Author:
Robert Simon
Date Of Creation:
20 June 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
To calculate the area of a triangle, you need to know its altitude. If the subject has not given these metrics, you can still easily find the high way based on what you know! This article will show you two different ways to find the height of a triangle, based on the information you have in the problem.
Steps
Method 1 of 3: Use base and area to find height
Repeat the formula for the area of a triangle. To find the area of a triangle, we have the formula A = 1 / 2bh.
- A = the area of the triangle
- b = length of the base of the triangle
- H = the height from the bottom edge

Look at the triangle and identify the variables you already know. In this case, you have an area to assign to the quantity's value A. You also know the side length; assign that value to the quantity "'b'". If you don't have both the area and length of an edge, you'll have to use a different method.- Any side of the triangle can become the base, depending on how you draw it. To see this, just imagine rotating the triangle in many directions until the side of a known length is at the base.
- For example, if the area of a triangle is 20 and one side is 4, we have: A = 20 and b = 4.

Plug your numbers into the expression A = 1 / 2bh and do the math. First, multiply (b) by 1/2, then divide the area (A) by the product you just found. The result of this calculation will be the height of the triangle!- In this example, we have: 20 = 1/2 (4) h
- 20 = 2 hours
- 10 = h
Method 2 of 3: Find the height of an equilateral triangle
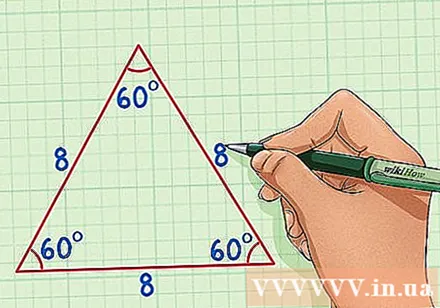
Recall the properties of an equilateral triangle. An equilateral triangle has three equal sides and three equal angles to 60 degrees. If you divide this triangle in half, you will get two identical right triangles.- In this example, we will find the height of an equilateral triangle with side length 8.
Recall the Pythagorean Theorem. According to the Pythagorean theorem, any right triangle has two right-angled sides a, b and hypotenuse c then: a + b = c. We can use this theorem to find the altitude of the equilateral triangle!
Draw a line that divides an equilateral triangle, and then assign the values a, b, and c in the picture. Hypotenuse c will be equal to the side length of the equilateral triangle, meanwhile, the side side a will be 1/2 the length of the side of the equilateral triangle and the side b is the height of the triangle we're looking for.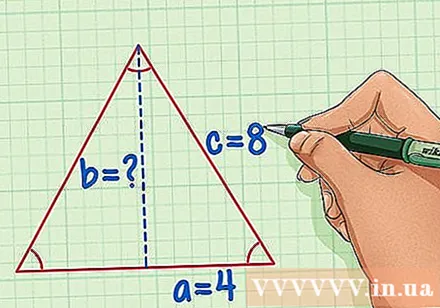
- Returning to the example of an equilateral triangle with side 8, we have c = 8 and a = 4.
Replace these values with the Pythagorean Theorem and calculate b. First, we squared c and a by multiplying each number by itself. Then, subtract c from a.
- 4 + b = 8
- 16 + b = 64
- b = 48
Calculate the square root of b to find the height of the triangle! Use the calculator's square root function to find the square root of b. The result is the height of the equilateral triangle!
- b = √48 = 6.93
Method 3 of 3: Find the altitude with corners and edges
Determine what values you have. We can calculate the height of a triangle in the following cases: if you have an angle and an edge; if you have a bottom edge, the side edge and the corner are between the two sides; if you have all three sides. Let's call the sides of the triangle a, b, c and the angles A, B, C.
- If you have all three sides, you can use Heron formula and the formula for the area of the triangle.
- If there are two sides and an angle, you can use the formula to calculate the area of a triangle with two corners and an edge. A = 1/2ab (sin C).
Apply Heron formula if you have three sides of the triangle. This formula has two parts. First you have to find the variable p, that is, the half-perimeter of the triangle. We have the formula: p = (a + b + c) / 2.
- For a triangle with three sides a = 4, b = 3 and c = 5, the half-circumference p = (4 + 3 + 5) / 2. = (12) / 2. We have p = 6.
- Next, you apply the second part of the Heron formula, which is the area A = √ (p (p-a) (p-b) (p-c)). Replace A in the equation with the equivalent expression: 1 / 2bh (or 1 / 2ah or 1 / 2ch) from the formula for area.
- Perform math to find h. In this example, we have 1/2 (3) h = √ ((6 (6-4) (6-3) (6-5)) .Then 3 / 2h = √ ((6 (2) ( 3) (1)) Continuing to calculate, we get 3 / 2h = √36. Using a calculator to calculate the square root, the expression becomes 3 / 2h = 6. So, by using side b as the base, We find that the height of this triangle is 4.
Use the formula for area with two sides and one angle if the problem tells you the lengths of one side and one angle. Plug the area into the formula with the equivalent expression: 1 / 2bh. You will have 1/2bh = 1/2ab (sin C). Simplifying the expression by eliminating the same variables, we get h = a (sin C).
- Solve the problem with the variables you have. For example, for a = 3, C = 40 degrees, the expression becomes: h = 3 (sin 40). Use a calculator to find out the answer. In this example, h after rounding will be 1.928.