Author:
Judy Howell
Date Of Creation:
4 July 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
The density of an object is defined as the mass per unit volume. Density is used in geology, metallurgy and other natural sciences as a property by which rocks, minerals and metals can be identified. In addition, it is used in calculations for the buoyancy of an object in a given fluid to determine whether it will float in that fluid. To find out the density of an object, follow these steps.
To step
Method 1 of 2: Determining the Density
 Determine the mass of an object. Simply put, the mass of an object is how much of a particular material it contains. You can determine the mass by weighing the object with a balance or a weighing hook.
Determine the mass of an object. Simply put, the mass of an object is how much of a particular material it contains. You can determine the mass by weighing the object with a balance or a weighing hook. - If the object must be placed in a container before it can be weighed, such as a liquid or powder in a graduated cylinder, then the container must first be weighed so that its mass can be determined and subtracted from the total object and container.
 Determine the volume of the object. The volume of an object is the amount of space it occupies. Volume can be determined in several ways, depending on the object:
Determine the volume of the object. The volume of an object is the amount of space it occupies. Volume can be determined in several ways, depending on the object: - If it is a fixed object with regular dimensions, measure the length, width and height (or the length and diameter for a cylinder) and calculate the volume, depending on the shape. There are a variety of formulas for finding the volume of a rectangle, cylinder, or pyramid, just to name a few.
- If the object is solid and non-porous with unclear dimensions, such as a jagged rock, you can determine its volume by submerging it in water and measuring the amount of water being displaced. (According to Archimedes' law: an object displaces a volume of a liquid equal to its own volume.)
- If the object is a liquid or powder, place it in a graduated cylinder and read from the graduation mark to what extent the substance fills the container. (If the substance is a liquid, read the graduation mark at the lowest point of the curve forming the liquid at the top.)
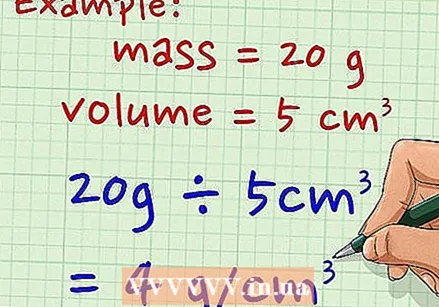 Divide the object's mass by its volume. This value is the density of the object and is expressed in unit mass per unit volume. As an example: for a mass of 20 grams that occupies 5 cm, the density is equal to 4 grams per cm.
Divide the object's mass by its volume. This value is the density of the object and is expressed in unit mass per unit volume. As an example: for a mass of 20 grams that occupies 5 cm, the density is equal to 4 grams per cm.
Method 2 of 2: Using an Example
 Write down the problem. Take the next issue, "Determine the density of a book with a mass of 49 grams and a volume of 7 cm.’
Write down the problem. Take the next issue, "Determine the density of a book with a mass of 49 grams and a volume of 7 cm.’  Record the mass. The mass is 49 grams.
Record the mass. The mass is 49 grams.  Record the volume. The volume is 7 cm.
Record the volume. The volume is 7 cm. 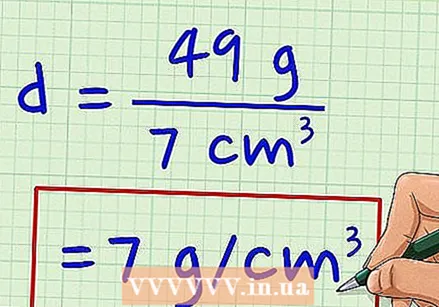 Divide the mass by the volume. 49 grams ÷ 7 cm = 7 g / cm.
Divide the mass by the volume. 49 grams ÷ 7 cm = 7 g / cm.
Tips
- Density is very similar to specific gravity, which compares the density of an object to that of water. Since the density of water is 1 gram per cm, the specific gravity will be the density without the units, provided the density of an object is measured in the same unit.
Necessities
- Balance or weigh hook
- Ruler or tape measure
- Calculator
- Measuring cylinder (for powders and liquids)