Author:
William Ramirez
Date Of Creation:
22 September 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- Steps
- Method 1 of 3: Treating hemorrhoid bleeding at home
- Method 2 of 3: Medical Assistance
- Method 3 of 3: What is hemorrhoids and how to identify them
Our body is literally riddled with a complex network of arteries and veins. Arteries deliver blood to various parts of the body and organs, and veins return it to the heart. Sometimes veins in the rectum and anus dilate and fill with blood, resulting in hemorrhoids. Hemorrhoids can be quite painful and can cause bleeding if they rupture. Find out what causes hemorrhoids and try to stop the bleeding at home. If bleeding and other symptoms persist, seek medical attention.
Attention:the information in this article is for informational purposes only. Before using any methods, consult your doctor.
Steps
Method 1 of 3: Treating hemorrhoid bleeding at home
 1 Sit in warm water or a sitz bath. To reduce irritation, relieve pain, and help your veins tighten, take warm (but not hot) baths for 15–20 minutes, three times a day. If you don't want to take a full bath of water, you can take a sitz bath by placing a plastic bowl of water on the toilet seat.This way you can soak your buttocks and pelvis in warm water, which will help relieve irritation and itching and relieve rectal spasms.
1 Sit in warm water or a sitz bath. To reduce irritation, relieve pain, and help your veins tighten, take warm (but not hot) baths for 15–20 minutes, three times a day. If you don't want to take a full bath of water, you can take a sitz bath by placing a plastic bowl of water on the toilet seat.This way you can soak your buttocks and pelvis in warm water, which will help relieve irritation and itching and relieve rectal spasms. - You can also add ¼ cup (60 ml) sea salt to the water and sit in a sitz bath for 30 minutes. Salt is an excellent antibacterial agent and is used to speed up wound healing and prevent infection.
- You can also add witch hazel, which is known to have a soothing and cooling effect on hemorrhoids. These sitz baths should be taken at least once a day for 15–20 minutes.
 2 Apply an ice pack to hemorrhoids. Place the ice pack in the freezer to freeze it properly. Do not apply it directly to your skin. Instead, wrap the bladder in a clean towel or rag and gently place it on the hemorrhoid. Do not apply the compress for a long time, otherwise it may damage the skin. It is best to apply the bladder for a few minutes, then remove it, wait until the skin warms up to room temperature, and reapply it.
2 Apply an ice pack to hemorrhoids. Place the ice pack in the freezer to freeze it properly. Do not apply it directly to your skin. Instead, wrap the bladder in a clean towel or rag and gently place it on the hemorrhoid. Do not apply the compress for a long time, otherwise it may damage the skin. It is best to apply the bladder for a few minutes, then remove it, wait until the skin warms up to room temperature, and reapply it. - This will help reduce inflammation and reduce pain and swelling. In addition, the cold will constrict blood vessels, which will help stop bleeding.
 3 Apply cream. Try a topical cream with phenylephrine to narrow blood vessels and thus reduce bleeding. In addition, the cream will help relieve pain, inflammation, and itching (which can also cause bleeding). However, the cream does not stop bleeding. Soothing creams may contain hydrocortisone, aloe, witch hazel extract, and vitamin E.
3 Apply cream. Try a topical cream with phenylephrine to narrow blood vessels and thus reduce bleeding. In addition, the cream will help relieve pain, inflammation, and itching (which can also cause bleeding). However, the cream does not stop bleeding. Soothing creams may contain hydrocortisone, aloe, witch hazel extract, and vitamin E. - If you are using hydrocortisone, apply morning and evening. Don't use it for more than one week. Excessive amounts of hydrocortisone can lead to an imbalance in the hypothalamus and pituitary hormones or cause thinning of the skin where the cream is applied.
 4 Use soft toilet paper and don't brush your anus. Hard toilet paper can scratch your skin and cause further irritation. Use wet sanitary napkins to relieve pain and irritation. You can also use witch hazel, hydrocortisone, aloe, or vitamin E sanitary napkins. Do not rub your anus too hard to avoid irritation and increase bleeding. Instead, blot the area gently.
4 Use soft toilet paper and don't brush your anus. Hard toilet paper can scratch your skin and cause further irritation. Use wet sanitary napkins to relieve pain and irritation. You can also use witch hazel, hydrocortisone, aloe, or vitamin E sanitary napkins. Do not rub your anus too hard to avoid irritation and increase bleeding. Instead, blot the area gently. - Scratching will only increase bleeding and irritation and put additional stress on your already painful hemorrhoids. This can lead to infection.
 5 Take nutritional supplements to reduce bleeding. Many of these supplements are rarely sold at drugstores, so look online or herbal stores for them. Always check with your doctor before taking any dietary supplement - this is especially important if you are taking other medications. If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, do not take dietary supplements without your doctor's approval, as most have not been tested in pregnant or breastfeeding women. These supplements and conventional remedies include the following:
5 Take nutritional supplements to reduce bleeding. Many of these supplements are rarely sold at drugstores, so look online or herbal stores for them. Always check with your doctor before taking any dietary supplement - this is especially important if you are taking other medications. If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, do not take dietary supplements without your doctor's approval, as most have not been tested in pregnant or breastfeeding women. These supplements and conventional remedies include the following: - Fargelin: These tablets are used in traditional Chinese medicine and should be taken 3-4 times a day to strengthen veins and reduce bleeding.
- Oral flavonoids. These drugs have been shown to reduce bleeding, pain and itching and reduce the likelihood of relapses. They increase the tone of the blood vessels and thus prevent the leakage of small vessels (capillaries).
- Calcium dobesilate. Take these tablets within two weeks according to the directions for use. It has been shown to inhibit the leakage of small blood vessels (capillaries), prevent blood clots and improve blood viscosity. All of these factors reduce tissue swelling that can cause hemorrhoids.
 6 Reduce the stress on your hemorrhoids. This will help relieve pressure on the hemorrhoids. Eat more fiber to soften stools and prevent constipation. Eat fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, or take nutritional supplements (daily fiber should be 25 grams for women and 38 grams for men). Drink plenty of fluids, use the bathroom regularly, and try not to strain yourself. In addition, you should not sit on the toilet for a long time, as this increases the pressure on the hemorrhoidal veins and causes bleeding. The stress on the hemorrhoids can be reduced by walking and exercising.
6 Reduce the stress on your hemorrhoids. This will help relieve pressure on the hemorrhoids. Eat more fiber to soften stools and prevent constipation. Eat fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, or take nutritional supplements (daily fiber should be 25 grams for women and 38 grams for men). Drink plenty of fluids, use the bathroom regularly, and try not to strain yourself. In addition, you should not sit on the toilet for a long time, as this increases the pressure on the hemorrhoidal veins and causes bleeding. The stress on the hemorrhoids can be reduced by walking and exercising. - Use a donut pillow to redistribute body weight and relieve pressure in the affected area. Sit in the center of the pillow with your anus over the opening. However, sometimes it backfires and puts more pressure on the anus, so stop using the pillow if symptoms worsen, bleeding persists, or recurs.
Method 2 of 3: Medical Assistance
 1 Talk to your doctor about hemorrhoidectomy for external or internal hemorrhoids. This is a common treatment for external hemorrhoids, especially if it is large and does not respond to less invasive treatments. The surgeon will remove the hemorrhoids using a variety of instruments, such as scissors, a scalpel, or rings, through which an electric current is passed to help relieve the bleeding. Before the procedure, local anesthesia is given and pain relievers are given, or spinal or general anesthesia is used.
1 Talk to your doctor about hemorrhoidectomy for external or internal hemorrhoids. This is a common treatment for external hemorrhoids, especially if it is large and does not respond to less invasive treatments. The surgeon will remove the hemorrhoids using a variety of instruments, such as scissors, a scalpel, or rings, through which an electric current is passed to help relieve the bleeding. Before the procedure, local anesthesia is given and pain relievers are given, or spinal or general anesthesia is used. - Hemorrhoidectomy is the most effective and fundamental way to treat severe or recurrent hemorrhoids. It can be painful, so anesthetics, sitz baths, and / or ointments are used after it to help relieve the pain.
- Compared to hemorrhoidectomy, stapling is associated with a higher risk of recurrence and rectal prolapse when part of the rectum protrudes from the anus.
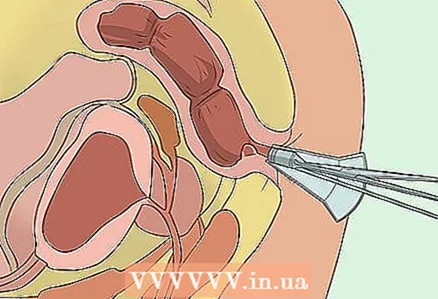 2 Ligate with rubber bands for internal hemorrhoids. The doctor will insert the probe using an anoscope (a plastic instrument that is inserted into the anus to view the rectum) and attach a rubber device to the base of the hemorrhoid. This device will cut off blood circulation and cause scarring of the hemorrhoid. Over time, the scars will shrink and eliminate the hemorrhoids.
2 Ligate with rubber bands for internal hemorrhoids. The doctor will insert the probe using an anoscope (a plastic instrument that is inserted into the anus to view the rectum) and attach a rubber device to the base of the hemorrhoid. This device will cut off blood circulation and cause scarring of the hemorrhoid. Over time, the scars will shrink and eliminate the hemorrhoids. - Discomfort is possible after the procedure. It can be relieved with sitz baths, warm wet compresses and / or ointments.
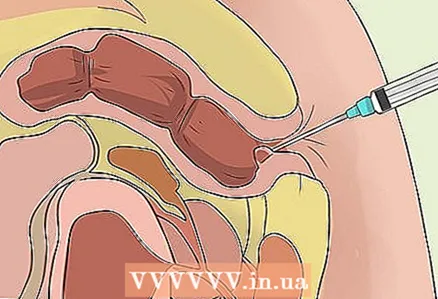 3 Get an injection (sclerotherapy) for internal hemorrhoids. In doing so, the doctor will insert a plastic device (anoscope) into the anus, which will allow him to examine the rectum. The doctor will insert the needle through the anoscope and inject the solution into the base of the hemorrhoid. This can be a 5% solution of phenol in oil, vegetable oil, quinine, and a solution of urea hydrochloride or hypertonic salt. These substances cause the veins to contract.
3 Get an injection (sclerotherapy) for internal hemorrhoids. In doing so, the doctor will insert a plastic device (anoscope) into the anus, which will allow him to examine the rectum. The doctor will insert the needle through the anoscope and inject the solution into the base of the hemorrhoid. This can be a 5% solution of phenol in oil, vegetable oil, quinine, and a solution of urea hydrochloride or hypertonic salt. These substances cause the veins to contract. - Sclerotherapy is believed to be less effective than rubber band ligation.
 4 For the treatment of internal hemorrhoids, laser coagulation and radiofrequency ablation are also used. At the same time, infrared laser or radio frequency radiation is used to coagulate veins near hemorrhoids. In the infrared method, the probe is applied to the base of the hemorrhoid. RF ablation uses a ball electrode that is connected to an RF generator. This electrode is pressed against the hemorrhoidal tissues, as a result of which they coagulate and evaporate.
4 For the treatment of internal hemorrhoids, laser coagulation and radiofrequency ablation are also used. At the same time, infrared laser or radio frequency radiation is used to coagulate veins near hemorrhoids. In the infrared method, the probe is applied to the base of the hemorrhoid. RF ablation uses a ball electrode that is connected to an RF generator. This electrode is pressed against the hemorrhoidal tissues, as a result of which they coagulate and evaporate. - Radiofrequency ablation is more likely to cause recurrence than rubber band ligation.
 5 Get cryotherapy for internal hemorrhoids. In this method, the doctor uses a probe to freeze the base of the hemorrhoid and destroy the corresponding tissue. This method is not very common, as relapses usually occur after it.
5 Get cryotherapy for internal hemorrhoids. In this method, the doctor uses a probe to freeze the base of the hemorrhoid and destroy the corresponding tissue. This method is not very common, as relapses usually occur after it. 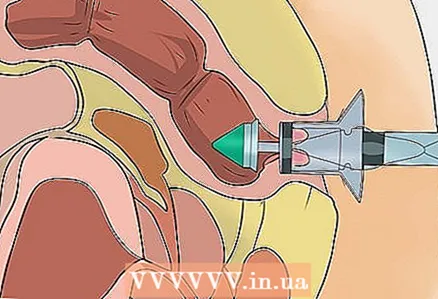 6 Use the stapling method to treat internal hemorrhoids. In this case, the surgeon uses a special device to place the shifted or fallen out internal hemorrhoids back into the anal canal. The staples will cut off the blood supply, and as a result, the hemorrhoidal tissue will eventually die off and the bleeding will stop.
6 Use the stapling method to treat internal hemorrhoids. In this case, the surgeon uses a special device to place the shifted or fallen out internal hemorrhoids back into the anal canal. The staples will cut off the blood supply, and as a result, the hemorrhoidal tissue will eventually die off and the bleeding will stop. - As a rule, after this operation, patients recover faster and experience less pain than after hemorrhoidectomy.
Method 3 of 3: What is hemorrhoids and how to identify them
 1 Learn about the causes of hemorrhoids. Chronic constipation, tension and prolonged sitting on the toilet contribute to hemorrhoids. All of this increases pressure on the veins, blocks them and makes it difficult for blood to circulate. Hemorrhoids can also occur during pregnancy, especially due to childbirth due to a lot of muscle tension.
1 Learn about the causes of hemorrhoids. Chronic constipation, tension and prolonged sitting on the toilet contribute to hemorrhoids. All of this increases pressure on the veins, blocks them and makes it difficult for blood to circulate. Hemorrhoids can also occur during pregnancy, especially due to childbirth due to a lot of muscle tension. - Hemorrhoids are more common in older people and those who are overweight.
- Hemorrhoids can be either internal (inside the rectum) or external (around the outside of the anus). Internal hemorrhoids are painless, while external ones are painful. Both types of hemorrhoids can lead to bleeding when they rupture.
 2 Recognize the symptoms of hemorrhoids. With internal hemorrhoids, symptoms are difficult to detect until it causes bleeding, which can be painless. At the same time, the following symptoms are characteristic of external hemorrhoids:
2 Recognize the symptoms of hemorrhoids. With internal hemorrhoids, symptoms are difficult to detect until it causes bleeding, which can be painless. At the same time, the following symptoms are characteristic of external hemorrhoids: - painless bleeding during bowel movements (usually there is not very much blood and it has a light red color);
- itching and irritation in the anus;
- pain and discomfort;
- swelling around the anus;
- a tender and painful lump around the anus;
- fecal incontinence.
 3 Check if you have hemorrhoids. Turn your back to the mirror and look for any lumps or lumps around your anus. Their color can range from normal skin tone to deep red. You may experience pain when you press on the lumps. This may indicate that you have external hemorrhoids. When you visit the restroom, look for traces of blood on the toilet paper. As a rule, with hemorrhoids, the blood is light red rather than dark (dark blood color can be a sign of bleeding deep in the digestive tract).
3 Check if you have hemorrhoids. Turn your back to the mirror and look for any lumps or lumps around your anus. Their color can range from normal skin tone to deep red. You may experience pain when you press on the lumps. This may indicate that you have external hemorrhoids. When you visit the restroom, look for traces of blood on the toilet paper. As a rule, with hemorrhoids, the blood is light red rather than dark (dark blood color can be a sign of bleeding deep in the digestive tract). - Internal hemorrhoids are difficult to detect at home without proper tools. Make an appointment with your doctor. Your doctor will look at your medical history to look for other possible causes of bleeding, such as colon cancer and polyps.
 4 Know when to seek medical attention. If symptoms and pain persist after a week of home treatment, you should see your doctor and get tested. Bleeding is a cause for concern, especially if you are at risk for other illnesses, such as inflammatory bowel disease or colon cancer. You should also see your doctor if your blood is dark red or if you have dark (tarry) stools. This could be a sign of bleeding in the intestines.
4 Know when to seek medical attention. If symptoms and pain persist after a week of home treatment, you should see your doctor and get tested. Bleeding is a cause for concern, especially if you are at risk for other illnesses, such as inflammatory bowel disease or colon cancer. You should also see your doctor if your blood is dark red or if you have dark (tarry) stools. This could be a sign of bleeding in the intestines. - Try to estimate how much blood you are losing. If you start to feel tired or anxious, pale, cold hands and feet, heart palpitations, or confusion with persistent bleeding, you should see your doctor right away. Seek medical attention even if bleeding worsens.
 5 Know what to expect from your medical examination. Your doctor will determine if you have hemorrhoids by examining your anus and performing a digital rectal examination. In this case, the doctor will insert a lubricated index finger into the anus and feel the walls of the rectum to determine if there are any lumps, seals and traces of blood on them. If you suspect internal hemorrhoids, an anoscope (plastic tube) may be inserted through your anus and into your rectum. This will allow the doctor to illuminate the rectum and see the swollen, swollen, and bleeding veins.
5 Know what to expect from your medical examination. Your doctor will determine if you have hemorrhoids by examining your anus and performing a digital rectal examination. In this case, the doctor will insert a lubricated index finger into the anus and feel the walls of the rectum to determine if there are any lumps, seals and traces of blood on them. If you suspect internal hemorrhoids, an anoscope (plastic tube) may be inserted through your anus and into your rectum. This will allow the doctor to illuminate the rectum and see the swollen, swollen, and bleeding veins. - The doctor may take a guaiac sample - a swab of faeces is taken on a strip of paper. This test detects microscopic blood cells in the stool, which can indicate a variety of conditions, including hemorrhoids, colon cancer, and polyps.
- Avoid eating red meat, turnips, radishes, horseradish, melons and raw broccoli for the three days before sampling guaiac, as this can lead to deceptive positive results.