Author:
Louise Ward
Date Of Creation:
10 February 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
The TB skin test is also known as the Mantoux test, a test that measures the immune system's response to bacteria that cause TB. After two days, the test results will be explained by your doctor, but if you want to learn how to read them, this article will guide you through the process. However, you should keep in mind that the test results should be read by a qualified person. Although you can read it yourself, the results still need to be recorded by a medical professional to ensure an appropriate treatment thereafter.
Steps
Part 1 of 2: Reading Test Results
See your doctor for a test. Pure-extracted protein will be injected into your forearm. At the injection site, a small blister about 6-10 mm will appear, but will disappear within a few hours.

Leave the injection site open. Do not cover the injection site for 48 to 72 hours. You can wash your hands and dry them gently.- You should not scratch or rub the injection site, as this will cause the area to be reddened and give false results. If it is itchy, you can use a cold washcloth to apply it to your hands.

Re-examination. The test should be read within 48-72 hours. If you return to the doctor after 72 hours, the test will no longer be effective and must be repeated.
Find and mark the bump. Use your fingertips to find the bump on the forearm. It is a hard, thick, and distinctly raised halo. When you find it, mark the edges with the widest distance from the bump, only this part is important to your test results, and areas of mild redness or swelling should not taken into account.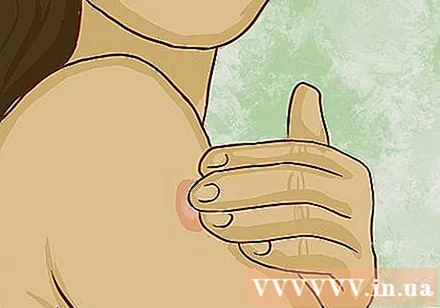
- The swelling is not always visible, so do a fingertip scan.

Measure stiff bumps. If you have a red rash on the test area, it does not mean you have tuberculosis, as it will be necessary to measure a hard bump to know the results. Use the millimeter ruler to measure it horizontally. Place the ruler so that the zero line is at the left edge of the bump, where you marked it, and then measure the distance from the mark on the right edge.- If the marking is between two divisions, use a ruler with a smaller unit.
Part 2 of 2: Interpretation of test results
Identify groups at high risk. If the bump size is 5 mm or more, the tester is in the susceptible group to tuberculosis. This group includes people who:
- HIV disease
- liver transplant
- weakened immune system for many reasons
- have recently been in contact with someone with tuberculosis
- Chest x-ray examination of past TB
- end stage renal failure
Identify the medium-risk group. If the bump size is 10 mm or more, the tester is in the moderate risk group for TB. This group includes people who:
- recently immigrated from a country with common TB
- injecting drugs
- work in health care settings, prisons, nursing homes, or similar settings
- are at risk of getting TB from conditions like diabetes, leukemia, or being underweight
- Children under 4 years old
- Children or teenagers who have contact with an adult who is at high risk of TB
Where the bump is large. If the bump size is 15 mm or more, the person is not in the high and medium risk group. This group may include everyone, regardless of people at high risk of TB. In addition, even if a slight blister appears, the test result is positive.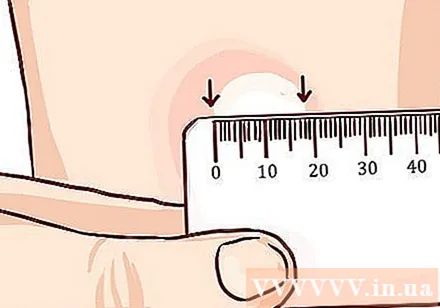
The results were negative. If there is no firm swelling the result is negative. If you experience only slight swelling or redness, but no stiffness, the result is also negative.
- Even if you believe your test result is negative, you still need to go back to your doctor for a professional checkup.
Advice
- Do more tests as directed by your doctor if the result is positive or near positive.
Warning
- False positive or negative results can occur in TB tests. If you have questions about the results, consult your doctor as soon as possible.
- Within 72 hours, a TB test should be checked by a qualified, trained and trained person to read the most accurate results.