Author:
Monica Porter
Date Of Creation:
13 March 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
A miscarriage occurs when a pregnancy ends before the 20th week of pregnancy. Miscarriage is a fairly common phenomenon, affecting 25% of all known pregnancies. To find out if you have a miscarriage, you need to assess your risk factors and monitor for symptoms like heavy vaginal bleeding and pain. However, a miscarriage can be difficult to determine as some of the same symptoms occur in healthy pregnancies where medical confirmation is needed. Always follow your doctor's advice in case a miscarriage is suspected.
Steps
Part 1 of 2: Causes and symptoms of a miscarriage
Understand the cause of a miscarriage. Miscarriages most commonly occur during the first few weeks of pregnancy. Chromosomal abnormalities are the most common cause of miscarriage, and in most cases there is nothing a woman can do to prevent it. The risk of miscarriage decreases after 30 weeks of pregnancy. By then, most of the chromosomal abnormalities had already miscarried. The following factors pose a risk of miscarriage:
- Older women have a higher risk. Women 35 to 45 years of age have a 20-30% risk of miscarriage, and the risk of miscarriage is 50% for women over 45.
- Women with serious chronic medical conditions such as diabetes or lupus have a higher risk of miscarriage.
- Abnormalities in the uterus, such as scar tissue, can lead to a miscarriage.
- Smoking, drug and alcohol use can cause miscarriages.
- Women who are overweight or underweight are at increased risk of miscarriage.
- Women who have had a miscarriage more than once have a higher risk of miscarriage.
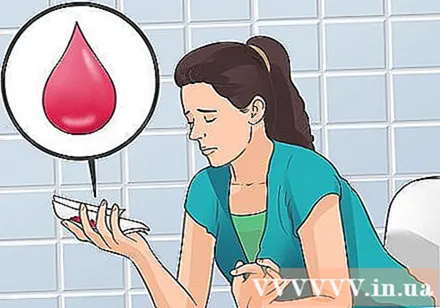
Watch out for vaginal bleeding. Heavy vaginal bleeding is the most common sign of a miscarriage. Vaginal bleeding is often accompanied by spasms similar to those seen during menstruation. Vaginal blood is usually brown or bright red.- Bleeding, even relative bleeding, can occur in healthy pregnancies. Heavy bleeding and clumping can be a sign of a miscarriage. Tell your doctor if you experience bleeding during pregnancy.
- According to the American Association of Obstetricians, 50-75% of miscarriages belong to biochemistry, which means that the miscarriage occurs immediately after conception. Usually, women do not realize they are pregnant and assume that bleeding is normal menstruation. The blood may flow more than usual and the spasm may be worse.
Check for vaginal mucus. Symptoms of a miscarriage include pink-white mucus, which may include fetal tissue. If the vaginal discharge looks like tissue is clumping or solids, it may be a sign that a miscarriage is happening or has occurred; You need to see a doctor right away.- Most pregnant women experience increased discharge of a colorless or milky vaginal discharge called Leukorrhea. Don't worry if you have a lot of these secretions.
- You can also mistake the leaking urine for vaginal discharge. Incontinence usually occurs during healthy pregnancy.

Pay attention to pain and soreness. Pregnancy is often accompanied by soreness. During a miscarriage, pain is usually localized in the lower back and can be mild or severe. If you have lower back pain, you should notify your doctor immediately.- Stinging or aching pain in the abdomen, pelvis and back is usually caused by the body making adjustments to the fetus's growth. If the pain is severe, persistent, or painful in episodes, you may have a miscarriage, especially if you haven't had bleeding.
- There can also be a "real spasm" phenomenon during a miscarriage. Contractions happen 15-20 minutes apart and are often very painful.
Analysis of symptoms of pregnancy. Pregnancy often comes with a variety of symptoms, all due to an increase in hormone levels in the body. If these symptoms subside, it could be a sign that a miscarriage has occurred, and that hormone levels return to the way they were before pregnancy.
- If you have had a miscarriage, you may notice less morning sickness, less swelling and pain in your breasts, and less feeling of pregnancy. In healthy pregnancies, these early symptoms usually subside on their own by 13 weeks, also when the risk of miscarriage decreases.
- Symptoms and severity vary with pregnancy. Call your doctor if you notice a sudden change in the 13th week of your pregnancy.
See your doctor to be sure. Go to your doctor's office, emergency room or hospital maternity ward for a sure answer. Even if you have all of the above symptoms, the fetus is still able to survive, depending on the type of miscarriage.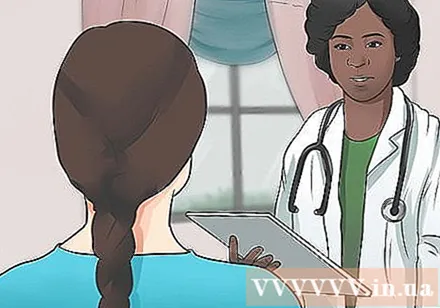
- Based on the gestational age, the doctor will order a blood test, a pelvic exam or an ultrasound to diagnose the viability of the fetus.
- If you experience heavy bleeding early in pregnancy, your doctor may not tell you to go to the clinic unless you want to.
Part 2 of 2: Treatment of miscarriage
Know the different types of miscarriage. The effects of a miscarriage vary slightly from woman to woman. In some cases, the fetal tissue is rapidly eliminated from the body, in others the miscarriage may take longer and be more difficult. The following are the different types of miscarriage and their impact on the body: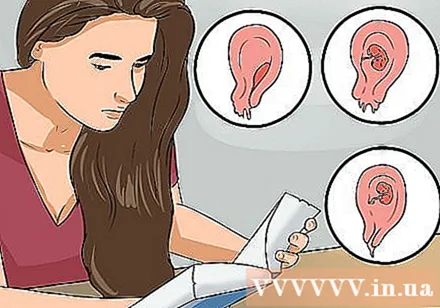
- Threatened miscarriage: The cervix remains closed. It is possible that the bleeding and other symptoms of a miscarriage will stop, and the pregnancy will continue to progress normally.
- Inevitable miscarriage: Heavy bleeding and the cervix begins to open. At this point the pregnant woman will not have a chance to continue the pregnancy.
- Incomplete miscarriage: Some pregnancy tissue leaves the body, but some remains inside. Sometimes surgery is needed to remove remaining fetal tissue.
- Complete miscarriage: All fetal tissue is eliminated from the body.
- Stillbirth: Even though the pregnancy has ended, the fetal tissue remains in the body. Sometimes fetal tissue comes out on its own, but sometimes treatment is needed to remove it.
- Ectopic pregnancy: Technically this is not one form of miscarriage, but it is another form of miscarriage. Instead of implantation in the uterus, a fertilized egg implants in the fallopian tubes or ovaries, where the fetus cannot develop.
Call your doctor if the bleeding goes away on its own. If the bleeding a lot but eventually subsides, and it occurs early in pregnancy, you may need to go to the hospital. Many women do not like to go to the hospital and want to rest at home. You may not need to go to the hospital if the bleeding stops within 10 days or 2 weeks.
- If you experience pain or cramps, your doctor can recommend methods to make you more comfortable with a miscarriage.
- If you want to know for sure you've had a miscarriage, you can go for an ultrasound.
Seek treatment if the bleeding doesn't stop. If you have heavy bleeding and other symptoms, and you're not sure if this is a complete or incomplete miscarriage, your doctor may decide on the following options:
- Waiting and watching: You will wait and see if the remaining tissue comes out and the bleeding stops on its own.
- Medical treatment: Medical treatment is needed to remove remaining tissue from the body. You need a short hospital stay and could bleed up to three weeks after that.
- Surgical treatment: Your doctor will perform cervical dilatation and curettage, also known as D&C, to remove any leftover tissue. The bleeding time will stop faster than with medical treatments. You may be given medicine to help slow the bleeding.
Keep track of symptoms. If the bleeding continues after the time your doctor thinks it will slow down and go away, you need to seek treatment promptly. If other symptoms such as fever or cold are accompanying you, see your doctor or hospital immediately.
Consider finding a grief counselor. Miscarriage at any stage can cause emotional trauma. You will have a grieving time with loss, and talking to a counselor can help. Ask your doctor for a grief counselor or make an appointment with a therapist near you.
- It may take a while to feel relieved; This depends on each person. Give yourself time to grieve.
- When you are preparing to get pregnant again, talk with your doctor about making an appointment with a doctor who specializes in high-risk pregnancies. This is necessary for women who have had two or more miscarriages.
Advice
- In the majority of cases, impending miscarriage cannot be prevented, nor is it due to the mother's health or lifestyle. Pregnant women should take prenatal vitamins, avoid using drugs, tobacco and alcohol, but even women with a good sense of maternal health care cannot completely avoid miscarriage.
Warning
- If you are more than 20 weeks pregnant and experience heavy bleeding or cramps, go to the hospital right away. Pregnancy terminated after this point is called stillbirth.