Author:
Lewis Jackson
Date Of Creation:
11 May 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
A computer's basic input / output system (BIOS) is where one or more groups of commands are stored on the motherboard firmware. This is the software that runs first when you start your computer to control functions such as the CD drive, mouse and keyboard. This article will guide you to properly update your BIOS. Each computer has a different BIOS manufacturer and uses different keyboard shortcuts to access it, but the update method is generally the same.
Steps
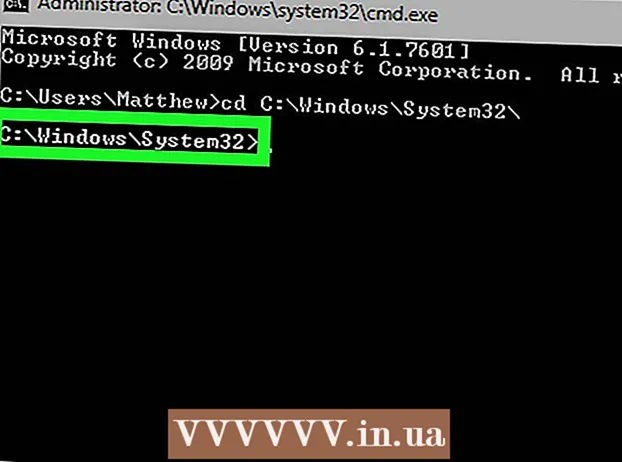
Determine current BIOS version. You can visit the manufacturer's website to find this information.
- Open the System Information app on Windows. On Windows Vista and Windows 7 operating systems, enter msinfo32 go to the search bar (or the Run dialog box in Windows XP), then click System Summary (System Summary).
- The BIOS version will be displayed below the processor speed of your computer. Rewrite the version number and date (if applicable).

Traceability of the system. This is an important step in locating and downloading the correct updated BIOS version.- Do you buy pre-assembled computers, or buy components and assemble them? If it is a pre-assembled machine, for example a Dell computer, check their website; if you did assemble it yourself, visit the motherboard manufacturer's website. Search for "Drivers and Downloads".
- Be sure to download the correct BIOS update for your computer. Downloading another line's update by mistake will damage your computer.
- Remember to download the Read me and other documents and read them! This is no time to ignore these documents. There are many important precautions you should learn before updating your BIOS, and ignoring them can have serious consequences.

Backup current BIOS first! If you use Windows BIOS update software or another operating system, please first backup the BIOS image.Most BIOS update programs come with this function ("Save" or "Backup"), and it is recommended that you take the backup step. Visit the manufacturer's website for recommendations on how to back up the BIOS.
Prepare the system. The biggest danger in BIOS update process is power failure. You cannot control the utility, but you "can" control its influences.- If you update the laptop, fully charge the battery, and keep charging. In the event of a power failure, the machine will continue to run because of the battery.
- If you are updating your desktop computer, it is recommended that you use an uninterruptible power supply (UPS). Like laptop batteries, UPS will keep everything working even during power outages.
Proceed to update. Run the downloaded installation program or the ..exe file to update the BIOS.
- If the software asks you to use the floppy, use the 1.44MB 3.5 "format. Some of the imaging floppy disks with the file" autoexec.bat "will automatically run the BIOS update. Others only contain the software. update, updated BIOS image and may contain a 'readme' file with instructions. If instructions are not available, but there are at least two files ("A06_123.bin" and "awflash.exe"), please Follow these steps: Enter the command "awflash A06_123.bin" and press Enter. This will update the software and locate the file A06_123.bin to update the BIOS.
- Compare the two versions. Most BIOS update software will read the current BIOS image and identify that version, then compare it with the downloaded version. If the current version of the system is older it will perform the update. The user interface of the BIOS software is often different, but there are menu buttons or basic options like "Write", "Update", or "Confirm" to proceed. BIOS update.
Restart the computer. Once completed, a lot of update programs will automatically restart your computer. Some programs will ask for your permission, while others will issue a startup warning before performing updates. A few programs require you to manually restart your computer. To do this manually:
- Completely shut down the computer by pressing the power button or using the operating system command.
- Turn off the master power switch on the back of the computer, if available.
- Wait a minute.
- Turn on master power switch, if available.
- Start the computer.
Clear the current BIOS setting if recommended. This is not always necessary, it depends on the features that have been changed between the current version and the update. Please follow these steps:
- As soon as the machine is turned on, boot the BIOS utilities. On most systems, you can do this by pressing the Delete key for the first 2-10 seconds of starting up. Some other operating systems may use the keys F2, F10, CTRL, Enter, and so on.
- If you do not understand the key combination sequence to access the BIOS, observe the screen to see if the computer has instructions.
- To clear the BIOS settings, look for the "Restore Defaults" or "Load Fail-Safe Defaults". They can be on the main page of the BIOS utility or on the last page of the menu. Use the arrows to navigate, and follow the instructions on the screen. Once done, save the settings and exit the BIOS utility.
BIOS configuration. You can change the settings if you want. If you have never changed BIOS settings before then don't give it a try. Most computers will only function normally when using the default BIOS settings. advertisement
Advice
- BIOS updates roll out to fix existing bugs, add new standard and hardware support, or add functionality. Read the BIOS update's introductory notes or other documentation to find out what upgrades your computer will get.
- The BIOS provides the operating system with hardware information, and is designed to support within a specific range of components. The BIOS is often the EEPROM, also known as the Lossless Memory when the power is turned off, is programmed with the "firmware" and is capable of storing small amounts of information critical to the user's settings. Parts of the BIOS are usually soldered to the motherboard, making it inconvenient for the user. Other components are inserted in a blank drive, making it easier to replace.
- If the BIOS firmware fails and you have a similar motherboard with the same CPU socket and the same type of BIOS chip, you can restore the BIOS if you are willing to risk another BIOS chip. Please refer to the articles on recovering corrupted BIOS Firmware.
- If the system is still working fine, you should update the BIOS only when you are ready to quit the current version (for a long time) in case the update fails. System manufacturers often take care of system repairs and motherboards fail to update the BIOS, as long as they are under warranty. However, this process is quite time consuming and involves many of the following sequences:
- Contact technical support and verify BIOS update issues.
- Get a Product Return Warranty (RMA) or a similar tracking number.
- Transfer the product to the manufacturer.
- Waiting for approval (inspection) and repair or replacement.
- Wait for the product to return for refund.
Warning
- Do not update the BIOS unless you are sure what you are doing. Because if you do not follow the manufacturer's instructions correctly you can damage the BIOS.
- Make sure the power is stable when updating the BIOS. Any major fluctuations or power outages occurring during this process can damage the BIOS. Therefore, do not turn off the computer or restart the machine while updating the BIOS. If updating the BIOS from a bootable operating system, disable all unnecessary applications and run in the background.
- Download BIOS update software from a trusted source. Downloading BIOS from another source, not the manufacturer's website, is dangerous. For example, the developer version of the same software BIOS for one manufacturer's motherboard may not work with another manufacturer's motherboard. Using the incorrect BIOS version can "damage" the machine, so it is necessary to replace or reprogram the BIOS by the manufacturer and rebuild the non-bootable computer until the process is completed.
- This process is very susceptible so any variation from the power supply could result in a firmware failure. You need to be very careful to go through the process safely.