Author:
Peter Berry
Date Of Creation:
13 February 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
The wasps family includes thousands of species present around the world, most of which are predators. The most common species of wasps are the wasp, wasp, and wasp. You can observe the color, shape and place of the bees to identify different species of bees. Knowing some of the basic differences between wasps and honey bees will help you distinguish them. This article does not cover the parasitoid wasps, a very small insect that is best left to an expert to identify.
Steps
Method 1 of 3: Identify wasps by body features
Look at the yellow and black on the bee body. You can identify the golden bees and European paper wasps by the yellow and black stripes on their stomachs. The cicada killer is a ground-digging bee that looks similar to a yellow bee but is larger and rounder. You can identify the European wasps by the tail with yellow and black stripes, the chest is reddish brown. The mud bee is also black and yellow.
- Note that mud bees can also be black or bluish black, similar to spider bees, including tarantula hawks.

Identify wasps by other colors. The paper hornet native to North America is golden brown with red and yellow markings. You can distinguish this bees from bald wasps with black and white stripes and a white face. In addition, the wasp is brown-orange, yellow and black with iridescent blue wings.- Contrary to the name, the velvet ant is actually a black, wingless and hairy wasp with patches of magenta, yellow, orange or white.

Estimate the size of wasps. Yellow bees are about 1.3 cm long. Contrary to this are the larger species of bees, including bald wasps about 2-3 cm long, European wasps around 2-3.5 cm, and significantly larger bees were spider bees ( tarantula hawks) about 2.5 - 6.3 cm long and cicada killer about 3.8 cm long. Paper hornets and mud bees are usually about 1.3-2 cm in length.
Observe the bee's body shape. Except for a few rather rare - like the European wasps - the wasps can normally be identified by their smooth, hairless body and slim waist. Learn how to recognize yellow bees through its small waistline and tapered and pointed belly. Observe the paper hornets' characteristic long legs and diamond-shaped waist. In addition, you may notice that the mud bee has a very small waist, long and thin body. advertisement
Method 2 of 3: Identify where wasps are located
Find the paper nests. Unlike honey bees, which often build waxy hives, yellow bees, wasps and paper wasps build nests of paper and saliva. Look for the nest of golden bees in low spaces and niches, look for beehives painted on trees, bushes and under key roofs, for paper plow's nests below the roof overhang. Note that the paper hornet's honeycomb will open at the top.
Identify mud bee nests. Look for long cylindrical beehives built on walls, in attics, corridors, garden furniture, and under unused equipment. You may also observe that the mud hives appear more lumpy. Look for mud bees around fountains, puddles, lakeside banks and wet lawns, where they often return mud to build nests.
Find the cave of the bee digging. You can find caves the size of a pencil in well-drained, sandy soil. There are usually very few plants growing around the burrows of the wasps. Note that they often burrow in areas with direct sunlight. advertisement
Method 3 of 3: Differentiate wasps from wasps and honey bees
Distinguish the body characteristics of wasps and honey bees. Look at the insect's waist. Note that wasps have "waist", while the waist of honey bees is as big as the rest of their body. Next, look at the hair on the bee. As mentioned above, most wasps are hairless, while honey bees often have more feathers to help them transport pollen. Finally, look at the insect's length - wasps are typically longer than most honey bees.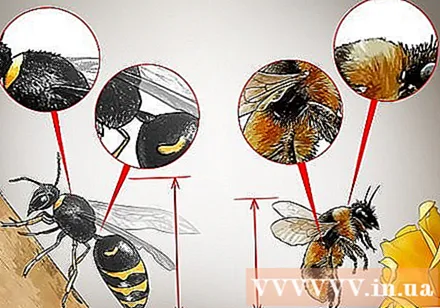
Check the color of the bee. In general, you'll find wasps and honey bees share the same primary colors. However, it should be noted that wasps have more colors and "pattern" more prominent than honey bees. Pay attention to the hornets' vibrant colors, as opposed to the faint colors of honey bees.
Watch what they eat. The wasps often eat other insects. Yellow bees are scavengers, and you may find them eating or searching for human food or trash. In contrast to wasps, honey bees live on pollen and nectar. advertisement