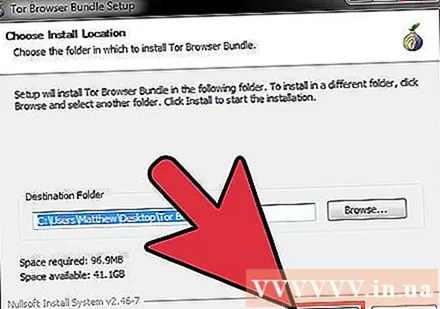
Click the "Connect" button. This is the first Tor configuration option. button.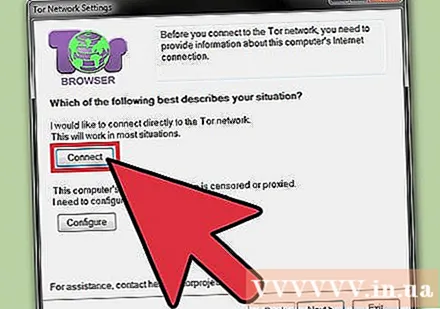
Start with internet access. You should see the words "Congratulations!" (Congratulations) after successfully connecting to the Tor network, you can now start accessing the blocked websites.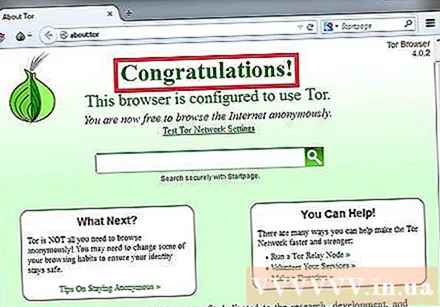
- When you want to use Tor, you just need to start the Tor browser. You don't need to go through the initial installation again.
Method 6 of 6: Connecting Modem directly
- Determine if this approach is feasible. OpenDNS interferes with the router settings, meaning any computer connected to the router is affected. If you want to connect the computer directly to the modem, completely bypassing the router, you can bypass OpenDNS.
- Unplug the router from the modem. As long as you don't restart your router, the settings won't change and no one will know.
- Disconnect the computer from the router. If using wireless network, disconnect from the network. If using a wired network, disconnect the Ethernet cable connecting the computer to the router.
- Connect the modem directly to the computer via Ethernet cable. Computers can access the internet immediately.
- Most modems do not have a wireless functionality because its only job is to manage the router.
- If your modem is a combination of router and modem then you're out of luck.
- Access the website you want. Now that you're connected to the modem, you can access any websites that were previously blocked by OpenDNS. Remember to reconnect everything after you are done. advertisement