Content
- Steps
- Method 1 of 4: Perform Breathing Exercises
- Method 2 of 4: Lifestyle Changes
- Method 3 of 4: Dealing with Difficulty Breathing
- Method 4 of 4: When to see a doctor
- Tips
- Warnings
Feeling out of breath is both frightening and stressful. To cope with this, do breathing exercises - breathe deeply, calm down and restore natural breathing. Also, change your lifestyle to improve breathing. If you feel short of breath, try changing your position to make breathing easier. However, you should see your doctor if you have intermittent breathing difficulties, anxiety disorder, or panic attacks.
Steps
Method 1 of 4: Perform Breathing Exercises
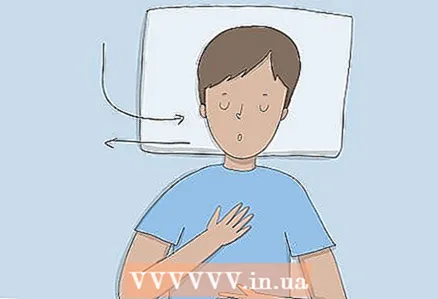 1 To inhale deeper, do it with your stomach (abdominal or diaphragmatic breathing). Lie in a comfortable position, then place one hand on your chest and the other on your stomach. Inhale slowly through your nose to fill your abdomen with air. Feel your belly lift up with your hand. Then exhale slowly through your mouth, pulling your lips out with a tube.
1 To inhale deeper, do it with your stomach (abdominal or diaphragmatic breathing). Lie in a comfortable position, then place one hand on your chest and the other on your stomach. Inhale slowly through your nose to fill your abdomen with air. Feel your belly lift up with your hand. Then exhale slowly through your mouth, pulling your lips out with a tube. - Repeat 5-10 times.
- The arm on the chest should be motionless during this exercise. Only the belly rises.
- Repeat this exercise 2-3 times a day and your breathing will improve.
- Once you have mastered the exercise, you can do it while sitting. Over time, you will be able to do it while standing.
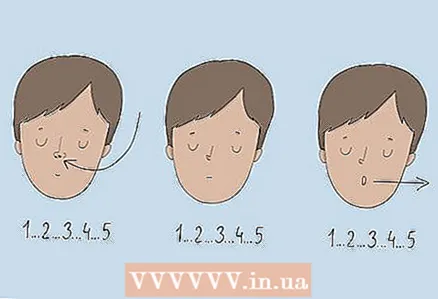 2 Practice counting breathing to calm you down. You can slow down rapid breathing if you count to yourself: when you exhale, hold your breath, exhale. Inhale, slowly counting to five to yourself, then hold your breath, again counting to five. Then exhale, slowly counting to 5. Repeat 5 times so that the breath comes into a natural rhythm.
2 Practice counting breathing to calm you down. You can slow down rapid breathing if you count to yourself: when you exhale, hold your breath, exhale. Inhale, slowly counting to five to yourself, then hold your breath, again counting to five. Then exhale, slowly counting to 5. Repeat 5 times so that the breath comes into a natural rhythm. - You can count in different ways, this is normal. For example, if you want, you can count not to five, but to three. Do as you see fit.
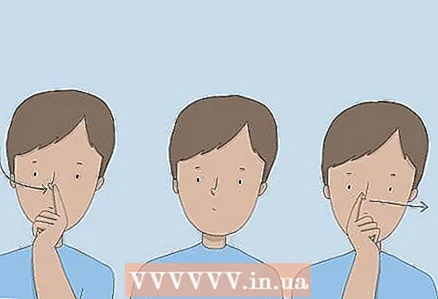 3 Do alternating breathing through your nostrils to deal with stress. Pinch one nostril with your finger. Then inhale slowly through the free nostril until the lungs are full. Hold your breath for 1 second, then pinch that nostril and slowly exhale through the other. Now inhale through it, pinch it and exhale through the first nostril.
3 Do alternating breathing through your nostrils to deal with stress. Pinch one nostril with your finger. Then inhale slowly through the free nostril until the lungs are full. Hold your breath for 1 second, then pinch that nostril and slowly exhale through the other. Now inhale through it, pinch it and exhale through the first nostril. - Continue breathing alternately for 3-5 minutes to restore natural breathing.
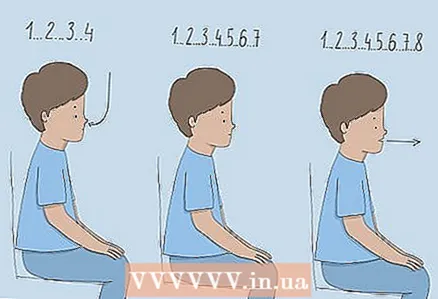 4 Use the 4-7-8 breathing method to relax. Sit, straighten your back, then press the tip of your tongue to your upper palate. Your tongue should remain in this position at all times. Exhale air through your mouth to clear your lungs. Cover your mouth, now begin to inhale through your nose, counting in your head to 4. Then hold your breath for a count of 7. On the count of 8, exhale the air while making a whistling sound.
4 Use the 4-7-8 breathing method to relax. Sit, straighten your back, then press the tip of your tongue to your upper palate. Your tongue should remain in this position at all times. Exhale air through your mouth to clear your lungs. Cover your mouth, now begin to inhale through your nose, counting in your head to 4. Then hold your breath for a count of 7. On the count of 8, exhale the air while making a whistling sound. - Complete the 4-7-8 breathing cycle to calm and relax.
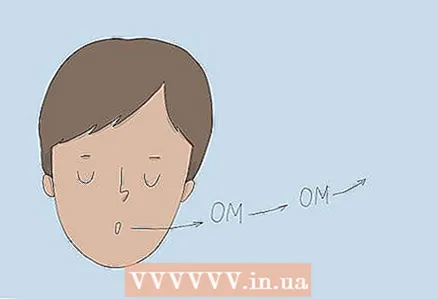 5 Slowly draw in the air, then exhale while making a sound to slow your breathing. Inhale slowly through your nose until your lungs are full. Then, while exhaling through your mouth, make a low humming sound. Keep humming until your lungs are empty. It can help you slow down your breathing and relax.
5 Slowly draw in the air, then exhale while making a sound to slow your breathing. Inhale slowly through your nose until your lungs are full. Then, while exhaling through your mouth, make a low humming sound. Keep humming until your lungs are empty. It can help you slow down your breathing and relax. - Take a few of these breaths, so that your breathing slows down and becomes even.
- If you like, say the mantra Om as you exhale.
Method 2 of 4: Lifestyle Changes
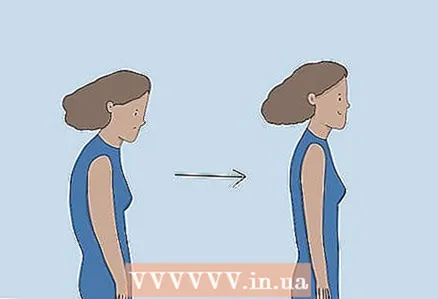 1 Hold back straightto make breathing easier. When stooping, the lungs are compressed and the airways blocked, making it difficult to breathe. Straighten your back when you are sitting and when you are standing. Also, bring your shoulders back and lift your chin up. This will help you breathe more freely.
1 Hold back straightto make breathing easier. When stooping, the lungs are compressed and the airways blocked, making it difficult to breathe. Straighten your back when you are sitting and when you are standing. Also, bring your shoulders back and lift your chin up. This will help you breathe more freely. - Look in the mirror to make sure you have the correct posture. Practice standing or sitting up straight until you feel comfortable.
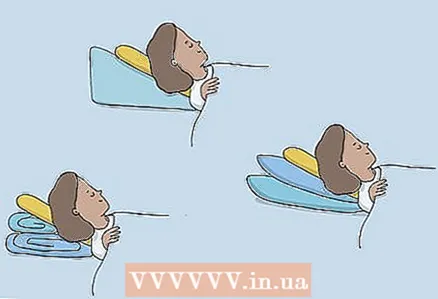 2 Raise your headboard if you find it difficult to breathe during sleep. You may find it difficult to breathe while lying down, especially at night. If this happens, use pillows or otherwise elevate your upper body. This will relieve the pressure on your lungs so you can breathe better while you sleep.
2 Raise your headboard if you find it difficult to breathe during sleep. You may find it difficult to breathe while lying down, especially at night. If this happens, use pillows or otherwise elevate your upper body. This will relieve the pressure on your lungs so you can breathe better while you sleep. - You can also try placing a folded blanket under your pillow.
 3 Limit exposure to airborne pollutants and other irritants. Polluted air is harmful to the lungs and respiratory tract and makes breathing difficult. Although you cannot completely isolate yourself from atmospheric pollutants, you can reduce your presence in such places. Here are some tips for avoiding exposure to polluted air:
3 Limit exposure to airborne pollutants and other irritants. Polluted air is harmful to the lungs and respiratory tract and makes breathing difficult. Although you cannot completely isolate yourself from atmospheric pollutants, you can reduce your presence in such places. Here are some tips for avoiding exposure to polluted air: - avoid outside contaminants as much as possible;
- beware of allergens;
- do not use perfume or cologne;
- give up air fresheners;
- Choose odorless personal care products and cleaners;
- do not light candles and incense;
- Do a wet cleaning of the house more often to prevent the accumulation of dust and mold;
- step aside when someone smokes to avoid secondhand smoke.
 4 Eat a hypoallergenic diet to get rid of leaky gut. Eating unsuitable food can cause microscopic holes in the intestines that allow bacteria and food particles to seep where they should not. As a result, inflammation and pain begins in the body, which is trying to get rid of the "invaders". Inflammation can cause breathing problems and allergies. Eat a hypoallergenic diet to improve gut health.
4 Eat a hypoallergenic diet to get rid of leaky gut. Eating unsuitable food can cause microscopic holes in the intestines that allow bacteria and food particles to seep where they should not. As a result, inflammation and pain begins in the body, which is trying to get rid of the "invaders". Inflammation can cause breathing problems and allergies. Eat a hypoallergenic diet to improve gut health. - Avoid common food allergens such as milk, gluten, eggs, soy, sugar, nuts, and caffeine for 3-4 weeks. As soon as you start to feel better, reintroduce foods one at a time to see if they are harming you. Stop eating food that is causing your symptoms to return.
 5 Use an air filter to improve indoor air quality. Unfortunately, the air inside your home can be filled with pollutants. They can irritate your lungs and make breathing difficult. Fortunately, indoor air filters help remove these pollutants so you can breathe easier. Use HEPA filters (for fine air purification) to improve the air quality in your home.
5 Use an air filter to improve indoor air quality. Unfortunately, the air inside your home can be filled with pollutants. They can irritate your lungs and make breathing difficult. Fortunately, indoor air filters help remove these pollutants so you can breathe easier. Use HEPA filters (for fine air purification) to improve the air quality in your home. - Install HEPA filters in the air conditioner. Alternatively, a fan with an air filter is available to improve air quality.
Option: indoor plants also purify the air. Decorate the interior with your favorite plants to keep the air in your home clean.
 6 Exercise to improve airway health for 30 minutes daily. You may have shortness of breath after exercise. Regular exercise will help you improve your fitness and breathe easier. Get 30 minutes of moderate cardio at least 5-6 times a week to get fit. Here are some exercises to try:
6 Exercise to improve airway health for 30 minutes daily. You may have shortness of breath after exercise. Regular exercise will help you improve your fitness and breathe easier. Get 30 minutes of moderate cardio at least 5-6 times a week to get fit. Here are some exercises to try: - do brisk walking;
- run;
- work out on an elliptical trainer;
- ride a bike;
- swim;
- take dance lessons;
- join an active sports team.
 7 If you smoke, quit. You probably know that smoking has a negative effect on the respiratory system. If you are aware of the dangers of smoking but are still struggling to quit, talk to your doctor about using smoking cessation aids. This will take care of your respiratory health.
7 If you smoke, quit. You probably know that smoking has a negative effect on the respiratory system. If you are aware of the dangers of smoking but are still struggling to quit, talk to your doctor about using smoking cessation aids. This will take care of your respiratory health. - For example, your doctor may prescribe patches, chewing gum, or prescription medications to help you deal with the urge to smoke. They can also give you tips on where to get group therapy to help you quit smoking.
Method 3 of 4: Dealing with Difficulty Breathing
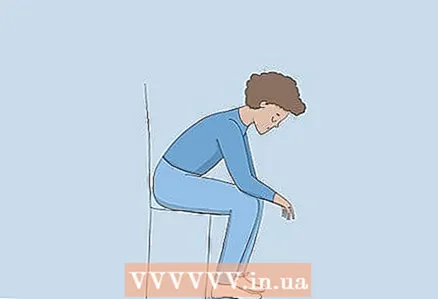 1 Sit and bend forward with your elbows on your knees. Sit back in a chair with your feet flat on the floor, then lean your chest forward slightly. Bend your arms and place your elbows on your knees. Relax your neck and shoulders as much as possible. Stay in this position until breathing has returned to normal.
1 Sit and bend forward with your elbows on your knees. Sit back in a chair with your feet flat on the floor, then lean your chest forward slightly. Bend your arms and place your elbows on your knees. Relax your neck and shoulders as much as possible. Stay in this position until breathing has returned to normal. - You should feel better in 2-3 minutes.
Option: Sit back at the table with your hands in front of you. Lean forward slightly, lower your head into your hands. Relax your shoulders and neck.
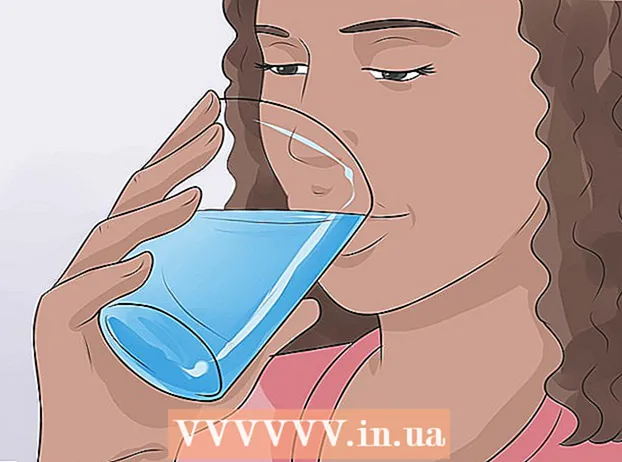
 2 Drink something warm to relax your airways. Warm liquids naturally relax the airways and thin mucus. Sip warm liquids when breathing is difficult. This will help you breathe more freely.
2 Drink something warm to relax your airways. Warm liquids naturally relax the airways and thin mucus. Sip warm liquids when breathing is difficult. This will help you breathe more freely. - For example, you can drink warm tea or water.
 3 Lean your lower back against a wall, lean forward slightly, and relax. Stand with your back to the wall, feet shoulder-width apart. Lean forward slightly, place your hands on your hips. Relax your shoulders and arms, then focus on your breathing. Stay in this position until breathing has returned to normal.
3 Lean your lower back against a wall, lean forward slightly, and relax. Stand with your back to the wall, feet shoulder-width apart. Lean forward slightly, place your hands on your hips. Relax your shoulders and arms, then focus on your breathing. Stay in this position until breathing has returned to normal. - After 2-3 minutes, your breathing will become easier.
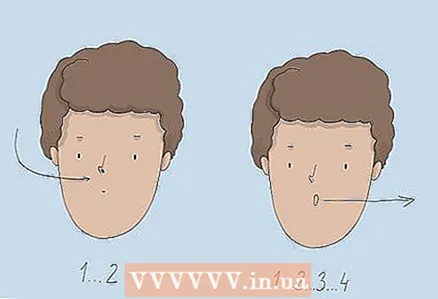 4 When breathing difficulties are caused by exertion or anxiety, breathe with your lips in a tube. This should help normalize breathing. Pinch your lips, then begin to inhale slowly through your nose, mentally counting to 2. Curl your lips as if you are about to whistle, and then slowly blow out air for a count of 4. Repeat until breathing is normal.
4 When breathing difficulties are caused by exertion or anxiety, breathe with your lips in a tube. This should help normalize breathing. Pinch your lips, then begin to inhale slowly through your nose, mentally counting to 2. Curl your lips as if you are about to whistle, and then slowly blow out air for a count of 4. Repeat until breathing is normal. - You should feel better breathing out through your cupped lips for 2-3 minutes. If that doesn't work, you may need to try other breathing exercises or call your doctor.
- Include pursed lip breathing in your daily routine to help manage chronic breathing problems. Do this 4-5 times a day for 1-2 minutes to help you breathe easier.
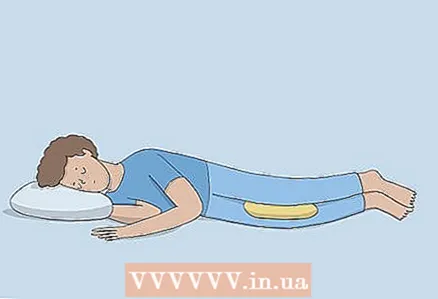 5 Sleep on your side with a pillow between your knees. You may feel short of breath while sleeping, especially if you are sick or snoring. To help you breathe easier, sleep on your side. Place pillows under your head to raise your upper body and a pillow between your legs to align your spine.
5 Sleep on your side with a pillow between your knees. You may feel short of breath while sleeping, especially if you are sick or snoring. To help you breathe easier, sleep on your side. Place pillows under your head to raise your upper body and a pillow between your legs to align your spine. - If you are tossing and turning in your sleep, use blankets or pillows to make it uncomfortable to roll over to a different position.
Option: if you prefer to sleep on your back, try raising your head and knees. Place two pillows under your head to lift your upper body. Then place two pillows under your knees to lift them and straighten your spine.
Method 4 of 4: When to see a doctor
 1 Get immediate medical attention if you find it difficult to breathe. Try not to worry, but remember that shortness of breath can be a life-threatening symptom. If you are short of air, call an ambulance or have someone drive you to the nearest emergency room. First aid will be given to you, and it will become easier for you to breathe.
1 Get immediate medical attention if you find it difficult to breathe. Try not to worry, but remember that shortness of breath can be a life-threatening symptom. If you are short of air, call an ambulance or have someone drive you to the nearest emergency room. First aid will be given to you, and it will become easier for you to breathe. - Do not attempt to drive to the emergency room on your own if you are short of air. Ask someone around you about it.
 2 See your doctor if you have difficulty breathing regularly. You may not have much to worry about, but it may be that something serious is causing your breathing problems. You may have a medical condition that is causing breathing problems. The doctor will be able to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the appropriate treatment.
2 See your doctor if you have difficulty breathing regularly. You may not have much to worry about, but it may be that something serious is causing your breathing problems. You may have a medical condition that is causing breathing problems. The doctor will be able to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the appropriate treatment. - For example, you may have asthma that requires treatment with inhaled steroids. You may have chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Tell your doctor about any other symptoms and how long you have had them.
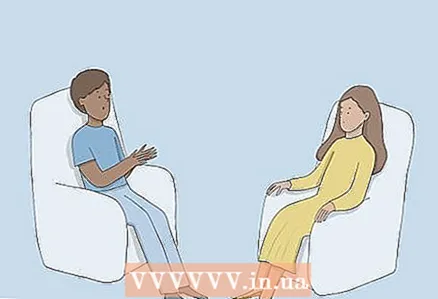 3 See a therapist to help you manage your anxiety disorder or panic attacks. Chronic anxiety and panic disorder can lead to breathing difficulties.If so, see a therapist who can teach you how to deal with anxiety or panic attacks. It will help you change your thoughts and behavior so that you can improve your breathing.
3 See a therapist to help you manage your anxiety disorder or panic attacks. Chronic anxiety and panic disorder can lead to breathing difficulties.If so, see a therapist who can teach you how to deal with anxiety or panic attacks. It will help you change your thoughts and behavior so that you can improve your breathing. - For a recommendation, contact your doctor or look for a psychotherapist online. # * Unfortunately, compulsory medical insurance in Russia (as in most CIS countries) does not cover the services of a psychotherapist. However, in some cities there are centers for free psychological assistance to the population, where highly qualified specialists are employed. If your employer or yourself pays for voluntary health insurance (VHI) with the fullest coverage, it probably includes psychotherapy as well. Find out from your insurance company whether your policy covers such services, to what extent and what specialists working on VHI can advise.
- If you experience anxiety or panic attacks on a daily basis, your doctor or therapist may prescribe medications to help you manage the condition. It may help you to deal with breathing difficulties.
 4 Talk to your doctor if you develop symptoms of sleep apnea. When pulmonary ventilation stops for a while during sleep, this condition is called sleep apnea. This condition can be life-threatening if left untreated. Fortunately, your doctor can prescribe you to use a CPAP machine that maintains constant positive airway pressure and breathes at night. See your doctor if you experience any of the following symptoms:
4 Talk to your doctor if you develop symptoms of sleep apnea. When pulmonary ventilation stops for a while during sleep, this condition is called sleep apnea. This condition can be life-threatening if left untreated. Fortunately, your doctor can prescribe you to use a CPAP machine that maintains constant positive airway pressure and breathes at night. See your doctor if you experience any of the following symptoms: - dry mouth on waking;
- Loud snoring;
- convulsive breathing during sleep;
- headaches in the morning;
- trouble falling asleep;
- very tired;
- trouble concentrating;
- irritability.
Tips
- If you find it difficult to breathe due to physical activity, slow down until breathing returns to normal.
- If the nose is blocked, put 1–2 drops of saline solution into each nostril every 2–4 hours. If that doesn't work, use a nasal decongestant to relieve the congestion, but only if there are no contraindications.
Warnings
- If you feel short of breath and understand that this is not an attack of panic or anxiety, immediately call an ambulance or ask someone around to do it.