Author:
Charles Brown
Date Of Creation:
4 February 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- To step
- Method 1 of 4: Moisturize your skin
- Method 2 of 4: Nutrition to keep your skin healthy
- Method 3 of 4: Treating a sunburn
- Method 4 of 4: Treating a rash through a tanning bed
- Warning
Tanning can improve your mood, produce vitamin D and give you the healthy glow you desire. However, doctors recommend avoiding sunbathing as it causes premature skin aging and increases the risk of cancer. When you start tanning, you can help keep your tan longer and keep your skin as healthy as possible by providing your skin with moisture and the right nutrition after you sunbathe.
To step
Method 1 of 4: Moisturize your skin
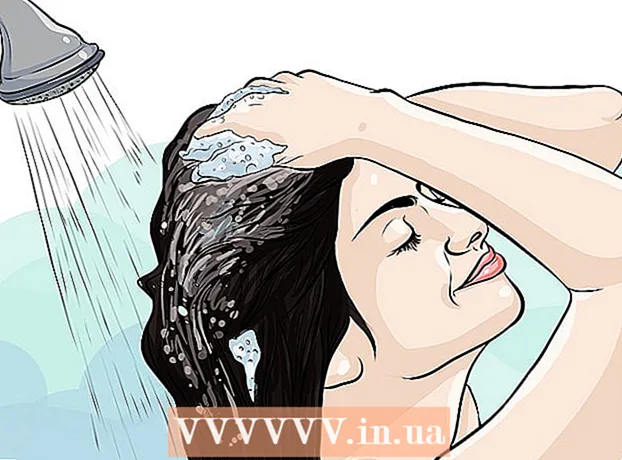
 Consider skipping a shower. This is not about being able to "wash away" a tan. The melanin production stimulated by UVA light is not stopped by a shower. However, studies show that showering and then applying a moisturizer doesn't moisturize your skin as effectively as applying a moisturizer alone. If you do shower, do the following:
Consider skipping a shower. This is not about being able to "wash away" a tan. The melanin production stimulated by UVA light is not stopped by a shower. However, studies show that showering and then applying a moisturizer doesn't moisturize your skin as effectively as applying a moisturizer alone. If you do shower, do the following: - Take a cold or warm shower, not a hot one.
- Limit your shower time. Showering too long removes oil from the skin.
- Avoid soap, or apply it only to the "smelly" areas, such as your groin, armpits, and feet. Soap will dry out your skin.
- Pat yourself dry to leave some moisture on your skin.
 Use a product with hyaluronic acid. Hyaluronic Acid is a naturally produced chemical that helps bind and retain water molecules on the skin. Cosmetics containing hyaluronic acid have been shown to improve skin hydration and elasticity. Massage such a cream into your skin before applying a moisturizing cream. If you shower, apply the cream immediately afterwards.
Use a product with hyaluronic acid. Hyaluronic Acid is a naturally produced chemical that helps bind and retain water molecules on the skin. Cosmetics containing hyaluronic acid have been shown to improve skin hydration and elasticity. Massage such a cream into your skin before applying a moisturizing cream. If you shower, apply the cream immediately afterwards.  Apply a moisturizer. Moisturizers help replace the thin layer of lipids that protect your skin from water loss. A moisturizer will do, but consider using a moisturizer with liposomes containing vitamin A for healthy skin. If you do shower, apply a moisturizer immediately afterward.
Apply a moisturizer. Moisturizers help replace the thin layer of lipids that protect your skin from water loss. A moisturizer will do, but consider using a moisturizer with liposomes containing vitamin A for healthy skin. If you do shower, apply a moisturizer immediately afterward. - Use a non-comedogenic (won't clog pores) moisturizer if you're prone to breakouts.
Method 2 of 4: Nutrition to keep your skin healthy
 Drinking water. The skin is made up of cells and all cells need water. If your skin doesn't get enough, it will become dry, tight and flaky. One of the main reasons skin ages is because it loses its ability to retain moisture. Drinking at least eight glasses of water (240 ml each) a day usually ensures that your skin gets enough water, but since tanning can dry you out, you will need to drink even more water on those days when you are tanning.
Drinking water. The skin is made up of cells and all cells need water. If your skin doesn't get enough, it will become dry, tight and flaky. One of the main reasons skin ages is because it loses its ability to retain moisture. Drinking at least eight glasses of water (240 ml each) a day usually ensures that your skin gets enough water, but since tanning can dry you out, you will need to drink even more water on those days when you are tanning.  Eat dark chocolate. Cocoa moisturizes your skin and contains flavonols, a powerful type of antioxidant. Antioxidants limit the damage from free radicals that form when the skin is exposed to ultraviolet light.
Eat dark chocolate. Cocoa moisturizes your skin and contains flavonols, a powerful type of antioxidant. Antioxidants limit the damage from free radicals that form when the skin is exposed to ultraviolet light.  Eat fruits with a high content of polyphenols. Grapes, apples, pears, cherries and berries are all high in polyphenols, which have both antioxidant and anti-cancer properties that help protect your skin from the UV rays of the sun and tanning beds.
Eat fruits with a high content of polyphenols. Grapes, apples, pears, cherries and berries are all high in polyphenols, which have both antioxidant and anti-cancer properties that help protect your skin from the UV rays of the sun and tanning beds.  Drink or eat pomegranate juice. Pomegranates contain flavonoids that have been shown to have a wide variety of health benefits, including an antioxidant that protects the skin and helps prevent cancer.
Drink or eat pomegranate juice. Pomegranates contain flavonoids that have been shown to have a wide variety of health benefits, including an antioxidant that protects the skin and helps prevent cancer.  Cook pasta with tomato sauce or order pizza. Tomatoes contain lycopene, a chemical that has been shown to help protect the skin from damage from ultraviolet rays. Tomato paste contains the most, meaning tomato sauces or even pizza can be a rich source.
Cook pasta with tomato sauce or order pizza. Tomatoes contain lycopene, a chemical that has been shown to help protect the skin from damage from ultraviolet rays. Tomato paste contains the most, meaning tomato sauces or even pizza can be a rich source.  Chew on sunflower seeds. They are packed with Vitamin E, a powerful antioxidant that helps protect the skin from damage caused by UV light.
Chew on sunflower seeds. They are packed with Vitamin E, a powerful antioxidant that helps protect the skin from damage caused by UV light.  Drink green tea. It contains polyphenols with antioxidant and anti-cancer properties, helping to protect your skin from the damage caused by UV rays.
Drink green tea. It contains polyphenols with antioxidant and anti-cancer properties, helping to protect your skin from the damage caused by UV rays.
Method 3 of 4: Treating a sunburn
 Keep in mind that your skin can burn if you have been tanning for too long. Tanning beds, like the sun, emit UVA rays, and if you are exposed to them for too long, it can burn your skin. The lighter your skin is, the faster you will burn.
Keep in mind that your skin can burn if you have been tanning for too long. Tanning beds, like the sun, emit UVA rays, and if you are exposed to them for too long, it can burn your skin. The lighter your skin is, the faster you will burn.  Treat the burned skin as soon as you notice it. The sooner you start the treatment, the less damage will occur. If your skin feels stinging or itchy, or if your skin feels pink or reddish, then you should start treating it immediately.
Treat the burned skin as soon as you notice it. The sooner you start the treatment, the less damage will occur. If your skin feels stinging or itchy, or if your skin feels pink or reddish, then you should start treating it immediately.  Drink lots of water. Burnt skin sucks water into your skin, dehydrating the rest of your body. You should always drink extra water after tanning, but if you are burned, you should drink as much water as you can (without overdoing it) to promote healing and maintain your hydration levels.
Drink lots of water. Burnt skin sucks water into your skin, dehydrating the rest of your body. You should always drink extra water after tanning, but if you are burned, you should drink as much water as you can (without overdoing it) to promote healing and maintain your hydration levels.  Place a cold, damp towel on your skin or take a cold shower or bath. Do this for 10 or 15 minutes, several times a day, to take the heat out of your skin and provide relief. If you take a bath or shower, pat yourself dry and leave some water on your skin. Apply a moisturizer immediately.
Place a cold, damp towel on your skin or take a cold shower or bath. Do this for 10 or 15 minutes, several times a day, to take the heat out of your skin and provide relief. If you take a bath or shower, pat yourself dry and leave some water on your skin. Apply a moisturizer immediately.  Use moisturizer regularly. Moisturizers with aloe vera are particularly soothing to burnt skin, and you can also consider products with vitamins C and E, which can help limit the damage to your skin. Avoid moisturizers that contain petroleum, as they trap heat in your skin.Also avoid benzocaine and lidocaine, which can irritate your skin. Do not apply moisturizer to blistered skin.
Use moisturizer regularly. Moisturizers with aloe vera are particularly soothing to burnt skin, and you can also consider products with vitamins C and E, which can help limit the damage to your skin. Avoid moisturizers that contain petroleum, as they trap heat in your skin.Also avoid benzocaine and lidocaine, which can irritate your skin. Do not apply moisturizer to blistered skin.  Apply hydrocortisone cream to particularly uncomfortable areas. You can buy hydrocortisone over the counter and it will help relieve painful burning or itching. Do not apply hydrocortisone to blistered skin.
Apply hydrocortisone cream to particularly uncomfortable areas. You can buy hydrocortisone over the counter and it will help relieve painful burning or itching. Do not apply hydrocortisone to blistered skin.  Take an over-the-counter anti-inflammatory. Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) and naproxen (Aleve, Naprosyn) can reduce pain as well as swelling, preventing long-term skin damage. Adults can also use aspirin, but never give it to children, as it can result in sudden acute brain and liver damage.
Take an over-the-counter anti-inflammatory. Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) and naproxen (Aleve, Naprosyn) can reduce pain as well as swelling, preventing long-term skin damage. Adults can also use aspirin, but never give it to children, as it can result in sudden acute brain and liver damage.  Leave blisters alone or cover them with dry bandages. Blisters indicate that you have a second degree burn. Do not put moisturizers on or squeeze them, as this will only make your sunburn worse. Leave them alone until they heal, or consider covering them with a dry bandage to prevent them from rubbing against your clothes.
Leave blisters alone or cover them with dry bandages. Blisters indicate that you have a second degree burn. Do not put moisturizers on or squeeze them, as this will only make your sunburn worse. Leave them alone until they heal, or consider covering them with a dry bandage to prevent them from rubbing against your clothes.  Protect yourself when you go out. The last thing you want to do is expose your burnt skin to even more sun. Keep your time outside to a minimum, and when you go out, cover all burned areas of your body with clothing made of tightly woven fabric (if you hold them up to a bright light, no light should shine through). If you have a burn on your face, apply a moisturizer that also works as a sunscreen.
Protect yourself when you go out. The last thing you want to do is expose your burnt skin to even more sun. Keep your time outside to a minimum, and when you go out, cover all burned areas of your body with clothing made of tightly woven fabric (if you hold them up to a bright light, no light should shine through). If you have a burn on your face, apply a moisturizer that also works as a sunscreen.
Method 4 of 4: Treating a rash through a tanning bed
 Know the causes of a tanning bed rash. Your skin may feel itchy or bumpy after using a tanning bed for several reasons:
Know the causes of a tanning bed rash. Your skin may feel itchy or bumpy after using a tanning bed for several reasons: - Your skin has overheated from the tanning bed.
- You have a light allergy, which causes red bumps on the skin after exposure to UV light.
- You have a reaction to the products that are used to clean the tanning bed.
- You can be sensitive to the tanning lotion you use while tanning.
- A medication you take (such as birth control, acne medication, or even Advil) makes your skin more sensitive to UV light.
- You may have a skin infection from a poorly cleaned couch.
 See your doctor if your rash is warm and sensitive or accompanied by a fever. Poorly cleaned tanning beds can contain bacteria and viruses that lead to infections that require medical treatment.
See your doctor if your rash is warm and sensitive or accompanied by a fever. Poorly cleaned tanning beds can contain bacteria and viruses that lead to infections that require medical treatment.  Talk to your doctor about the medications you are taking. You want to make sure the medications you are taking do not make your skin more sensitive to light before returning to the tanning salon.
Talk to your doctor about the medications you are taking. You want to make sure the medications you are taking do not make your skin more sensitive to light before returning to the tanning salon.  Stop tanning and see if the rash goes away. If not, see your doctor. If it does, you can go back to the tanning salon and try to diagnose and prevent the cause of the rash.
Stop tanning and see if the rash goes away. If not, see your doctor. If it does, you can go back to the tanning salon and try to diagnose and prevent the cause of the rash. - Apply a small, diluted amount of the cleanser used by the tanning salon to a small area of your skin to see if it develops a rash.
- Then try tanning without the tanning-accelerating lotion to see if this is the cause.
- Finally, try to tan for a shorter time so there is no chance of a heat rash.
 If the rash persists, consider other tanning methods. If you continue to develop a rash after tanning, you may have a light allergy (polymorphic light eruption) or even a UV allergy. Talk to your doctor and make sure to wear sunscreen when out and about. Stop using tanning beds and consider using tanning lotions if you want to look bronzed.
If the rash persists, consider other tanning methods. If you continue to develop a rash after tanning, you may have a light allergy (polymorphic light eruption) or even a UV allergy. Talk to your doctor and make sure to wear sunscreen when out and about. Stop using tanning beds and consider using tanning lotions if you want to look bronzed.
Warning
- Tanning ages your skin, produces wrinkles, and increases the risk of skin cancer. The Dutch Cancer Society recommends that you do not use tanning beds.