Author:
Marcus Baldwin
Date Of Creation:
14 June 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
The CPU (central processing unit) is used to calculate values or move entries in the registry. The GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) is used for similar functions.
Steps
 1 Find out what type of motherboard you have; different motherboards have different sockets. Make sure your processor is accepted by your motherboard, power supply, and cooling components. A list of the most common socket types is shown at the end of this page.
1 Find out what type of motherboard you have; different motherboards have different sockets. Make sure your processor is accepted by your motherboard, power supply, and cooling components. A list of the most common socket types is shown at the end of this page.  2 Open the computer case. This can usually be done by opening a latch, button, or other mechanism. If necessary, refer to the technical documentation to find out how to access the internal components. Depending on the type and model of your computer, you may need a screwdriver to open the case.
2 Open the computer case. This can usually be done by opening a latch, button, or other mechanism. If necessary, refer to the technical documentation to find out how to access the internal components. Depending on the type and model of your computer, you may need a screwdriver to open the case.  3 Remove any components, such as the power supply or heat sink cover, that are blocking access to the motherboard.
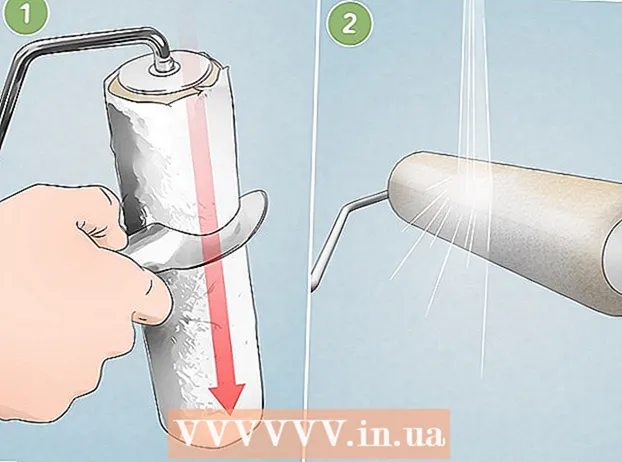
3 Remove any components, such as the power supply or heat sink cover, that are blocking access to the motherboard. 4 Remove the radiator. This is usually an aluminum block with heat dissipation fins. Attached to the radiator will usually be a fan. Disconnect the fan from the motherboard. Also remove any clips that secure the heat sink to the case or motherboard. The processor should now be open.
4 Remove the radiator. This is usually an aluminum block with heat dissipation fins. Attached to the radiator will usually be a fan. Disconnect the fan from the motherboard. Also remove any clips that secure the heat sink to the case or motherboard. The processor should now be open.  5 Lift the latch on the side of the socket that will lift the processor slightly, then lift it out.
5 Lift the latch on the side of the socket that will lift the processor slightly, then lift it out. 6 Insert the processor into the socket so that the corner with the fewest pins goes into the upper right corner of the socket.
6 Insert the processor into the socket so that the corner with the fewest pins goes into the upper right corner of the socket. 7 Press down on the socket latch until the processor is securely attached to the socket and to the motherboard.
7 Press down on the socket latch until the processor is securely attached to the socket and to the motherboard. 8 Apply the recommended amount of CPU Heat Transfer Grease (Thermal Grease) to the new processor so that it covers the top surface.
8 Apply the recommended amount of CPU Heat Transfer Grease (Thermal Grease) to the new processor so that it covers the top surface. 9 Place the heatsink on the installed processor and connect the fan power cable to the outlet on the motherboard.
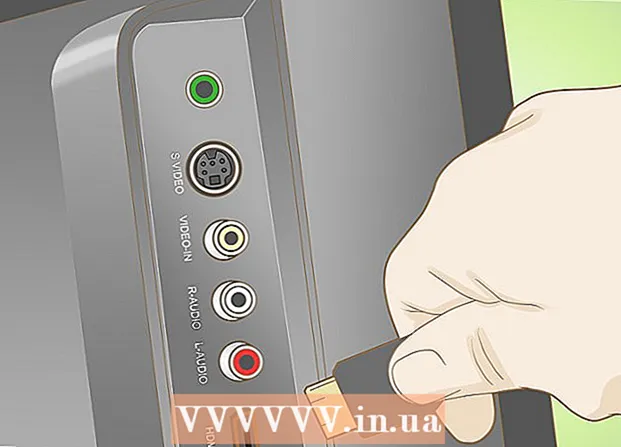
9 Place the heatsink on the installed processor and connect the fan power cable to the outlet on the motherboard. 10 Connect the components that you removed to access the CPU (power supply, various cables, etc.)etc.).
10 Connect the components that you removed to access the CPU (power supply, various cables, etc.)etc.).  11 Assemble or close the computer case. Make sure all internal cables are secured in place.
11 Assemble or close the computer case. Make sure all internal cables are secured in place.
Tips
- Make sure all cables go into their original ports; just because the connector on the cable matches the input connector does not mean that it is its native input ..
- If a component or cable does not fit in a slot that you think it fits into, make sure it is not jammed or damaged.
- Some processors are good for upgrading: Core 2 Duo, Pentium D, and Core 2 Quad. Stay away from Pentium, Celeron, and Atom processors. If you really want cutting edge power and aren't worried about the high price, go for the Core i7 or Core i7 extreme. Be careful because some motherboards do not support the new Core i7 socket configuration. Core 2 Quad Extreme is a good choice if your motherboard cannot support the new Core i7.
Warnings
- Be careful with this little piece of silicon: it is thin and expensive, sometimes worth over $ 1,000.
- Always ground yourself before touching the chassis. You can do this by touching a metal table or chair leg, or even a computer case if it is metal. Any static discharge can “fry” sensitive electronic components.
List of sockets
AMD sockets
- Socket 563 - AMD low-power mobile Athlon XP-M (µ-PGA Scket, mostly moving parts)
- Socket 754 - AMD single processor systems using single channel DDR-SDRAM, including AMD Athlon 64, Sempron, Turion 64
- Socket 939 - AMD single processor systems using dual channel DDR-SDRAM, including Athlon 64, Athlon 64 FX to 1 GHz2, Athlon 64 X2, Opteron 100-series
- Socket 940 - AMD single and multiprocessor systems using DDR-SDRAM, including AMD Opteron 2, Athlon 64 FX
- Socket AM2 - AMD uniprocessor systems using DDR2-SDRAM
- Socket AM2 + - Future AMD Socket for uniprocessor systems, support for DDR2 and HyperTransport 3 with split power strips. Planned mid 2007 to Q3 2007, replacements
- Socket AM2 (PGA 940 contacts)
Intel sockets
- Socket 478 - Intel Pentium 4, Celeron, Pentium 4 Extreme Edition, Pentium M
- Socket 771 (also known as Socket 771) - Intel Xeon
- Socket 775 (also known as Socket T) - Intel Pentium 4, Pentium D, Celeron D, Pentium Extreme Edition, Core 2 Duo, Core 2 Extreme, Celeron1, Xeon 3000 series, Core 2 Quad.
- Socket 1333 - Intel Core i7, Core i5, Core i3
- Socket N - Intel Dual-Core Xeon LV
- Socket P - based on Intel; replaces Socket 479 and Socket M. Released May 9, 2007.