Author:
Bobbie Johnson
Date Of Creation:
5 April 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- Steps
- Part 1 of 6: Doing Good Math in School
- Part 2 of 6: Learning Mathematics in School
- Part 3 of 6: Basic Math - Work on Addition
- Part 4 of 6: Fundamentals of Mathematics - Methods for Subtraction
- Part 5 of 6: Fundamentals of Mathematics - Methods of Multiplication
- Part 6 of 6: Fundamentals of Mathematics - Division
- Tips
- Warnings
- What do you need
“Mathematics is worth studying just because it puts the mind in order,” said Lomonosov.And in fact, everyone can study it, and it does not matter whether you are preparing for final exams or simply decided to repeat the very basics. In this article, you will learn about the main sections of mathematics, with an emphasis on the basic arithmetic needed for primary school students and all repetitives.
Steps
Part 1 of 6: Doing Good Math in School
 1 Don't miss lessons. After skipping a lesson, you will have to analyze the material either on your own or ask for help from one of your classmates. Of course, the teacher will explain something new better and more accessible.
1 Don't miss lessons. After skipping a lesson, you will have to analyze the material either on your own or ask for help from one of your classmates. Of course, the teacher will explain something new better and more accessible. - Don't be late. Better come early, not just before the call. Lay out the supplies and prepare for the lesson.
- Illness is the only good reason for skipping class. After skipping the lesson, be sure to ask your classmates about the covered topic and homework.
 2 Work with your teacher. If the teacher explains an example on the chalkboard, write it down carefully in your notebook.
2 Work with your teacher. If the teacher explains an example on the chalkboard, write it down carefully in your notebook. - Make sure all notes are clear and understandable. Rewrite not only the example, but also write down everything the teacher says, this will help you better assimilate the new material.
- Follow all the assignments given by the teacher. Be proactive: answer questions.
- If the teacher decides something on the board, participate. Do you know the answer to the question? raise your hand and answer Do not understand something? raise your hand and ask.
 3 Do your homework the same day it was assigned while the knowledge is still fresh. Sometimes this does not work, but, most importantly, never come to class unprepared.
3 Do your homework the same day it was assigned while the knowledge is still fresh. Sometimes this does not work, but, most importantly, never come to class unprepared.  4 If you need help, work outside the classroom. At recess, go to the teacher and ask about additional classes.
4 If you need help, work outside the classroom. At recess, go to the teacher and ask about additional classes. - Join a group of self-taught students. In such groups, there are usually guys of all levels. If you are a C grade, join the stronger guys, excellent students and good students. This will allow you to pull up your level. Avoid groups with weaker students.
Part 2 of 6: Learning Mathematics in School
 1 Start with arithmetic. In the vast majority of schools in elementary grades, they study arithmetic, which includes the basics of addition, subtraction, division and multiplication.
1 Start with arithmetic. In the vast majority of schools in elementary grades, they study arithmetic, which includes the basics of addition, subtraction, division and multiplication. - Work on examples. Re-solving numerous examples and problems will give you a good grasp of the basics. Look for computer programs that can solve many examples. To increase the speed of the solution, set yourself time limits.
- Arithmetic examples can be found on the Internet, you can download a suitable application to your phone.
 2 Move on to the basics of algebra. In this section, you will learn the important basics.
2 Move on to the basics of algebra. In this section, you will learn the important basics. - Learn fractions and decimals. You will learn how to add, subtract, divide and multiply both decimal and fractions. As for the ordinary ones, you will also learn how to reduce them, you will learn what mixed numbers are. As for decimals, you will learn all about the digits and learn how to use fractions to solve problems.
- Examine proportions and percentages. These concepts help you compare different quantities.
- Learn the basics of geometry. You will learn about all shapes, both 2D and 3D. You will also learn about concepts such as area, perimeter, volume, surface area, parallels, perpendiculars, and angles.
- Understand the basics of statistics. Graphs and different types of charts.
- Learn the basics of algebra. Learn to solve simple equations, draw their graphs, solve inequalities, find domains.
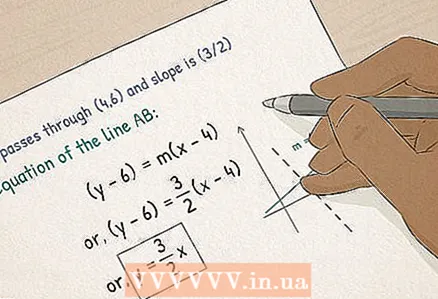 3 Transition to algebra. You will continue to study algebra, learn to:
3 Transition to algebra. You will continue to study algebra, learn to: - Solve equations and inequalities containing variables
- Solving problems. You will be surprised to learn how useful knowledge of algebra can be in everyday life. For example, algebra is needed when calculating interest rates at a bank or determining the length of a necessary trip by car.
- Working with degrees.Once you start solving equations with polynomials (containing both numbers and variables), you will need to understand the powers, after which you can perform arithmetic operations with polynomials.
- Finding squares and square roots. After studying this topic, you will know the squares of numbers and will be able to solve equations with square roots.
- Understanding functions and graphs. In algebra, you will come across graphic equations. You will learn how to find the slope of a line, make graphs of functions, find the points of intersection along the axes.
- Solving systems of equations. Sometimes you are given two separate equations with variables x and y to find for both equations. You will learn ways to solve similar systems of equations, including: graphing, substitution, addition, and more.
 4 Geometry. You will learn about the properties of lines, segments, angles, and various shapes.
4 Geometry. You will learn about the properties of lines, segments, angles, and various shapes. - You will master theorems and rules that will help you understand geometric concepts.
- You will learn how to find the area of a circle, use the Pythagorean theorem, and learn how angles are related to the lengths of the sides of triangles.
 5 Continuation of algebra. You will learn more deeply the concepts mastered earlier, you will come across new material such as quadratic equations and matrices.
5 Continuation of algebra. You will learn more deeply the concepts mastered earlier, you will come across new material such as quadratic equations and matrices.  6 Trigonometry. You will learn terms like: sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, etc. In the trigonometry course, you will learn many practical ways to find the angles and side lengths. These skills are especially useful for work in the field of construction, architecture, engineering.
6 Trigonometry. You will learn terms like: sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, etc. In the trigonometry course, you will learn many practical ways to find the angles and side lengths. These skills are especially useful for work in the field of construction, architecture, engineering. 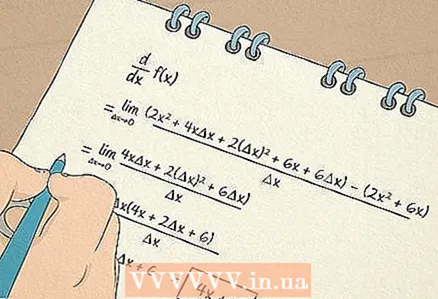 7 Mathematical analysis. It may sound intimidating, but this is a very important and interesting area of mathematics.
7 Mathematical analysis. It may sound intimidating, but this is a very important and interesting area of mathematics. - You will learn about functions and their limits, as well as about logarithmic functions.
- You will learn how to find derivatives. The first derivative contains information about the angle of the tangent. For example, thanks to the derivative, you can determine the frequency of changes in something in a non-linear situation. The second derivative lets you know if the function is increasing or decreasing in a certain interval.
- From the section on integrals, you will learn how to find area separated by a curve and volume.
- A school course in calculus usually ends with differential equations.
Part 3 of 6: Basic Math - Work on Addition
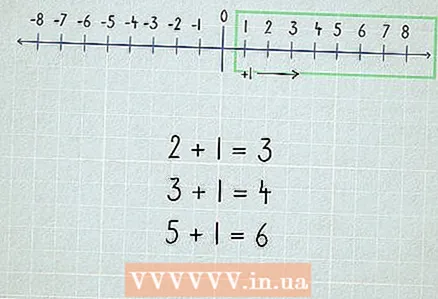 1 Start with "+1". By adding 1 to the number, you get the next number in order. For example, 2 + 1 = 3.
1 Start with "+1". By adding 1 to the number, you get the next number in order. For example, 2 + 1 = 3. 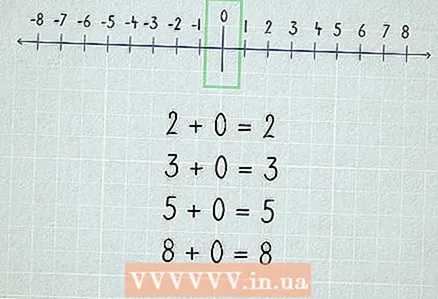 2 Understand what zero is. Zero is "nothing", adding zero to the number you get the same number.
2 Understand what zero is. Zero is "nothing", adding zero to the number you get the same number.  3 Learn to double up. Doubling is multiplying by two or adding to the number itself. For example, 3 + 3 = 6.
3 Learn to double up. Doubling is multiplying by two or adding to the number itself. For example, 3 + 3 = 6.  4 Use correspondence and you can learn addition faster. In the example below, you can clearly see what happens when you add 3 and 5, 2 and 1. Try adding 2 yourself.
4 Use correspondence and you can learn addition faster. In the example below, you can clearly see what happens when you add 3 and 5, 2 and 1. Try adding 2 yourself. 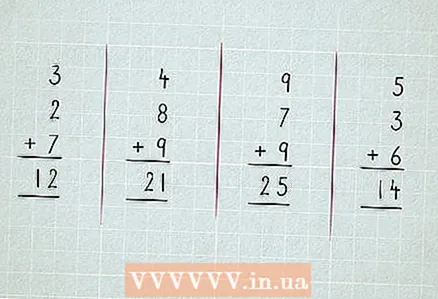 5 Addition after 10. Learn to add 3 or more numbers.
5 Addition after 10. Learn to add 3 or more numbers.  6 Add big numbers. Explore the digits of ones, tens, hundreds, etc.
6 Add big numbers. Explore the digits of ones, tens, hundreds, etc. - Add the numbers in the right column first. 8 + 4 = 12, which means that we have both 1 ten and 2 ones. We write 2 in the units column.
- We write down 1 column of tens.
- Add up the numbers in the tens column.
Part 4 of 6: Fundamentals of Mathematics - Methods for Subtraction
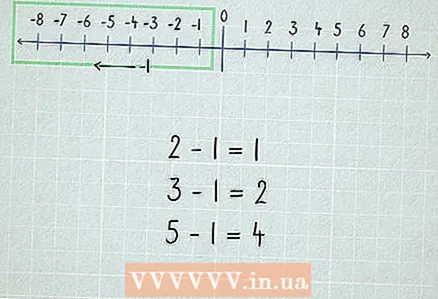 1 Start with "back to 1."Subtracting 1 from the number you just get the previous number. For example, 4 - 1 = 3.
1 Start with "back to 1."Subtracting 1 from the number you just get the previous number. For example, 4 - 1 = 3.  2 Learn subtraction after doubling. For example, doubling 5 + 5 we get 10. Let's write the other way around and get 10 - 5 = 5.
2 Learn subtraction after doubling. For example, doubling 5 + 5 we get 10. Let's write the other way around and get 10 - 5 = 5. - If 5 + 5 = 10, then 10 - 5 = 5.
- If 2 + 2 = 4, then 4 - 2 = 2.
 3 Remember. For example:
3 Remember. For example: - 3 + 1 = 4
- 1 + 3 = 4
- 4 - 1 = 3
- 4 - 3 = 1
 4 Find missing numbers. For example, ___ + 1 = 6 (the answer is 5).
4 Find missing numbers. For example, ___ + 1 = 6 (the answer is 5).  5 Memorize the subtraction to 20.
5 Memorize the subtraction to 20. 6 Practice subtracting single-digit numbers from two-digit numbers without engaging. Subtract the numbers in the first column (units) and simply move down the number in the second column (tens).
6 Practice subtracting single-digit numbers from two-digit numbers without engaging. Subtract the numbers in the first column (units) and simply move down the number in the second column (tens). 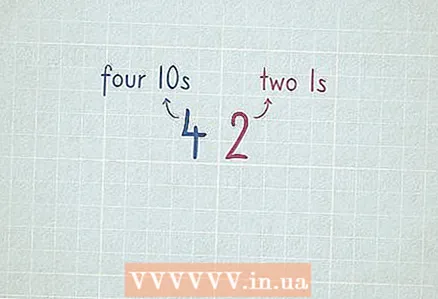 7 Try to sort numbers.
7 Try to sort numbers.- 32 = 3 tens and 2 units.
- 64 = 6 tens and 4 units.
- 96 = __ tens and __ units.
 8 Practice lesson subtraction.
8 Practice lesson subtraction.- You must subtract 42 - 37. You cannot subtract 2 - 7 in the first column!
- Borrow 10 in the column of tens and put it in the first column. Now, instead of 4 tens, there are 3 left, but instead of 2 units, we now have 12 of them.
- First, subtract in the first column: 12 - 7 = 5. Then go to the second column (tens): 3 - 3 = 0, 0 do not need to write. Answer: 5.
Part 5 of 6: Fundamentals of Mathematics - Methods of Multiplication
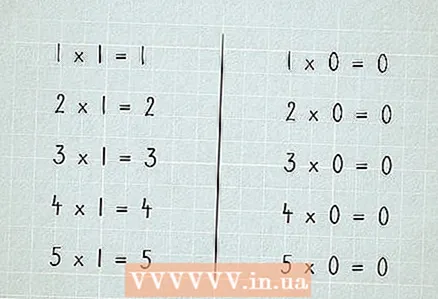 1 Start with 1 and 0. When we multiply the number by 1, we get this number. When multiplying the number by 0 - we get 0.
1 Start with 1 and 0. When we multiply the number by 1, we get this number. When multiplying the number by 0 - we get 0.  2 Remember the multiplication table.
2 Remember the multiplication table.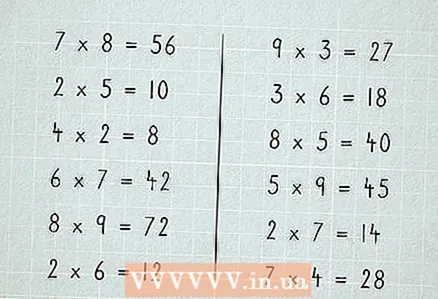 3 Decide examples of multiplication of single-digit numbers.
3 Decide examples of multiplication of single-digit numbers. 4 Multiply two-digit numbers by single-digit numbers.
4 Multiply two-digit numbers by single-digit numbers.- Multiply the bottom-right number by the top-right number.
- Multiply the bottom-right number by the top-left number.
 5 Multiply two two-digit numbers.
5 Multiply two two-digit numbers.- Multiply the bottom-right number by the top-right, and then by the top-right.
- Move the second row one space to the left.
- Multiply the bottom-left number by the top-right, and therefore by the top-left.
- Fold in a column.
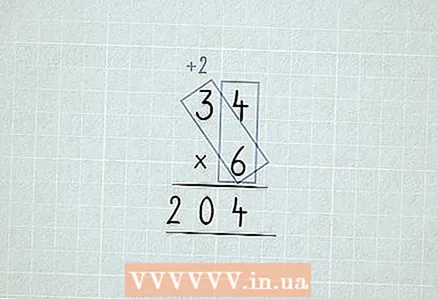 6 Multiplication with permutation of columns.
6 Multiplication with permutation of columns.- Multiply 34 x 6. We start by multiplying the first column (4 x 6), but you cannot write 24 in the first column.
- We leave 4 in the first column. 2 is transferred to the second column (tens).
- Multiply 6 x 3, we get 18. Add the carried over 2, it will be 20.
Part 6 of 6: Fundamentals of Mathematics - Division
 1 Division is the opposite of multiplication. If 4 x 4 = 16, then 16/4 = 4.
1 Division is the opposite of multiplication. If 4 x 4 = 16, then 16/4 = 4.  2 Write an example.
2 Write an example.- Divide the number to the left of the division sign, the dividend but the first divisor number. Since 6/2 = 3, we write 3 over the division sign.
- We multiply the number above the sign by the divisor. Write the result under the first number under the division sign. 3 x 2 = 6, then write 6 down.
- Subtract 2 written numbers. 6 - 6 = 0. You can leave 0.
- Write down the second number under the division sign.
- Divide the number below by the divisor. In our case, 8/2 = 4. Write 4 over the division sign.
- Multiply the number on the top right by the divisor and write the number down. 4 x 2 = 8.
- Subtract the numbers. The last subtraction gives 0, which means the example is solved. 68/2 = 34.
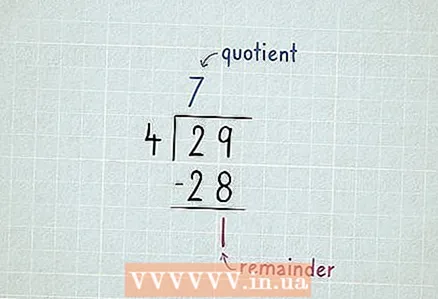 3 Consider leftovers. Some numbers are not divisible completely and the remainder, the last number, remains.
3 Consider leftovers. Some numbers are not divisible completely and the remainder, the last number, remains.
Tips
- Mathematics must be practiced: to solve examples and problems, you will not master mathematics of this level just by reading a book.
Warnings
- Don't get addicted to a calculator. Try to solve everything in your head or on paper, without a calculator.
What do you need
- Pencil
- Paper