Author:
Florence Bailey
Date Of Creation:
21 March 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
A nosocomial infection, also known as nosocomial infection, develops in patients after a hospital stay. Nosocomial infections can be bacterial or fungal and are often antibiotic resistant. Recent studies have shown that nosocomial infections can be associated with medical personnel who inadvertently spread infections to susceptible patients. There are ways to protect you and your patients. Each of these methods is simple but very effective.
Steps
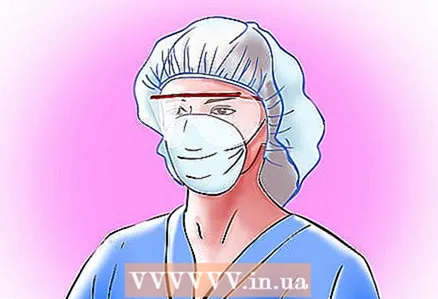 1 Use Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). PPE is specialized protective equipment used by staff to prevent the spread of infection among patients.
1 Use Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). PPE is specialized protective equipment used by staff to prevent the spread of infection among patients. - Hospital staff should always wash their hands according to protocol before donning PPE.
- The staff must first put on hospital gowns, then a mask, goggles and finally gloves.
 2 Only use safe injections. Healthcare professionals are usually responsible for needle infections. The following methods can help prevent such infections:
2 Only use safe injections. Healthcare professionals are usually responsible for needle infections. The following methods can help prevent such infections: - Never administer medications from the same syringe to multiple patients.
- Do not administer medicines from a single-dose vial to more than one patient.
- Before inserting the syringe into the vial, clean the very top of the medication vial with 70% alcohol.
- Dispose of used syringes and needles in a suitable container.
 3 Dispose of waste in appropriate containers. Hospitals have containers for various types of waste. They usually differ in color as follows:
3 Dispose of waste in appropriate containers. Hospitals have containers for various types of waste. They usually differ in color as follows: - Black canisters for non-biodegradable waste.
- Green canisters for biodegradable waste.
- Yellow canisters for infectious waste.
- Syringes and needles should be placed in designated puncture-resistant containers.
 4 Make sure the area where the medicine is prepared is disinfected. It is very important that the area where the medicine is prepared is clean, as contaminated medicine can become a source of infection.
4 Make sure the area where the medicine is prepared is disinfected. It is very important that the area where the medicine is prepared is clean, as contaminated medicine can become a source of infection.  5 Keep the hospital clean. Hospital corridors, laboratories, and wards should be as clean as possible, as these areas can harbor germs that can be easily transmitted to patients.
5 Keep the hospital clean. Hospital corridors, laboratories, and wards should be as clean as possible, as these areas can harbor germs that can be easily transmitted to patients. - Make sure areas that have been contaminated with various body fluids are quickly cleaned up.
- Clean frequently touched surfaces, such as workstations and medicine tables, at least twice a day.