Author:
Peter Berry
Date Of Creation:
19 February 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
As a wonderful, easy-to-grow flower, lavender deserves to be added to any garden. Everything you need to grow and care for this scented flower is a suitable place in the garden and a bit of gardening knowledge.
Steps
Method 1 of 3: Prepare
Choose a location with plenty of light. As a herb native to the Mediterranean region, lavender grows well in hot climates with plenty of sun. Choose a corner in the garden where the plant can receive light for at least eight hours a day. You should also choose an sheltered place to protect your tree from strong winds.

Make sure the soil is well drained. Wet soil is the enemy of lavender, so the most important thing to take into account is choosing a well-drained area. Light, porous and well-ventilated soil is the optimal condition for lavender to grow.- For better drainage, you can mix a little sand before planting. Sand offers many benefits: well drained, non-cohesive and reflective, allowing sunlight to reflect off the plants. This is especially useful in cold and humid climates.
- Alternatively, you can try growing lavender on high ground, on a slope, or beside a wall for maximum drainage.

Check the pH of the soil. Lavender grows best in lightly alkaline soils, with an ideal pH between 6.7 and 7.3. You can test your soil pH with test kits available at home appliance stores and gardening centers.- If necessary, you can increase soil alkalinity by adding a little more lime. The amount of lime added will depend on the soil type and the test results.
Buy lavender. Many varieties of lavender can be grown at home. Whether or not Lavender does well depends on soil conditions. Flower varieties sold at local nurseries are generally appropriate for the conditions in which you live, but you can also check the plant label or ask the staff at the nursery if you are unsure.- Mustead and Hidcote are two varieties of lavender with very good stamina.
- Although lavender can be grown with seeds, this approach is not recommended as it requires a cold brewing step, which can take nearly a month to germinate.
Method 2 of 3: Planting trees
Dig a hole enough for the roots to spread. Use the trowel to dig a hole at the selected location. The planting hole should be deep and wide enough to spread the roots.
- If you are planting lavender in a pot, choose a large pot - the roots of the lavender plant will be much wider than they are now.
Prepare the land. Prepare the soil for the lavender plant and provide optimal conditions for plant growth. Spread two rounds of round gravel about 2.5 cm in diameter with half a cup of mixed lime, compost, and bone meal into the hole. Mix. Cover this mixture with soil.
- Gravel helps to drain water, lime will increase alkalinity in the soil, bone meal and fertilizer will provide the plant with nutrients to grow well.
Water the lavender plants in the nursery pots before planting. You should water the plant in its nursery pot at least an hour before planting. This step is to make sure the roots are moist but not too wet before planting.
Prune. Prune a little before planting. This step is to shape the tree, ensure air circulation through the branches, stimulate the plant to sprout new shoots and prevent the inner core of the stem from woody, a common lavender problem. Good air circulation is especially important when you live in a humid climate.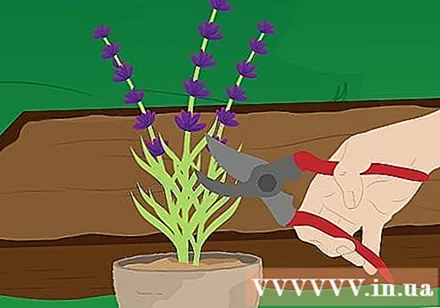
Prepare the roots. Lift the plant from the nursery pot and gently shake it to remove the soil. Plant the lavender plant in a new place with its soil-free roots so that it can quickly and easily adapt to the new environment.
Plant tree. Carefully plant the lavender plant in the prepared spot, placing it on top of the gravel mixture that was prepared earlier. Make sure the roots are not in direct contact with the mixture. Cover the roots with soil, gently pat the soil around the base of the plant.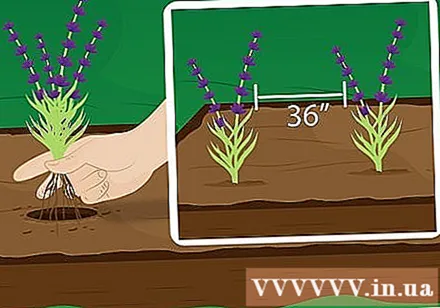
- If you plan to grow more lavender plants, plant plants about 90 cm apart. This distance allows for good air circulation and enough space for the plant to grow.
Method 3 of 3: Take care of plants
Fertilize once a year. Lavender is a plant that requires little care, and if fertilized, it is only necessary to fertilize once a year. Spread a thin layer of the compost and bone meal mixture around early spring.
- The ideal time to fertilize a newly planted lavender plant is after first watering. Let the soil dry, then fertilize.
Limited watering. As noted above, moisture is the enemy of lavender, and if the roots are soaked in water, the plant will die faster even during drought and freezing temperatures. The fact that over-watering in the spring is the main cause of lavender planting failure. When the lavender plant has taken root, every 7-10 days, water it with water.
- To water the right amount of water, you need to let the soil dry completely between watering; however, you should not let the plant become dehydrated.
- If you're growing lavender in northern climates, make sure you water it very little until summer, when the temperature soars and the soil dries faster. You should then start watering your plants every 7-10 days.
- If you are planting flowers in a pot, make sure the pot is well drained to prevent water from standing on the bottom.
Watch out for weeds. You can prevent weeds from growing around lavender plants by spreading a thin mulch on the soil. Use light-colored coatings such as coarse sand, gravel, or shells. The mulch will also help protect the roots from frost during winter.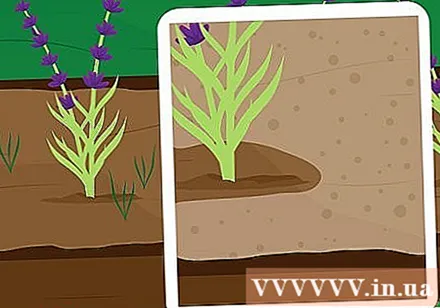
- Do not use wood chip mulch to avoid moisture retention leading to root rot.
Prune. Lavender should be pruned once a year, preferably in the spring before the plant starts to sprout new ones. You should prune about 1/3 -1/2 of the plant when it is sprouting. Use pliers to trim the tree or hedge clippers to create a neat and rounded shape for the tree.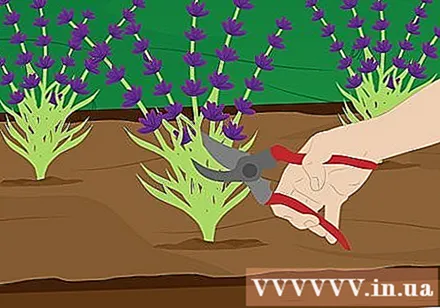
- Thin, long shoots grow from leafy branches. The lavender plant will also begin to flower. This is a good time to fertilize your plants.
- Pruning will stimulate the tree to sprout and prevent the tree from breaking down and lying flat.
- However, make sure not to prune too much as this can kill the young shoots.
Harvest flowers. The best time to harvest fresh lavender is when the stalks of each flower begin to bloom. This is the time when lavender flowers are most fragrant and full of life. Cut flowers at the base, near the foliage.
- Prune to where new leaves are growing. This may stimulate the plant to flower for a second time in the fall.
- Once all the flowers on the plant are in bloom, it is too late to harvest the lavender for medicinal purposes. If you want to dry the lavender, harvest it when only 3/4 of the flowers are in bloom.
- To dry the lavender, bundle about 100 flowers together, tie it with an elastic band and hang it upside down in a warm, dark, and dry place indoors for 10-14 days.
- If you want to remove the flowers from the stem, you can roll the bouquet on a metal net over a bucket. This work is called “sifting” of the lavender.
- If you want to adorn your house with lavender flowers, place flowers in the vase, but don't put the flower roots in the water. Water will only cause the flower to fall off faster and the stems will soften.
Advice
- Lavender leaves usually range in color from bluish gray to silvery gray, and some species are light green in color. Not all types are available, but you can find them on the ordering websites.
- Perennial lavender plants can be between 30 cm-90 cm tall depending on the species. Plants need at least 6 hours of direct sunlight a day, more than possible. Lavender can grow well from 5 to 10 zones and is grown about 40 cm apart.
- Lavender blooms in mid-summer and ranges in color from gray to deep purple. Many varieties of lavender are available in other colors such as white, pink, and yellowish green. Lavender flowers are small, sometimes like flower buds, but sometimes large, they usually grow on sharp branches.
- Older branches often age wood and are not as easy to divide as many other perennials. If you need to move, switch in the spring and plant again. Lavender plants can be reproduced by cuttings.
- Some lavender species can be planted with seeds (especially "Munstead"), or you can buy potted plants in the spring. Popular species are "Grosso", "Provence", "Royal Purple", "Gray Lady", and "Hidcote".
Warning
- Lavender is prone to root rot. To avoid this, never over-water and in winter should only minimize watering.