Author:
Laura McKinney
Date Of Creation:
5 August 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
Regardless of the cause or at any age, female hair loss often makes women sad, discouraged, or even depressed. The most common type of hair loss among women is called female hair loss (FPHL). There are many factors that cause hair loss, including pathology, genetics, certain medications, use of harsh measures when handling hair or scalp, and hormonal changes. Hair loss treatments are effective in some cases, but surgical intervention or medication may be needed to restore hair growth.
Steps
Part 1 of 3: Determining the cause of hair loss
See your doctor to rule out the medical condition. Many conditions can temporarily or permanently affect normal hair growth. Some of these include:
- Iron deficiency anemia.
- Thyroid diseases.
- Deficiencies in zinc, vitamin D, and possibly B vitamins.
- Changes in levels of the hormones androgens, testosterone and estrogen.
- Autoimmune disease.
- Severe psychological stress.
- Physical injury.
- Scalp infections and skin disorders.
- Diabetes.
- Lupus disease.
- Hair pulling syndrome.
- Severe weight loss or major change in diet.
- Severe infections accompanied by high fever.
Cure. Many medical conditions can lead to temporary or permanent hair loss.- With the help of doctors, and possibly health care professionals in many specialized disciplines, the treatment of underlying medical conditions can solve the problem of hair loss.
- Your doctor needs to know as much information as possible about your patient's hair loss, so be prepared to discuss this in depth. You need a description of when hair loss began, the major life events that occurred before hair loss, the measures you have taken to deal with the problem, and how hair loss affects chimps. how is your god
- If an illness related to hair loss is found, treatment may involve doctors from specialties such as endocrinology, dermatology, nutrition, and psychiatry.
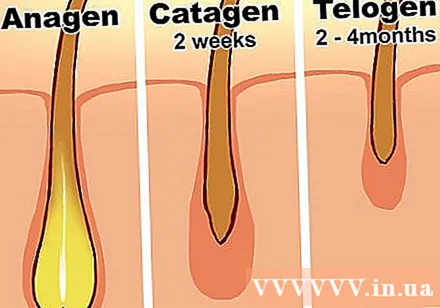
Understand hair growth. Many of the conditions listed above affect one of the three stages of hair growth.- The growth phase (anagen phase) is the period when hair grows strongly. Approximately 85% of our hair is in a growth phase at any time.
- The catagen phase is a short period of about 2 weeks that allows the hair follicles to regenerate. Hair will stop growing during this phase.
- The telogen phase is considered the resting period of the hair, lasting about 2-4 months. Hair will fall out at the end of this period. Most of us normally lose about 100 hairs a day due to the hair fibers are in the stage of degeneration.
- Many medical conditions cause the hair to turn into an early degenerative stage. This can cause you to lose about 300 strands of hair per day. The medical term for a lot of hair loss during this period is telogen effluvium.
Know that telogen effluvium is usually temporary. Many diseases that cause hair to degenerate are treatable.- Since hair remains in the degenerative stage for many months, hair loss is unlikely to occur immediately after the event that causes the problem. These events can include physical trauma or other traumatic factors.
Ask your doctor to check the medication you are taking. Many medications can cause temporary hair loss.
- Do not change medications for any reason. Talk to your doctor about your concerns. If you feel that a certain medication is the cause of your hair loss, your doctor can help you adjust your dosage or prescribe equivalent medicine instead.
- Some drugs known to cause hair loss include lithium, warfarin, heparin, and levodopa.
- Drugs classified as beta blockers can also cause hair loss. Drugs in this class include propranolol, atenolol, and metoprolol.
- Amphetamine derivatives can cause hair loss. Some examples of amphetamine drugs are amphetamine salts, commonly known by the trade names Adderall®, dextroamphetamine, and lisdexamfetamine.
- Chemotherapy drugs such as doxorubicin often cause sudden and complete hair loss as well as radiation therapy to treat cancer.
Consider the role of genes. Having a family member experiencing hair loss is also a factor that suggests you are at risk as well.
- Common forms of genetic hair loss include: hair loss at an earlier age than average, hair loss more than usual, and thinning hair in women.
- The rate of hair loss due to genes in women is about 21%.
Be aware of hair loss caused by hormonal changes. Some changes in hormone levels result in temporary hair loss, while others cause gradual but permanent hair growth.
- A prime example of temporary hair loss is hair loss caused by pregnancy and childbirth.
- The onset of menopause is often accompanied by significant hair loss. Menopause is a natural aging process, and the associated change in hormone levels results in thinning hair.
- Some women who experience hair loss earlier than average age or with a lot of hair loss have been tested for changes in levels of male sex hormones, including androgens like testosterone. The results of these studies have not determined the role these hormones play in female hair loss.
- Your doctor can help determine the role of hormones by conducting blood tests. In some cases, a severe hormonal imbalance has the potential for successful treatment.
Evaluation of diet. Sudden changes in diet and sudden weight loss can contribute to hair loss.
- In the majority of cases, nutritional or diet-related hair loss often falls into the form of telogen effluvium alopecia, which is temporary.
- Talk to your doctor or a registered dietitian. Your doctor can perform physical exams, and tests can provide evidence of vitamin or nutrient deficiencies.
- A registered dietitian can help you incorporate foods into your regular diet to correct vitamin and nutrient deficiencies identified by your doctor, thereby addressing hair loss problems.
Be aware of changes that happen with age. The natural aging process causes the hair follicles to gradually decrease in size.
- The reduced hair follicle size means the scalp area that supports the roots is also smaller, but the number of hair follicles is essentially unchanged.
- Although the size of the hair follicle is reduced, hair grows and grows as usual, with only smaller hair strands, resulting in thinner hair, as opposed to baldness.
- Studies conducted in women with female hair loss show that the aging process includes thinning hair. This usually starts around 40 years old and affects most women 70 years and older.
Part 2 of 3: Treatment of hair loss with medication
Try products containing minoxidil. Many brand name products contain minoxidil. The most familiar product has a trade name Rogaine.®
- Monixodil 2% and 5% concentrations are sold without a prescription. The products come in a topical solution or foam. Women are recommended to use a 2% concentration product.
- The product instructions recommend using a solution or foam no more than 2 times per day.
- The results showed that minoxidil helped to grow hair in 20-25% of women, but was effective in stopping hair loss in most women who tried the product.
- Once you have started using the product, it is essential to maintain its long-term use for continued good results. The product loses its effectiveness when you stop taking the drug.
- The most common side effects of minoxidil include scalp irritation and unwanted hair growth in areas of the face and hands. Sometimes the absorption of the drug into the body can cause a rapid heartbeat.
Ask your doctor about finasteride. Finasteride is one of two drugs approved for the treatment of hair loss, but is only used for men.
- Finasteride has been shown to improve hair growth and slow hair loss in men, but studies on the use of finasteride in women are continuing.
- Ongoing studies on the use of finasteride in women have initially shown promising results. Your doctor may consider taking finasteride or a similar substance depending on the person's behavior, other medications you are taking, and other medical conditions, if any.
- The use of finasteride in women has not been approved by the FDA (US Food and Drug Administration), so your doctor may prescribe this medication for you in what is known as a "non-prescription. label ”.
- Women of childbearing age should not even touch finasteride-containing pills due to the risk of birth defects in their infants.
- The most common side effects of finasteride when used in men are decreased libido and libido. Other side effects include dizziness or dizziness when getting up while sitting or resting, chills, and sweating.
Ask your doctor about other medications you can take. Some medicines have side effects that help with hair growth. In some cases, the use of these drugs by women to treat hair loss may be approved.
- These drugs are not FDA approved for hair loss treatment. Some drugs that may be effective include spironolactone, cimetidine, others in the same class as finasteride, birth control pills, and ketoconazole.
- These drugs or their analogues may be effective in the treatment of hair loss and have other therapeutic effects approved by the FDA. Discuss the use of these medications with your doctor. Your doctor will consider other medications you are taking and your current health condition when treating hair loss.
Part 3 of 3: Explore other treatment options
Seek advice from the hair transplant surgeon. The hair transplant process involves removing healthy hair follicles from other areas of oily skin with thick hair growth and transplanting to areas of thinning or most visible hair loss.
- This procedure involves taking hundreds of hair follicles and transplanting them into needed areas.
- Although hair transplant surgery is quite expensive, the results are very good and lasting.
Ask your doctor about low intensity light therapy (LLLT), discovered in the 1960s and shown to be effective in assisting with wound healing.
- Many products on the market are approved by the FDA to use low intensity light technology. Although the documented results of this form of treatment do not meet the scientific standards for efficacy, many patients have actually found positive results.
- The mechanism of action of LLLT is not well understood, but studies have shown a change in the cell level, improving hair growth in many people. However, much more remains to be done to develop more effective products.
Take vitamins and nutrients. Talk to a registered dietitian to develop a diet rich in vitamins or nutrients that you may not be consuming regularly or your doctor has identified as deficient. Take vitamins and supplements to supplement the dosage in addition to the foods in your diet.
- Use of products containing omega 3 and omega 6. Omega 3 and omega 6 products are not approved for the treatment of hair loss. However, a study conducted in women with female hair loss has shown good results when taking products containing omega 3 and omega 6 for 6 months.
- Another study showed positive results when women participated in taking products containing B vitamins and L-cysteine for a period of 4 months.
- There is a lot of scientific evidence that taking vitamins to treat hair loss is significantly effective in the case of nutritional disorders.
Ask your doctor about melatonin. A study conducted in a small group of women has shown good results in treating hair loss using melatonin.
- The women participating in this study showed an increase in the hair growth phase and an improvement in thinning hair as a result.
- The women in the study above were applied melatonin 0.1% solution to the scalp for 6 months.
- This is the first medical trial to take melatonin in this form. More research is still needed to determine possible risks in using melatonin in this manner.
Consider using lavender essential oil topically. One small study showed positive results using lavender.
- There is little evidence proving that herbal remedies are effective in treating hair loss, however a preliminary study has shown good results when using lavender in combination with other herbal essential oils. in the treatment of certain types of hair loss.
- Do not use lavender essential oil orally. Skin and scalp irritation can occur from the use of lavender essential oil.
Advice
- Cell-mediated therapy is a very promising research area. Although this form of treatment has not been implemented, studies are underway.
- Two other promising areas are being studied including hair follicle cell transplants and hair growth stimulators injection.
- While there is currently no known way to prevent genetic and aging female hair loss, you can take steps to prevent hair loss caused by damage. Avoid harsh methods while handling your hair, such as regular curling, applying harsh chemicals to your scalp, and styling that requires tightening. Sometimes these processes damage the scalp or hair follicles and cannot be repaired.