Author:
Louise Ward
Date Of Creation:
11 February 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
A hexagon is a polygon with six faces and six corners. Each hexagon has six faces and six equal angles and consists of six equilateral triangles. There are many ways to calculate the area of a hexagon regardless of whether it's a hexagon or an irregular hexagon. If you want to know how to calculate the area of a hexagon, just follow these steps.
Steps
Method 1 of 4: Calculate the area of a regular hexagon knowing the length of one side
Write down the formula for the area of a hexagon knowing the side lengths. Since a hexagon is composed of six equilateral triangles, its formula for area is derived from the formula for the area of an equilateral triangle. The formula for calculating the area of a hexagon is Area = (3√3 s) / 2 Inside S is the length of one side.
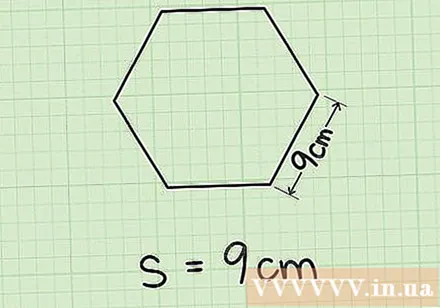
Determine the length of one side. If you already know the length of an edge, simply write it down; in this case, the side length is 9 cm. If you don't know the length of the side but know the circumference or the median line (the height of the perpendicular segment down from the center of the hexagon to one side), you can still find the side length of the hexagon. Here's how to do it:- If you know the circumference, simply divide it by 6 to get the side length. For example, if the circumference is 54 cm, divide it by 6 to get 9 cm, which is the side length.
- If you only know the median, you can find the side lengths by inserting the median value in the formula a = x√3 then multiply your answer by two. The reason is that the median line is the x√3 edge of the 30-60-90 triangle that it creates. For example, if the median is 10√3, then x is 10 and the side length is 10 * 2, or 20.
- If you know the circumference, simply divide it by 6 to get the side length. For example, if the circumference is 54 cm, divide it by 6 to get 9 cm, which is the side length.

Plug the side length value into the formula. Since you know that the length of one side of the triangle is 9, just replace 9 in the original formula. The results are as follows: Area = (3√3 x 9) / 2.
Shorten your answer. Find the value of the equation and write your answer with numbers. Since you're talking area, you have to leave your answer in square. Here's how to do it:
- (3√3 x 9) / 2 =
- (3√3 x 81) / 2 =
- (243√3)/2 =
- 420.8/2 =
- 210.4 cm
Method 2 of 4: Calculate the area of a regular hexagon when knowing the midway

Write down the formula for the area of a regular hexagon when you know the middle. The formula is simple Area = 1/2 x circumference x middle.
Write down the middle length. Assume that the median is 5√3 cm.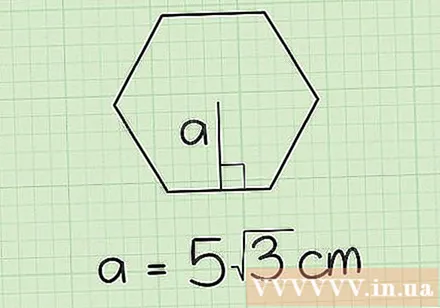
Use the middle to find the perimeter. Since the median is perpendicular to the side of the hexagon, it forms a 30-60-90 triangular face. Triangular faces 30-60-90 have the ratio of xx√3-2x, where the short side length opposite 30 degrees is represented by x, the length of the side facing the angle of 60 degrees is x√3, and the hypotenuse is 2x.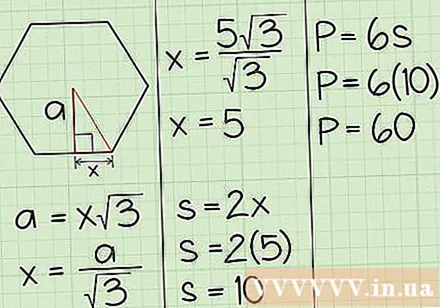
- Middle is the edge represented by x√3. Therefore, replace the median length into the formula a = x√3 and solve the equation. For example, if the median length is 5√3, replace it in the formula and get 5√3 cm = x√3, or x = 5 cm.
- By solving the equation for x, you have calculated the length of the short side of the triangle as 5. Since it is half the length of one side of the hexagon, multiply it by 2 to get the length of one side. 5 cm x 2 = 10cm.
- Now that you know the length of one side is 10, simply multiply it by 6 to find the perimeter of the hexagon. 10 cm x 6 = 60 cm
Substitute all known numbers into the formula. The hardest part is finding the perimeter. Now all you have to do is plug the median and perimeter values into your formula and solve the equation: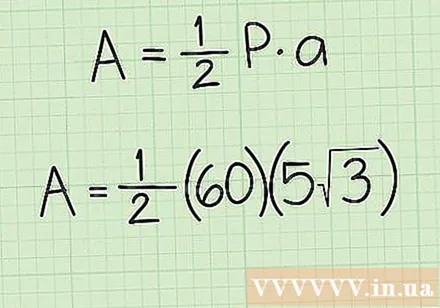
- Area = 1/2 x circumference x middle
- Area = 1/2 x 60 cm x 5√3 cm
Shorten your answer. Simplify the expression until you remove the radical sign from the equation. Remember to use square units in the final result.
- 1/2 x 60 cm x 5√3 cm =
- 30 x 5√3 cm =
- 150√3 cm =
- 259.8 cm
Method 3 of 4: Calculate the area of an irregular hexagon when knowing vertices
List the x and y coordinates of all vertices. If you know the vertices of the hexagons, the first thing you need to do is create a chart with two columns and seven rows. Each row will contain the names of six points (Point A, Point B, Point C, etc.) and each column will record the x and y coordinates of those points. Record the x and y coordinates of Point A to the right of point A, the x and y coordinates of Point B to the right of Point B, and so on. Record the coordinates of the first point at the bottom of the list. Suppose you have the following points, in the format (x, y):
- A: (4, 10)
- B: (9, 7)
- C: (11, 2)
- D: (2, 2)
- E: (1, 5)
- F: (4, 7)
- A (repeat): (4, 10)
Multiply the x coordinate of each point by the y coordinate of the next point. Record the results on the right side of the chart. Then, add up the results.
- 4 x 7 = 28
- 9 x 2 = 18
- 11 x 2 = 22
- 2 x 5 = 10
- 1 x 7 = 7
- 4 x 10 = 40
- 28 + 18 + 22 + 10 + 7 + 40 = 125
Multiply the y coordinate of each point by the x coordinate of the next point. After multiplying all of these coordinates, add up the results.
- 10 x 9 = 90
- 7 x 11 = 77
- 2 x 2 = 4
- 2 x 1 = 2
- 5 x 4 = 20
- 7 x 4 = 28
- 90 + 77 + 4 + 2 + 20 + 28 = 221
Subtract the sum of the first group of coordinates by the sum of the second group of coordinates. Just subtract 125 for 221. 125-221 = -96. Now, take the absolute value of the above result: 96. The area can only be positive.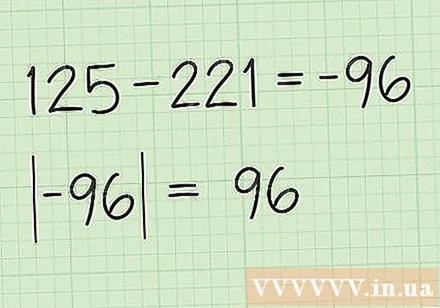
Divide the above signal by two. Just divide 96 by 2 and you'll get the area of the hexagon. 96/2 = 48. Don't forget to write your answer in square units. The final answer is 48 square units. advertisement
Method 4 of 4: Other methods of calculating the area of an irregular hexagon
Find the area of a hexagon with a triangle defect. If your regular hexagon has one or more triangles missing, then the first thing you need to do is find the area of the entire hexagon as if it were complete. Then simply find the area of the empty or "missing" triangle, and subtract the total area of the figure by the area of the missing part. The result will be the remaining area of the irregular hexagon.
- For example, if you calculate that the area of the hexagon is 60 cm and the area of the missing triangle is 10 cm, simply subtract the total area of the hexagon by the area of the missing triangle: 60 cm - 10 cm = 50 cm.
- If you know the missing hexagon is exactly a triangle, you can also calculate the area of the hexagon by multiplying the total area by 5/6, since this hexagon makes up 5 of the 6 triangles of it. If it's missing two triangles, you can multiply the total area by 4/6 (2/3), and so on.
Divide the irregular hexagons into triangles. You can see that the irregular hexagon is actually composed of four triangles of different shapes. To find the area of the entire hexagon, you need to find the area of each individual triangle and then add them up. There are many ways to find the area of a triangle depending on what information you have.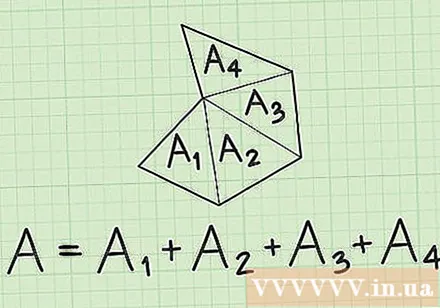
Find other shapes in irregular hexagons. If you can't divide the hexagon into a few triangles, see if you can divide it into other shapes - be it a triangle, rectangle, and / or square. Once you've identified the shapes, just find their area and add them together to get the area of the entire hexagon.
- There is an irregular hexagon type consisting of two parallelograms. To calculate the area of a parallelogram, simply multiply the base by their height, just like calculating the area of a rectangle, and then add the results together.