Author:
Lewis Jackson
Date Of Creation:
12 May 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
You've been given a homework that asks you to calculate the area of a quadrilateral, but you don't even know what a quadrilateral is. Don't worry - this article will help you! A quadrilateral is any shape with four sides, such as a rectangle, square, and diamond. To calculate the area of a quadrilateral, all you have to do is distinguish the quadrilateral type and follow a simple formula. That is all!
Steps
Method 1 of 4: Square, rectangle and parallelogram
Know how to distinguish parallelogram. A parallelogram is a four-sided shape with two pairs of parallel sides, opposite sides of equal length. Parallelogram includes:
- Square: Four sides of equal length. Four 90 degree angles (right angle).
- Rectangle: Four sides, the opposite sides have equal lengths. Four 90 degree angles.
- Rhombus: Four sides, the opposite sides have equal lengths. Four corners, no angle is 90 degrees but the opposite angles should be equal.

Multiply the base edge by the height to get the area of a rectangle. To find the area of a rectangle, you need length measurements of: length (longer side) and width (shorter side). Then multiply the two values to get the area. In other words:- Area = length × width, or A = b × h.
- For example: If the length of a rectangle is 10 cm long and the width is 5 cm, then the area of the rectangle is 10 × 5 (b × h) = 50 square centimeters.
- You remember to use units square gives the results found when calculating the area of any shape (square centimeter, square decimeter, square meter ...).

Multiply the length of one side by itself to find the area of the square. Basically a nectar is a special rectangle, so you can use the same formula to find the area. However, since the four sides of the square are of equal length, you only need to multiply the length of one side by itself. This is similar to multiplying the bottom edge by the height because the square has the same base and the height. Use the following equation:- Area = side × edge or A = s
- For example: If a square side is 4 meters long (t = 4) then the square area is t, or 4 x 4 = 16 square meters.

Multiply the lengths of the diagonal lines by 2 to find the area of the rhombus. Be careful with this one - when you find the area of a rhombus, you cannot multiply the side lengths by two adjacent sides. Instead you have to find the diagonal lengths (the lines connecting pairs of opposite corners), multiply them and divide by two. In other words:- Area = (Diagonal 1 × Diagonal 2) / 2 good A = (d1 × d2)/2
- For example: If a rhombus has 2 diagonal lines with lengths of 6 meters and 8 meters, then its area is (6 × 8) / 2 = 48/2 = 24 square meters.
Another way is to use base × height to get the area of a rhombus. In theory, you can multiply the base edge by the height to find the area of a rhombus. However, the "bottom edge" and the "height line" in this case are not adjacent sides. First you select an edge as the bottom, then draw a line from the bottom to the opposite edge. This line should be perpendicular to both sides. The length of this line is the height of the line.
- For example: A diamond has side lengths of 10 km and 5 km. The length of the segment perpendicular to the pair of sides is 3 km. If you want to find the area of this rhombus, you get 10 × 3 = 30 square kilometers.
Remember that the rhombus and rectangle formulas work for squares. Using the edge × edge formula for squares is the easiest way to find the area of these shapes. However, theoretically squares are also rectangles and rhombuses, so you can use the formulas for calculating their areas for squares. In other words, for a square: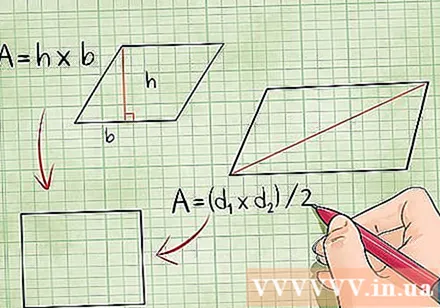
- Area = base × height or A = b × h
- Area = (Diagonal 1 × Diagonal 2) / 2 good A = (d1 × d2)/2
- For example: A four-sided shape has two adjacent sides 4 meters long. You can find the area of this square by multiplying the base by the height: 4 × 4 = 16 square meters.
- For example: The diagonal lines of a square are equal to 10 centimeters in length. You can calculate the area of this square using the formula: (10 × 10) / 2 = 100/2 = 50 square centimeters.
Method 2 of 4: Calculate the area of a trapezoid
Know how to distinguish a trapezoid. A trapezoid is a quadrilateral with at least one pair of parallel sides. The trapezoid has no regulation of the angle. Each side of the trapezoid can have a different length.
- There are two ways to calculate the area of a trapezoid, depending on what information you have. Here are two ways to calculate the area of a trapezoid.
Find the height of the trapezoid. A trapezoidal height is a straight line connecting and perpendicular to two parallel sides. Usually high street are not are the same length as the sides because these edges usually run in oblique direction. You need the height of the road for both area formulas. Here's how to calculate the length of the trapezoid:
- Find the shorter edge of the two parallel bottom edges. Place the pen at an angle between the bottom edge and a non-parallel edge. Draw a line perpendicular to both bottom edges. Measure this line to find the altitude.
- You can also sometimes use trigonometry to calculate the length of a line if the high, bottom and other sides form a square. See our trig article for more information.
Calculate the area of a trapezoid when you know the length of the high line and the two bottom sides. If you know the length of the line as well as the length of the trapezoidal base, use the following equation:
- Area = (Bottom 1 + Bottom 2) / 2 × height or A = (a + b) / 2 × h
- For example: If a trapezoid has two base sides that are 7 meters long and 11 meters long, and the height connecting the bottom sides is 2 meters long, you can find the area as follows: (7 + 11) / 2 × 2 = (18) / 2 × 2 = 9 × 2 = 18 square meters.
- If the length of the line is 10 and the base sides are 7 and 9, you can find the area by simply doing the following: (7 + 9) / 2 * 10 = (16/2) * 10 = 8 * 10 = 80
Multiply the median by 2 to find the area of the trapezoid. The median is an imaginary line that runs parallel to the base of the trapezoid and equidistant from them. Because of the average line is always equal to (Bottom 1 + Bottom 2) / 2 So if you know its length, you can use the following formula:
- Area = median × altitude or A = m × h
- This formula is essentially similar to the original formula, but you use "m" instead of (a + b) / 2.
- For example: The median line of the trapezoid in the above example is 9 meters long. That is, we can calculate the area of a trapezoid by taking 9 × 2 = 18 square meters, as well as the first way.
Method 3 of 4: Calculate the area of a kite
Know how to distinguish a kite. A kite is a four-sided shape with two pairs of equal sides, and two equal sides lying edge together, not facing each other. In general, the kite resembles a kite in real life.
- There are two ways to calculate the area of a kite, depending on what information you have. Here are two ways to calculate the area of a kite.
Use the rhombus diagonal formula to find the area of a kite. Since a rhombus is a special form of a kite where all four sides have the same length, you can use the diagonal rhombus area formula to find the area of the kite. Remember that the diagonal is the straight line connecting the two opposite corners of the kite. Like a rhombus, the kite surface formula is:
- Area = (Diagonal 1 × Diagonal 2) / 2 good A = (d1 × d2)/2
- For example: If a kite has 2 diagonal lines with lengths of 19 meters and 5 meters, then its area is (19 × 5) / 2 = 95/2 = 47.5 square meters.
- If you do not know and cannot measure the length of two diagonal lines, you can use trigonometry to calculate. See the kite article for more information.
Use the lengths of the sides and the angle between them to find the area. If you know the lengths of the pairs of sides and the angles between them, solve the area of a kite using the trigonometric principle. This method requires you to know how to use the sine function (or at least have a calculator with a sine function). See our trig article for more information, or use the following formula:
- Area = (Side 1 × Side 2) × sin (angle) or A = (s1 × s2) × sin (θ) (where θ is the angle between side 1 and edge 2).
- For example: You have a kite with a pair of sides 6 meters in length and 4 meters on the other side. The angle between them is 120 degrees. In this case, you can solve for the area like this: (6 × 4) × sin (120) = 24 × 0.866 = 20.78 square meters
- Note that in this case you must use two edges different and the angle between them - using a pair of sides of equal length will give false results.
Method 4 of 4: Solution for any quadrilateral
Find the lengths of all four sides. Does your quadrilateral belong to any of the above groups of shapes (ie, all four sides have different lengths and no parallel pairs of sides)? There are actually many formulas for calculating the area of any quadrilateral, regardless of its shape. In this section you will learn how to use the most common formula. Note that this formula requires you to know how to use trigonometry.
- First you have to find the lengths of each side of the quadrilateral. For this article, we call the edges a, b, c and d. Edge a opposite to the edge c and edge b opposite to the edge d.
- For example: If you have an oddly shaped quadrilateral that doesn't belong to any of the above groups of shapes, you must first measure the four sides. Let's say they are 12, 9, 5, and 14 centimeters long. In the section below you will use this information to find the area of that quadrilateral.
Find the middle corners a with d and b with c. When dealing with an asymmetric quadrilateral, you cannot find the area from the side lengths. You have to find two of the opposite corners. For this section, we will use angles A between the edges a and d, and the angle C between the edges b and c. However, you can also use the other two opposite angles.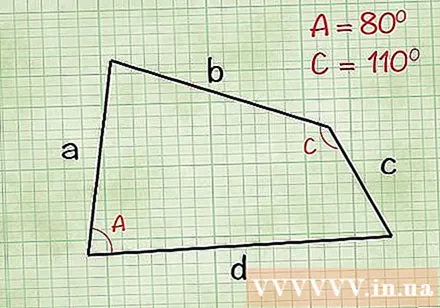
- For example: Suppose in your quadrilateral A equal to 80 degrees and C equal to 110 degrees. In the next step you will use these values to find the area.
Use the area formula of a triangle to find the area of a quadrilateral. Imagine a straight line connecting the corner between the edge a and b with the middle corner c and d. This line divides the quadrilateral into two triangles. Because the area of the triangle is absineC, Inside C is the middle corner a and b, you can use this formula twice (one for each triangle) to get the area of the entire quadrilateral. In other words, for any quadrilateral:
- Area = 0.5 Side 1 × Side 4 × sin (Side 1 & 4 angle) + 0.5 × Side 2 × Side 3 × sin (Side 2 & 3 angle) good
- Area = 0.5 a × d × sin A + 0.5 × b × c × sin C
- For example: Now that you have the necessary edges and angles, solve the following:
- = 0.5 (12 × 14) × sin (80) + 0.5 × (9 × 5) × sin (110)
- = 84 × sin (80) + 22.5 × sin (110)
- = 84 × 0,984 + 22,5 × 0,939
- = 82,66 + 21,13 = 103.79 square centimeters
- Note that if you are looking for the area of a parallelogram with equal opposite angles, the equation will be simplified to Area = 0.5 * (ad + bc) * sin A.
Advice
- This triangle area calculator is very convenient for calculations in the "Any Quadrilateral" method mentioned above.
- For more information, see the articles on specific shapes: How to find the area of a square, How to calculate the area of a rectangle, How to calculate the area of a rhombus, How to calculate the area of a trapezoid, and How to Find the area of a kite.