Author:
Eric Farmer
Date Of Creation:
9 March 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- Steps
- Method 1 of 3: Recognizing grassy weeds
- Method 2 of 3: Recognizing broadleaf weeds
- Method 3 of 3: Recognizing tree weeds
- Tips
- What do you need
Weeds are pests that take away nutrients from garden and garden plants. This article will help you learn to recognize weeds by species, whether grassy, broadleaf or tree weeds, and you will also learn about some of the most common varieties of each species. Weed species may differ depending on the country, region, state or hardiness zone in which they grow, therefore it is recommended to look for the necessary information in the electronic library, the link to which is given below, in order to most accurately identify specific weed varieties. But first, you should read the article and find out the main signs of weeds.
Steps
Method 1 of 3: Recognizing grassy weeds
 1 Take a closer look at the weed. Many grassy weeds have common characteristics that make them easy to identify. For example, herbaceous weeds usually have subtle and unobtrusive flowers. Their leaves are usually narrow and ribbon-like with parallel veins. Many of them are tightly rolled up.
1 Take a closer look at the weed. Many grassy weeds have common characteristics that make them easy to identify. For example, herbaceous weeds usually have subtle and unobtrusive flowers. Their leaves are usually narrow and ribbon-like with parallel veins. Many of them are tightly rolled up. - 2 Consider the stem of the weed. The stems of herbaceous weeds are usually round, but usually not an indicator. On the stems of many weeds of this species, there are clearly delineated nodes to which the leaves are attached. In many species, the stems are hollow in the middle, except for the nodes.
- 3 Consider the flower head of the weed. Unfortunately, the flower heads of herbaceous weeds do not have common characteristics, but they can still be distinguished.
- They have pointed or spike-shaped flower heads. There are no branches on the main stem of the flower of such weeds; instead, the small flowers attach directly to the plant and are spike-like in shape. Some of the more popular types of such weeds include foxtail, chaff, and wheatgrass.

- The pointed heads of the foxtail are cylindrical, dense, bristly and straight. Their length reaches 5-12.7 cm, the color is yellow and they bloom from June to September.
- Chaff inflorescences are straight, narrow spikelets, reaching 20 cm in length. Secondary spikelets are attached to them on opposite sides of the curly pedicel.
- Wheatgrass flowers are narrow and dense in the form of spikelets at the top, their length is 5-15 cm. The flowering period lasts from late May to September.
- Weeds with cluster-shaped seed heads. The inflorescence and seed head of this weed variety are unbranched, each flower growing on a short stalk or stem. The dewdrop is one of the most common varieties of this weed. This plant reproduces mainly by seeds, but it can also propagate with long root shoots, which allows the weed to grow in narrow strips or destroy the grass growing nearby, gradually taking over the entire area.

- Bloody crabby flowers grow in clusters with 3-13 lilac spikelets up to 15 cm in length. They grow from a bunch of leaves at the end of a thick stem and bloom from August to September. The flowers of the crabgrass grow in clusters with 2-6 lilac spikelets at the end of the flower stem, reaching 10 cm in length. The flowering period is also from August to September.
- Weeds with finger-shaped flower heads. This group of grassy weeds is distinguished by unbranched spikelets growing from the flower head like open fingers. Perennial Bermuda grass is a prime example of finger weeds.

- The inflorescence of Bermuda grass consists of 3-7 spikelets in one cluster, located finger-like and reaching 2.5-10 cm in length. The number of spikelets of more lush varieties reaches ten, and sometimes they grow in double bunches.
- Weeds with flower panicles. This category of weeds is easier to distinguish due to the fact that the main stem of the flower has several branches. Herbaceous and Johnson's grass are prime examples of this weed variety.
- A mature barbarian grows up to 1.5 m in height and takes on a variety of forms. The barnyard's stems are flat at the base. The leaf blades are also flat, wrapped in a bud, and the upper surface is smooth. The stem of the leaf is usually hollow and relatively smooth.
- Jones grass flowers are a branched pyramidal bunch (panicle), reaching 40.6 cm in length. Secondary spikelets grow in pairs along the lower edge of the flower stem and branch into three spikelets at the top of the stem.
- They have pointed or spike-shaped flower heads. There are no branches on the main stem of the flower of such weeds; instead, the small flowers attach directly to the plant and are spike-like in shape. Some of the more popular types of such weeds include foxtail, chaff, and wheatgrass.
Method 2 of 3: Recognizing broadleaf weeds
 1 Note the flowering of broadleaf weeds. Broadleaf weeds are flowering grassy weeds with broad leaves that are usually reticulate in veins.
1 Note the flowering of broadleaf weeds. Broadleaf weeds are flowering grassy weeds with broad leaves that are usually reticulate in veins. - 2 Consider the leaves of a broadleaf weed. Unlike herbaceous weeds, the main difference of which is flower heads, broadleaf weeds can be identified due to the peculiarities of growth.
- Creeping broadleaf weeds. These weeds grow close to the ground and have horizontal rather than vertical stems. The varieties of clover, buttercups and woodlice are prime examples of creeping broadleaf weeds. Large-flowered purslane is another common species that, incidentally, is edible and is a great alternative to spinach.
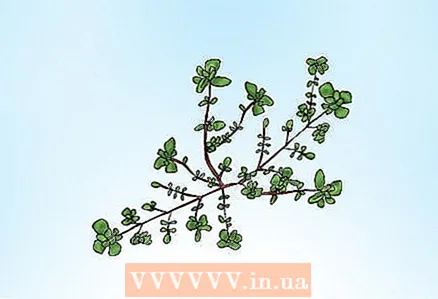
- White clover is one of the most common broadleaf weeds. Composite leaves consist of three stemless oval leaves, reaching 2 cm in length. Clover leaves are dark green in color, often with inconspicuous crescent white veins.
- The leaves of wood lice are bright green, opposite, simple, oval in shape and usually less than 2.5 cm in length. Outlines are clear.
- Woodlice has a heavy taproot from which succulent, smooth and fleshy stems grow, usually purple-red, appearing on the lower nodes of the stem. The branchy stems reach 61 cm in length and spread along the ground in the form of a carpet.
- Broadleaf weeds with rosettes. The leaves of this broad-leaved weed grow outward from the base of the stem. Dandelions are the most recognizable variety in this broadleaf weed category. When you get rid of dandelions, you need to root them out before the cotton-like seed head blows away. Apply corn glutin to your lawn and garden in early spring to slow weed growth.

- Dandelions have long, strong taproots, on which rosettes of narrow lobular leaves form.
- Broadleaf weeds with whorled leaves. The leaves of this type of weed are located several together, they twine around the stem and grow 3-6 pieces per node. The various varieties of bedstraw are referred to as whorled leaf weeds.
- The flowers of the bedstraw are white or greenish with four petals, each of which reaches 3.2 mm in width. Leaves are simple, with smooth edges, elongated and whorled. Stems are weak, with tendrils that stick to clothing.
- Creeping broadleaf weeds. These weeds grow close to the ground and have horizontal rather than vertical stems. The varieties of clover, buttercups and woodlice are prime examples of creeping broadleaf weeds. Large-flowered purslane is another common species that, incidentally, is edible and is a great alternative to spinach.
- 3 Pay attention to the distinguishing features of the mature leaves of the weed. In addition to the peculiarities of growth, broadleaf weeds can be identified by the appearance of mature leaves. They are distinguished by an elliptical or heart-shaped shape, serrated edges and deep grooves.
- Mary white is a prime example of a broadleaf weed with serrated leaves. The leaves of this plant are triangular or diamond-shaped, up to 10 cm in length, white on the underside.

- The field bindweed is an excellent example of a broadleaf weed with lobbed mature leaves.It is also considered one of the most difficult to eradicate weeds in temperate agricultural regions. Among other things, the leaves of this plant are characterized by a staggered arrangement, have a more or less arrow-shaped shape and pointed or blunt branches at the base.

- Other broadleaf weeds, such as broadleaf sorrel, have ovoid or oval leaves. The leaves also have slightly curly edges. The lower leaves appear petioled and have red streaks. Closer to the peduncle, the leaves are smaller.
- Examples of all varieties of this type of weed can be found here.
- Mary white is a prime example of a broadleaf weed with serrated leaves. The leaves of this plant are triangular or diamond-shaped, up to 10 cm in length, white on the underside.
Method 3 of 3: Recognizing tree weeds
- 1 Find out the lifespan of the weed. Most tree weeds are perennials. This means that they have been growing for over two years. Many of them shed their leaves for the winter. As it grows, most tree weeds begin to curl or form complex fruits.
- 2 Pay attention to curly weeds. It is the most common type of tree weed. Such plants spread along the ground or even weave along the fence. Some curly varieties twine around the walls of houses.
- Poison ivy is the most well-known tree weed. It has triple leaves on a woody stem and grows throughout the United States. Poison ivy also has a complex inflorescence up to 7.5 cm in length with yellowish-white or greenish-white flowers, blooms from May to July. This plant is toxic and must be fought as it damages the skin. Wear gloves and long sleeves when handling poison ivy.

- Bindweed is another example of tree weeds. This flowering climbing plant spreads rapidly in warm climates. The bindweed grows in flower beds and must be separated from other flowers with solid objects, otherwise it will take over the entire area. The flowering period of the bindweed begins in mid-summer and ends in autumn. This plant blooms for two to three months. Each flower blooms once in the morning and blooms for only one day, hence the name - Morning Glory.

- Poison ivy is the most well-known tree weed. It has triple leaves on a woody stem and grows throughout the United States. Poison ivy also has a complex inflorescence up to 7.5 cm in length with yellowish-white or greenish-white flowers, blooms from May to July. This plant is toxic and must be fought as it damages the skin. Wear gloves and long sleeves when handling poison ivy.
 3 Pay attention to woody shoots. One of the easiest ways to recognize a tree weed is to track its rate of reproduction. Tree weeds are colonizing plants by nature and displace all surrounding vegetation. If you notice multiple debris that spreads rapidly across the ground in early spring or summer, this is most likely a tree weed.
3 Pay attention to woody shoots. One of the easiest ways to recognize a tree weed is to track its rate of reproduction. Tree weeds are colonizing plants by nature and displace all surrounding vegetation. If you notice multiple debris that spreads rapidly across the ground in early spring or summer, this is most likely a tree weed.
Tips
- Use the Weed Identification Tool on [1] to find out which weed you are dealing with and how to eradicate it. Pick a state and search for weed traits.
- Broadleaf weeds are the most common weed in the United States.
- If your garden has dandelions, purslane, bamboo, kudzu, white gauze, Sakhalin mountaineer, watercress, and red clover, use these plants for cooking.
- Mulch the soil with a layer of leaves, straw, or commercially available mulch at least 5 cm thick. This will prevent many weeds from growing due to the lack of light needed for them to grow. Cover the ground with a layer of newspaper and apply mulch for extra protection.
What do you need
- Gardening scissors
- Gardening Gloves
- Long-sleeve shirt
- Corn glutin
- Hoe
- Garbage bags
- Pre-emergence herbicide
- Newspapers
- Shovel



