Author:
Alice Brown
Date Of Creation:
26 May 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
Heat cramps are muscle cramps or cramps that occur during exercise at a high temperature, such as outside in hot summers. Muscle cramps differ from heat cramps in that they are caused by sodium deficiency caused by increased sweating (rather than the hottest heat). ). Pain usually occurs due to the body's inability to maintain water balance in order to compensate for perspiration. As a result, your body's electrolyte levels drop too low (hyponatremia). Most often, these cramps occur in the calves, thigh muscles, and abs (however, heat cramps can affect any muscle). But don't worry, heat cramps are fairly easy to heal.
Steps
Method 1 of 2: Treating Heat Cramps
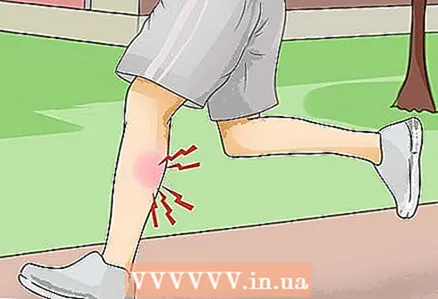 1 Determine if you have a heat cramp. Heat cramps are painful muscle spasms caused by dehydration, usually during exercise in a hot environment. Although heat cramps are called like this, they are not actually caused by the heat itself or the hot environment. Increased sweating during exercise leads to the loss of fluids and electrolytes (salts), which the muscles need to function properly.Although heat cramp can affect any muscle group, it is most common in the calf muscles, arm muscles, abdomen, and back muscles.
1 Determine if you have a heat cramp. Heat cramps are painful muscle spasms caused by dehydration, usually during exercise in a hot environment. Although heat cramps are called like this, they are not actually caused by the heat itself or the hot environment. Increased sweating during exercise leads to the loss of fluids and electrolytes (salts), which the muscles need to function properly.Although heat cramp can affect any muscle group, it is most common in the calf muscles, arm muscles, abdomen, and back muscles.  2 Stop doing the exercise. Heat cramps cannot be simply "endured". This tells your body that it needs a break. To relieve a heat cramp, the first step is to stop the exercise that triggered it.
2 Stop doing the exercise. Heat cramps cannot be simply "endured". This tells your body that it needs a break. To relieve a heat cramp, the first step is to stop the exercise that triggered it.  3 Relax in a cool place. Heat cramps are often associated with overuse on a hot summer day. If that's the case, get out of the sun. Find a cool place in the shade or in the house, get some rest and cool down.
3 Relax in a cool place. Heat cramps are often associated with overuse on a hot summer day. If that's the case, get out of the sun. Find a cool place in the shade or in the house, get some rest and cool down. - Help your body cool off by placing a wet towel on the back of your neck.
 4 Drink plenty of fluids. The cramp is caused by dehydration and loss of electrolytes, so while you rest, you should drink, preferably a sports drink (such as Gatorade) or electrolyte drinks (such as Pedialyte). Sports drinks containing 25-200 mg sodium are ideal.
4 Drink plenty of fluids. The cramp is caused by dehydration and loss of electrolytes, so while you rest, you should drink, preferably a sports drink (such as Gatorade) or electrolyte drinks (such as Pedialyte). Sports drinks containing 25-200 mg sodium are ideal. - Also try clear juices. They will saturate your body with essential electrolytes and fluids.
- If you only have water, then dissolve a quarter or half teaspoon of salt in a liter of water. Although this water will not taste like sports drinks, it will do the trick.
 5 Stretch the affected muscle group lightly. If you want to help the cramp go away quickly, stretch the affected muscles lightly. Do not stretch your muscles vigorously; instead, do a wide-range stretch. This will help relieve muscle spasms and pain.
5 Stretch the affected muscle group lightly. If you want to help the cramp go away quickly, stretch the affected muscles lightly. Do not stretch your muscles vigorously; instead, do a wide-range stretch. This will help relieve muscle spasms and pain.  6 Monitor your spasms. If you rest and restore fluid and electrolyte balance, heat cramps will soon disappear. Remember the time when you had the seizures. If after an hour your condition does not improve (or even worsens), then you should see a doctor.
6 Monitor your spasms. If you rest and restore fluid and electrolyte balance, heat cramps will soon disappear. Remember the time when you had the seizures. If after an hour your condition does not improve (or even worsens), then you should see a doctor.  7 Do not return to physical activity immediately after the cramps have subsided. The fact that the cramps are gone does not mean that you have restored the water balance and the electrolytes in the body. So don't think you can get back to training already. You should continue to consume fluids and return to training only after a few hours. Otherwise, you might get a seizure again or worse, such as heatstroke.
7 Do not return to physical activity immediately after the cramps have subsided. The fact that the cramps are gone does not mean that you have restored the water balance and the electrolytes in the body. So don't think you can get back to training already. You should continue to consume fluids and return to training only after a few hours. Otherwise, you might get a seizure again or worse, such as heatstroke.  8 Take care to minimize the possibility of seizures. If you work outside or jog in the summer, you are unlikely to be able to avoid the summer heat, but you can prepare and minimize the chances of recurring heat cramps. Drink plenty of fluids before exercising and drink sports drinks from time to time to prevent heat cramps.
8 Take care to minimize the possibility of seizures. If you work outside or jog in the summer, you are unlikely to be able to avoid the summer heat, but you can prepare and minimize the chances of recurring heat cramps. Drink plenty of fluids before exercising and drink sports drinks from time to time to prevent heat cramps. - Heat cramps may recur in the first few days, but once you get used to the high temperature, the cramps can be avoided by just drinking fluids.
- At a temperature of 39.4 - 46.1 ° C, you should drink at least 1 liter of water per hour.
Method 2 of 2: Treating Heat Exhaustion
 1 Pay attention to other symptoms. If you have other symptoms along with the cramp, it is possible that a simple heat cramp has developed into heat exhaustion. If you experience the following symptoms, you are most likely experiencing heat exhaustion:
1 Pay attention to other symptoms. If you have other symptoms along with the cramp, it is possible that a simple heat cramp has developed into heat exhaustion. If you experience the following symptoms, you are most likely experiencing heat exhaustion: - Weakness
- Headache
- Dizziness or loss of consciousness
- Nausea and / or vomiting
- Heart palpitations
- Cool and moist skin
- Heavy sweating
 2 Measure the temperature. Heat conditions make your body no longer able to control its core temperature through its habitual perspiration and evaporation. Measure your temperature to find out how high your temperature has risen. A temperature above normal but below 40 ° C indicates heat exhaustion.
2 Measure the temperature. Heat conditions make your body no longer able to control its core temperature through its habitual perspiration and evaporation. Measure your temperature to find out how high your temperature has risen. A temperature above normal but below 40 ° C indicates heat exhaustion. - If your temperature is 40 ° C or higher, you have heatstroke and need urgent medical attention.
- Other symptoms of heatstroke include confusion and loss of consciousness, profuse sweating, and red, hot, and dry skin.
 3 Find a cool place. Get out of the heat immediately and start taking steps to cool your body so that heat exhaustion doesn't turn into heatstroke. Get out of the sun and heat in a well-ventilated area.
3 Find a cool place. Get out of the heat immediately and start taking steps to cool your body so that heat exhaustion doesn't turn into heatstroke. Get out of the sun and heat in a well-ventilated area.  4 Drink cold water or sports drinks. Just like with heat cramps, your body needs extra fluids and electrolytes that it lost from excessive sweating. Drink sports drinks, drinks with electrolytes, or stir a quarter or half teaspoon of salt in a liter of water.
4 Drink cold water or sports drinks. Just like with heat cramps, your body needs extra fluids and electrolytes that it lost from excessive sweating. Drink sports drinks, drinks with electrolytes, or stir a quarter or half teaspoon of salt in a liter of water. - Your body will continue to sweat. This is necessary to lower core body temperature. Failure to saturate the body with the fluids and salts it needs to sweat will lead to heatstroke.
 5 Take off unnecessary clothing. Even lightweight cotton can retain heat. Take off as many clothes as possible. Make sure the remaining clothing is light and loose, and does not fit snugly against your body.
5 Take off unnecessary clothing. Even lightweight cotton can retain heat. Take off as many clothes as possible. Make sure the remaining clothing is light and loose, and does not fit snugly against your body.  6 Take extra steps to cool your body. Don't rely on sweating alone. To lower core body temperature, do the following:
6 Take extra steps to cool your body. Don't rely on sweating alone. To lower core body temperature, do the following: - Take a cool shower or bath.
- Splash yourself with cool water and sit in front of a fan or in an air-conditioned room.
- Soak a towel in cold water and place it on your skin.
- Place ice packs on your armpits and on the back of your neck.
 7 Relax while raising your legs above your head. Loss of consciousness from heat malaise (heatstroke) is caused by dilatation (dilation) of blood vessels, which results in decreased blood flow to the head. To prevent this, rest with your legs raised above your head to improve blood flow.
7 Relax while raising your legs above your head. Loss of consciousness from heat malaise (heatstroke) is caused by dilatation (dilation) of blood vessels, which results in decreased blood flow to the head. To prevent this, rest with your legs raised above your head to improve blood flow.  8 Seek medical attention immediately. Heat exhaustion can quickly develop into heatstroke, so keep an eye on your condition and know when to seek medical attention. See your doctor if:
8 Seek medical attention immediately. Heat exhaustion can quickly develop into heatstroke, so keep an eye on your condition and know when to seek medical attention. See your doctor if: - An hour later, the symptoms did not go away.
- Nausea and vomiting make it difficult to restore fluid and electrolyte levels
- Your body temperature is above 40 degrees Celsius
- You have confusion, delirium, or seizures
- After exercising, you have rapid breathing and heartbeat.
Warnings
- Heatstroke is life-threatening, so if you experience symptoms of heatstroke, call the emergency number immediately.
- Do not treat heat cramps by chewing or using salt tablets. You will not replace lost fluids and will only cause stomach upset.