Author:
Judy Howell
Date Of Creation:
26 July 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- To step
- Method 1 of 3: Diagnose the problem
- Method 2 of 3: Analyze the report
- Method 3 of 3: Fix the problem
- Tips
- Warnings
A Windows blue screen, or "stop error", can be quite frustrating. In English it is not called the "Blue Screen of Death" for nothing. The error message usually doesn't get to you any wiser, and the blue screen seems to strike at random times. In this article, we'll tell you more about the blue screen, how to diagnose the problem, and how to fix the errors.
To step
Method 1 of 3: Diagnose the problem
 Check to see if you have changed anything recently. The most common cause of the blue screen is a recent change in your computer or hardware settings. It is often related to new drivers being installed or updated. Drivers are pieces of software that provide communication between the hardware and Windows.
Check to see if you have changed anything recently. The most common cause of the blue screen is a recent change in your computer or hardware settings. It is often related to new drivers being installed or updated. Drivers are pieces of software that provide communication between the hardware and Windows. - An infinite number of hardware configurations are possible, so drivers cannot be tested for all possible setups. Therefore, installing or updating a driver can cause a critical error.
 Check the computer's internal hardware. Sometimes a bad connection inside the computer causes the blue screen. Open the computer to make sure all cables and cards are properly seated.
Check the computer's internal hardware. Sometimes a bad connection inside the computer causes the blue screen. Open the computer to make sure all cables and cards are properly seated. - It is a bit more difficult with laptops. You can at least check if the hard drive and RAM are properly connected and stuck. Use a small Phillips screwdriver to unscrew the laptop case. Press down on the various components firmly.
 Check the computer's temperature. Overheating can lead to hardware failure. The graphics card and processor are the most likely candidates for overheating.
Check the computer's temperature. Overheating can lead to hardware failure. The graphics card and processor are the most likely candidates for overheating. - You can check the temperatures of the various components from the BIOS menu, or with software from Windows.
 Test the working memory. A problem with the RAM, or RAM, is a common cause of a blue screen. If there is something wrong with the RAM, the system will become unstable. You can test your RAM with a program called “memtest86”. This program is available online for free, you can run it by burning it to a boot disk (CD).
Test the working memory. A problem with the RAM, or RAM, is a common cause of a blue screen. If there is something wrong with the RAM, the system will become unstable. You can test your RAM with a program called “memtest86”. This program is available online for free, you can run it by burning it to a boot disk (CD). - Restart your computer and let the software begin. Memtest should automatically run RAM tests. It may take several minutes. The best results are obtained by performing the tests a number of times. Memtest will continue to test until you manually stop it.
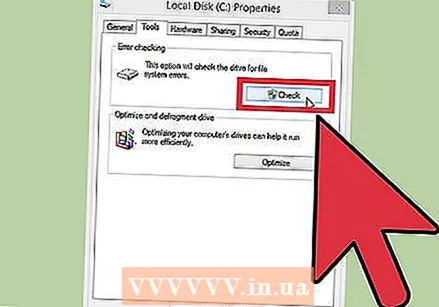 Test your hard drive. Use the "chkdsk" function of your hard drive to scan for errors and fix potential problems. You start chkdsk by opening "Computer" / "My Computer" and clicking with your right mouse button on the disk you want to check. Select "Properties".
Test your hard drive. Use the "chkdsk" function of your hard drive to scan for errors and fix potential problems. You start chkdsk by opening "Computer" / "My Computer" and clicking with your right mouse button on the disk you want to check. Select "Properties". - Click on the "Tools" tab.
- Under "Error checking", click "Check now". When prompted for the Administrator password or confirmation, type the password or confirmation.
 Turn off all unnecessary components. One way to determine what may be going on is to delete anything that is not essential for the computer to work. If this clears the error, you know the problem is with one of the removed components.
Turn off all unnecessary components. One way to determine what may be going on is to delete anything that is not essential for the computer to work. If this clears the error, you know the problem is with one of the removed components. - A desktop computer needs at least a motherboard, a hard drive, power supply, RAM and a keyboard. Connect your display directly to the monitor output of your motherboard (if present) so that you can remove the graphics card. You can also remove everything else during the diagnosis.
- If the computer functions without problems after removing components, it is important to add the components back one by one and see if the problem returns. This way you can find out which component is causing the problems.
- This method does not work with laptops, because there it is a lot more difficult (or even impossible) to remove the various components.
Method 2 of 3: Analyze the report
 Set the computer so that it does not restart on a blue screen. Often the default setting is that a computer reboots with a blue screen, so you don't have time to analyze what the error message is. Set the computer to stop in the event of a blue screen so that you can copy the necessary information.
Set the computer so that it does not restart on a blue screen. Often the default setting is that a computer reboots with a blue screen, so you don't have time to analyze what the error message is. Set the computer to stop in the event of a blue screen so that you can copy the necessary information. - Open "System Properties". Press the Windows key and the Pause key on your keyboard at the same time (works on all Windows versions) to open the system properties.
- Click on the "Advanced" tab. Windows XP users are immediately in the Advanced System Properties.
- Under "Startup and Recovery", click "Settings" (or "Startup and Recovery").
- Uncheck the box next to "Automatically restart the computer". Click on "Apply" to save the changes. The next time a blue screen appears you will be able to view the error message until you manually reboot the system.
 Wait for the problem to recur. When the blue screen pops up again, copy the following information. Enter the found information into a search engine to find out which piece of hardware or software is causing the problem:
Wait for the problem to recur. When the blue screen pops up again, copy the following information. Enter the found information into a search engine to find out which piece of hardware or software is causing the problem: - The problem seems to be caused by the following file: Write down which file is listed after this sentence and the error message below it.
- "STOP:" Copy the first code after the STOP message.
Method 3 of 3: Fix the problem
 Boot in safe mode. If Windows won't boot because of the stop errors, try booting in safe mode so you can try to fix the problem. When the computer boots up, press the F8 key repeatedly until the boot menu appears. Select "Safe Mode with Networking" to boot in Safe Mode, but with the network drivers and services you need to connect to the Internet or other computers on your network.
Boot in safe mode. If Windows won't boot because of the stop errors, try booting in safe mode so you can try to fix the problem. When the computer boots up, press the F8 key repeatedly until the boot menu appears. Select "Safe Mode with Networking" to boot in Safe Mode, but with the network drivers and services you need to connect to the Internet or other computers on your network.  Scan for viruses. Viruses and malware can underlie the problems that cause the blue screen. Always keep your anti-virus software up to date and run a full scan to look for possible causes of your problem.
Scan for viruses. Viruses and malware can underlie the problems that cause the blue screen. Always keep your anti-virus software up to date and run a full scan to look for possible causes of your problem. 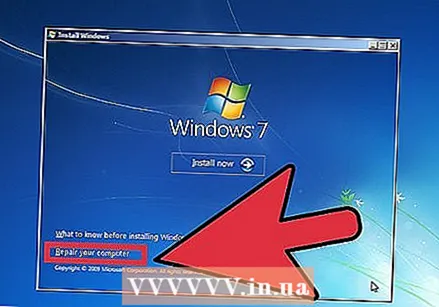 Perform a "Repair Installation". A recovery installation is a quick alternative to a full Windows reinstallation as it only copies system files to your computer. This can be useful if an essential file is causing the computer to malfunction.
Perform a "Repair Installation". A recovery installation is a quick alternative to a full Windows reinstallation as it only copies system files to your computer. This can be useful if an essential file is causing the computer to malfunction. - To perform a recovery installation, insert the Windows installation disc into the CD tray and boot from this disc. Select "Repair Installation" from the menu. Windows will now delete old Windows files and install new ones. You will not lose your documents and personal files.
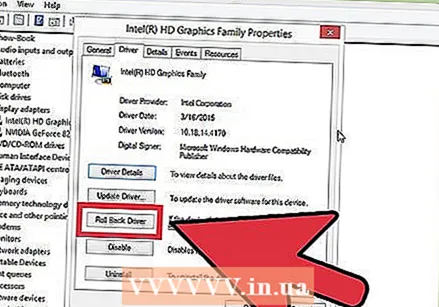 Go back to previous versions of your drivers. If the hardware is causing the problem, it is a good idea to try older drivers. This process will install a previous version of driver software, and that may fix the problem.
Go back to previous versions of your drivers. If the hardware is causing the problem, it is a good idea to try older drivers. This process will install a previous version of driver software, and that may fix the problem. - Open Device Manager. Click Start> Control Panel> System and Security, then under "System" click "Device Manager". In Windows 8, press Windows key + X and select "Device Manager".
- Double-click the category that contains the device driver, then double-click the name of the device that you want to restore to a previous driver version.
- Click the "Driver" tab and then click "Roll Back Driver".
- Continue to use the computer as usual. Once you have restored the driver, you can start using the computer as normal again. Do not update the driver until a newer version is released.
 Uninstall Windows updates. If restoring the drivers did not work, try reverting to an older, working version of Windows. This will help you determine if the problem is caused by a recent system update.
Uninstall Windows updates. If restoring the drivers did not work, try reverting to an older, working version of Windows. This will help you determine if the problem is caused by a recent system update. - Open System Restore. Type "System Restore" in the search box of the start menu. Open the program and select a date on the calendar before the problems started.
- This will revert all updates and settings from that date. Use this to determine if a Windows update is causing the problems.
 Free up space on your hard drive. Problems can arise if there is not enough free space on the disk where Windows is installed. Delete unnecessary files and programs if you have less than 15% free space left on the disk.
Free up space on your hard drive. Problems can arise if there is not enough free space on the disk where Windows is installed. Delete unnecessary files and programs if you have less than 15% free space left on the disk.  Perform updates and install new versions of drivers. If restoring updates and drivers did not work, you can try installing the latest updates and drivers. Check Windows Update to see what system and hardware updates are available.
Perform updates and install new versions of drivers. If restoring updates and drivers did not work, you can try installing the latest updates and drivers. Check Windows Update to see what system and hardware updates are available. - Click on Start and search for “Windows Update”. In Windows 8, tap the Windows key and type “Windows Update”.
 Reinstall Windows. If you still can't find the source of the problem, you can try a full Windows reinstallation. Make sure you have a good backup of all your documents and files. Your hard drive will be formatted and all data will be erased.
Reinstall Windows. If you still can't find the source of the problem, you can try a full Windows reinstallation. Make sure you have a good backup of all your documents and files. Your hard drive will be formatted and all data will be erased. - If the blue screen is caused by hardware, reinstalling Windows will not solve the problem. Only replacing the hardware will solve the problem.
 Replace hardware. If the above steps did not work, you may have to replace components. On a laptop it is not easy and often expensive to replace hardware, except for the RAM and hard disk.
Replace hardware. If the above steps did not work, you may have to replace components. On a laptop it is not easy and often expensive to replace hardware, except for the RAM and hard disk. - If the RAM test shows that there is a problem with the RAM, you will have to replace your RAM as soon as possible.
- If hard drive errors show up, back up the drive and install a new hard drive. In that case, you will have to reinstall Windows on your new drive.
- Replacing a graphics card is often very expensive. In most laptops it is almost impossible to replace the graphics card. In a desktop computer you can open the case and replace the old graphics card with a new one.
Tips
- If stop errors appear, always try to start the computer with only the essential hardware first. If the computer then works without problems, you can check the components and drivers one by one.
Warnings
- Do not make changes to registry settings or startup programs if you are not sure what you are doing.
- Back up your data before running System Restore and before analyzing error checks.