Author:
Laura McKinney
Date Of Creation:
8 August 2021
Update Date:
20 June 2024

Content
While interesting and adorable, caterpillars are capable of stinging people. A moth sting can cause minor symptoms or lead to a dangerous allergic reaction. To treat a caterpillar sting, clean the sting, treat your symptoms and consult a medical professional if the symptoms are severe. That way, it's easier to recover from a moth bite.
Steps
Part 1 of 3: Cleaning the sting
Get rid of moths without touching them. If the caterpillar is still on your skin, use pliers, tweezers, or thick gloves to remove the worm. Absolutely do not touch the caterpillar with bare hands because it may be stung again.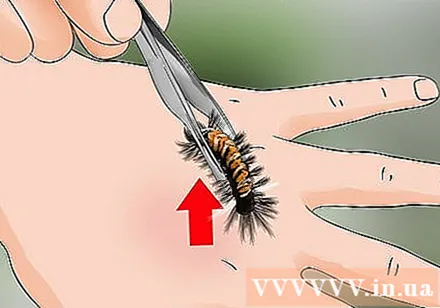
- Moth bites are caused by small, pointed, hair-like spines that pierce the skin. Avoid touching the caterpillar with bare hands.

Use tape to remove spikes from your skin. Use Scotch tape, cloth tape or something similar. Place the tape on the sting, then quickly remove it. The adhesive tape will stick to the poisonous hairs or thorns that remain on the skin. This step is very important to minimize the symptoms of the sting and prevent further stings.- The sticky part of the bandage can be used to remove hairs or spikes.
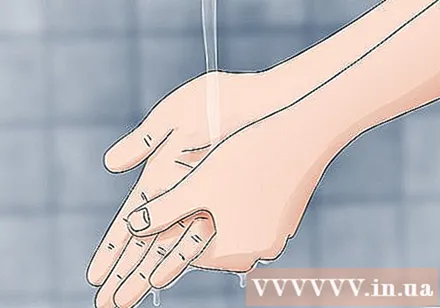
Clean the sting. Use soap and warm water to clean the sting. Besides, you should wash the surrounding skin. Finally, be sure to wash your hands well, just in case you have come into contact with poison or caterpillars. advertisement
Part 2 of 3: Symptomatic treatment

Apply a mixture of baking soda and water. Mix 1 teaspoon of baking soda with 1-2 teaspoons of warm water. Rub a generous amount of the mixture onto the sting, then let it sit for a few minutes. The baking soda mixture helps relieve itching and other unpleasant symptoms. Reapply the mixture every few hours.
Use hydrocortisone cream. If baking soda doesn't help relieve your symptoms, rinse the mixture off, then apply plenty of hydrocortisone cream to the sting and let it sit. It may take about an hour for the cream to soothe the sting. Reapply the cream according to the instructions on the product packaging.
Use an antihistamine cream. If hydrocortisone cream is also not working, rinse it off and then apply plenty of antihistamine cream to the sting. Wait about 30 minutes to see if there is a difference. In many cases, antihistamine creams have been shown to be ineffective in relieving symptoms caused by caterpillars, but you may find the cream to work for you.
Use a cold compress. After applying baking soda or cream, you can apply cold compresses to the sting. Place a bag of frozen ice cubes or vegetables on the sting every 10-20 minutes. Continue using cold compresses every 1-2 hours. advertisement
Part 3 of 3: Medical treatment
Watch for signs of severe symptoms. Moth bites can cause a variety of symptoms. Depending on the type of moth and the type of allergic reaction, symptoms can be very mild or very severe. Common symptoms include:
- Itching and contact dermatitis, blisters, skin blisters, small, painful red bumps
- Conjunctivitis if caterpillar hair gets into the eye
- Rash and hives
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea and vomiting
- Hemorrhage and kidney failure can occur after exposure to caterpillars Lonomia South America
See your doctor if symptoms get worse. If you develop blisters, large streaks or a widespread rash, see your doctor right away. This step is very important because some people may experience a deadly, potentially allergic reaction from a caterpillar bite.
Call the Poison Control Center for more information. Call a Poison Control Center (eg Bach Mai Hospital Poison Center) as soon as possible if you have any questions about how to treat a caterpillar bite. An antitoxin specialist will answer the phone and give you recommendations on how to treat the sting.
Get a tetanus shot. If you haven't had a tetanus shot in the past 5-10 years, you should get one shot within 72 hours of being stung by a moth. The wound or bite can become infected and infected. advertisement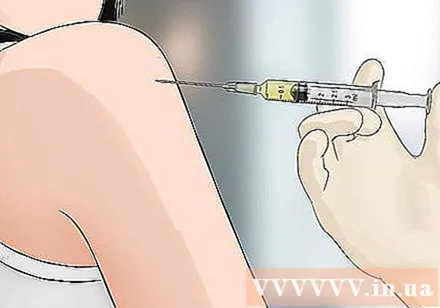
Advice
- Do not touch or handle fluffy or brightly colored moths.
- Don't scratch the sting.
- Take note of the geographic area where you were burned, and make sure not to let children or pets go to the area. Warn authorities if the number of moths increases abnormally.
- Unless professionally trained, wild insects should not be kept as pets. If you want to raise moths into moths or moths, you can order eggs and breeding equipment at a number of special websites and brochures.
- Never play with strange animals or insects. They can be dangerous.
Warning
- Do not let pets or young children play with strange creatures, even small creatures such as caterpillars. Teach young children especially to stay away from bright, spiky moths because their bright colors and sharp bristles are often signs of natural toxicity.
- Even if a caterpillar doesn't bite, it can harm your garden. Look for white, spider web-like nests in the tree; The evergreen moth cocoon and the Gypsy Moth moth are parasitic and can kill plants.
What you need
- Adhesive tape (cloth tape, Scotch tape, transparent tape) or face mask are commercially available
- A mixture of baking soda (bicarbonate salt) and water
- Ice pack or frozen food (anything cold or frozen will do)
- Clean water and soap
- Analgesic
- Cold pack
- Hydrocortisone cream
- Antihistamone cream