Author:
Charles Brown
Date Of Creation:
5 February 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024
Content
- To step
- Method 1 of 3: Stop the bleeding
- Method 2 of 3: Improve gum health
- Method 3 of 3: Understanding the causes of bleeding gums
- Tips
- Warnings
Bleeding gums are one of the first signs of gum disease. Good oral hygiene and a nutritious diet are the cornerstones of healthy gums and teeth. If you suffer from bleeding gums, take steps to understand the possible causes of the condition and how to treat it.
To step
Method 1 of 3: Stop the bleeding
 Apply a cold compress to the gums. As an immediate remedy for bleeding gums, you can apply a cold compress to the area.
Apply a cold compress to the gums. As an immediate remedy for bleeding gums, you can apply a cold compress to the area. - This helps slow blood flow to the area, resulting in less blood loss.
- Make a cold compress by wrapping an ice cube in a clean paper towel. Gently press this against the bleeding gums.
 Use a different toothbrush and brushing technique. Gum bleeding is often caused by a toothbrush whose bristles are too hard, or by brushing your gums too vigorously.
Use a different toothbrush and brushing technique. Gum bleeding is often caused by a toothbrush whose bristles are too hard, or by brushing your gums too vigorously. - While you may think that brushing harder results in cleaner teeth, this is actually not the case. Brushing too hard can damage tooth enamel (the protective surface on teeth) and irritate sensitive gums, causing redness, swelling and bleeding.
- Buy a toothbrush with soft nylon bristles that are rounded (instead of pointed). When brushing, move gently in circles to brush all sides of the teeth, almost as if you were massaging the teeth. Brushing vertically from the edge of the gum across the tooth surface removes the highest percentage of bacteria compared to other movements. Most people tend to make a vigorous back and forth motion, which is incorrect. This can lead to gum recession and erosion, making your teeth look longer and discolored.
- It is a good idea to invest in an electric toothbrush with a rotating and oscillating head. These toothbrushes are gentler on teeth and gums and more effective at removing plaque. Look for toothbrushes approved by the American Dental Association.
- Read this article to learn more about the correct brushing method.
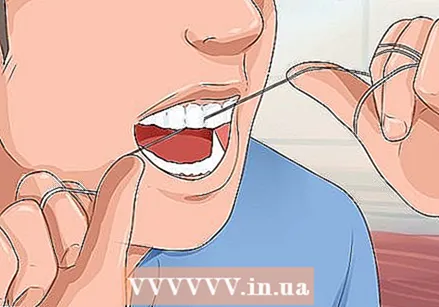 Be careful with flossing. Flossing is an essential part of good oral hygiene and should be done at least once a day.
Be careful with flossing. Flossing is an essential part of good oral hygiene and should be done at least once a day. - However, many people make the mistake of letting the floss "snap" between their teeth, which can irritate the gums and cause inflammation and bleeding.
- It is important to floss gently. Slowly and carefully slide the floss between your teeth, following the curve of each tooth.
- Hold the floss so that it creates a U-shape around the tooth, slide the floss under the edge of the gum, then move the floss firmly up and down to remove plaque.
- While it can be a bit tricky, don't forget the backs of your teeth. Read this article for more information on how to floss correctly.
- You can also use an oral irrigator that plugs into your bathroom faucet and directs a small but powerful jet of water at your gum line to remove dirt. A professional oral irrigator is also a good choice if you have dental implants, bridges, or even periodontal disease.
 Avoid alcohol-based mouthwashes. Mouthwash is a great way to get fresh breath and get rid of bacteria from your mouth. However, alcohol-based mouthwash is very drying, can be irritating to swollen gums and cause bleeding.
Avoid alcohol-based mouthwashes. Mouthwash is a great way to get fresh breath and get rid of bacteria from your mouth. However, alcohol-based mouthwash is very drying, can be irritating to swollen gums and cause bleeding. - Instead of alcohol-based mouthwash, you can also rinse your mouth with hydrogen peroxide or salt water. This keeps your mouth clean and fresh without irritating your gums.
Method 2 of 3: Improve gum health
 Brush and floss daily. While many people's response to painful, bleeding gums is to brush and floss less until the irritation has gone, this is the worst thing you can do. The only way to get your gums back to health is through good oral hygiene, such as regular brushing and flossing.
Brush and floss daily. While many people's response to painful, bleeding gums is to brush and floss less until the irritation has gone, this is the worst thing you can do. The only way to get your gums back to health is through good oral hygiene, such as regular brushing and flossing. - While dentists usually recommend brushing twice a day, people with gum problems may benefit from brushing more often, preferably after every meal or snack.
- You can also use a gum stimulator, which improves blood flow in the gums and can prevent inflammation.
- You should also floss at least once a day, making sure to get below the gum line of each tooth to remove the maximum amount of plaque.
- Floss in front of brushing your teeth, so that any food particles and bacteria you have loosened between your teeth can be brushed away.
- Also, don't forget to brush your tongue, as this is an important breeding ground for bacteria.
 Eat healthy. A balanced diet is important for healthy teeth and gums and can help prevent gum disease.
Eat healthy. A balanced diet is important for healthy teeth and gums and can help prevent gum disease. - Eat lots of whole grains, vegetables and fruits, as these will provide you with the vitamins and minerals you need to stay healthy and ward off disease. Fruits and vegetables rich in vitamin C, such as bell peppers, kale, broccoli, berries and citrus fruits, are especially important.
- Dairy products such as milk, yogurt and cheese provide calcium and are important for strong teeth and healthy gums, especially in children, and should be consumed in place of soda or other acidic drinks. They help to remove sugars from the mouth, thus fighting bacteria and plaque.
- Avoid eating foods with sugar or processed carbohydrates, as these can contribute to plaque build-up and be harmful to teeth. Also, avoid too many snacks and eat right before bed.
 Stop smoking. In case you didn't know, smoking is bad for the health of your teeth and gums.
Stop smoking. In case you didn't know, smoking is bad for the health of your teeth and gums. - Toxins in cigarettes and tobacco make your gums more susceptible to inflammation and disease. They also negatively affect your body's immune response, making it more difficult to fight infections.
- Smoking also hinders the circulation in your gums, because nicotine closes blood vessels. This causes your gums to become malnourished, making them fibrous and swelling.
- Smokers are six times more likely to develop gingivitis than nonsmokers and are more likely to develop more serious gum disease, resulting in tooth extraction, as smoking reduces the chances of success of other treatments.
 Limit your stress. When you are stressed, your body produces more of the hormone cortisol, which negatively affects the health of your teeth and gums.
Limit your stress. When you are stressed, your body produces more of the hormone cortisol, which negatively affects the health of your teeth and gums. - More specifically, cortisol reduces inflammation and thus vasoconstriction, thereby increasing blood pressure. It also affects the immune system, making it more difficult for your body to fight disease. Stress also increases adrenaline and glucose levels, which can contribute to diabetes.
- You can reduce your stress by sleeping more and better, with more exercise, and by spending time with friends and family.
 Go to the dentist at least twice a year. Visit your dentist at least twice a year, or more often if you have frequent complaints with your teeth or gums.
Go to the dentist at least twice a year. Visit your dentist at least twice a year, or more often if you have frequent complaints with your teeth or gums. - Only your dentist can clean your teeth professionally and thoroughly, using instruments that clean areas of your mouth that brushing and flossing cannot reach.
- Don't let the cost put you off; identifying gingivitis or other dental problems early can save you money in the long run by avoiding more extensive treatment.
- You can also ask your dentist during a periodic check-up how often you should have your teeth checked.
Method 3 of 3: Understanding the causes of bleeding gums
 Identify the cause of bleeding gums. Bleeding is a sign of unhealthy gums and can be caused by gum disease or other medical conditions. It is important to understand the cause of the bleeding in order to take the necessary steps to prevent it in the future. Bleeding gums can be caused by:
Identify the cause of bleeding gums. Bleeding is a sign of unhealthy gums and can be caused by gum disease or other medical conditions. It is important to understand the cause of the bleeding in order to take the necessary steps to prevent it in the future. Bleeding gums can be caused by: - Bad oral hygiene. Irregular or improper brushing and flossing can lead to gum disease such as gingivitis and periodontal disease, which are common causes of gum bleeding.
- Brushing your teeth with a toothbrush older than three months. Brushing too roughly or with an old toothbrush can inflame sensitive gums and cause bleeding.
- Hormonal changes. Hormonal changes caused by pregnancy, menopause, or menstruation can increase blood flow to the gums, making it more prone to bleeding.
- Medical conditions. Bleeding gums can be a symptom of many medical conditions, such as blood or coagulation disease, immunodeficiency, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, cancer and scurvy.
- Certain medications. Blood thinners can make gums bleed more quickly, as can many other medications (such as anti-seizure or contraceptive medications) that dry out or thicken your gums.
- Vitamin K deficiency. This vitamin helps your blood to clot. A vitamin K deficiency can cause bleeding gums.
- Hereditary factors. People with certain genetic markers are more prone to developing gingivitis than others, which also makes them more prone to bleeding gums.
- An unbalanced bite. An unbalanced bite due to crooked teeth, tight teeth, clenched jaws or grinding teeth can lead to overpressure in certain areas of your teeth, which can lead to gum disease and bleeding gums.
 Understand the Effects of Gum Disease. It is estimated that in the United States, gum disease affects about 3/4 of adults 35 or older.
Understand the Effects of Gum Disease. It is estimated that in the United States, gum disease affects about 3/4 of adults 35 or older. - The main cause of bleeding gums is gingivitis, a condition characterized by inflammation and swelling of the gums.
- Gingivitis is caused by too many bacteria in the mouth. The bacteria come from the fermentation of carbohydrates. This in turn leads to inflammation, which is a protective reaction of the gums. Bacterial growth usually develops as a result of poor oral hygiene. Fortunately, gingivitis is often reversible, provided good oral hygiene is introduced and maintained.
- If left untreated, gingivitis can lead to a more serious form of gum disease called periodontal disease. Periodontal disease significantly weakens the gums and bone that hold teeth in place, ultimately leading to tooth loss.
- Research links gum disease to a higher risk of other health problems, such as cardiovascular disease, stroke, chronic kidney disease, pneumonia, osteoporosis, cancer and premature birth. That is why it is very important to detect and treat gum disease early.
 Go to the dentist. If you notice bleeding from your gums and suspect you may have gum disease, it is strongly recommended that you make an appointment with your dentist right away.
Go to the dentist. If you notice bleeding from your gums and suspect you may have gum disease, it is strongly recommended that you make an appointment with your dentist right away. - Your dentist can confirm the presence of gum disease and come up with a plan for reversing or treating the damage.
- Your dentist can clean your teeth properly and professionally and give you instructions on how to properly care for your teeth and gums yourself.
- If gum disease is more advanced, your dentist may suggest scaling and root planing treatments to remove stubborn plaque and heal gums.
- In addition, medication can be prescribed to reduce the number of mouth bacteria.
- In severe situations, tooth extraction, laser treatment or dental surgery may be necessary to stop the progression of the periodontal disease.
Tips
- Use plaque-licking tablets (also called "disclosing tablets") to temporarily discolor the plaque on your teeth. This gives you an indication of the effectiveness of brushing and flossing your teeth. Plaque tellers are available at the drugstore.
- Brush your teeth daily and possibly use a plaque detector to get an idea of how effectively you brush your teeth. These are available at drug stores and usually not too expensive.
Warnings
- If the bleeding gums persists, see your doctor (and not just the dentist) as it could be a symptom of a more serious underlying condition.