Author:
Tamara Smith
Date Of Creation:
27 January 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024
Content
- To step
- Method 1 of 4: Focus on the most important trigonometric concepts
- Method 2 of 4: Insight into the applications of trigonometry
- Method 3 of 4: Study ahead
- Method 4 of 4: Take notes during class
- Tips
- Warnings
Trigonometry is the branch of mathematics that deals with triangles and cycles. Trigonometric functions are used to describe the properties of angles, the relationships in a triangle, and the graphs of a recurring cycle. Learning trigonometry helps you understand, visualize and map out these relationships and cycles. If you combine self-study with attention during class, you can begin to understand basic trigonometric concepts and probably start noticing cycles in the world around you.
To step
Method 1 of 4: Focus on the most important trigonometric concepts
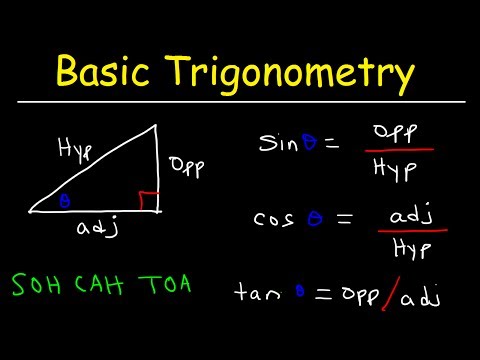
 Define the parts of a triangle. At its core, trigonometry is the study of relationships in triangles. A triangle has three sides and three corners. By definition, the sum of the angles of a triangle is 180 degrees. You must become familiar with triangles and triangle terminology to be able to master trigonometry properly. Some commonly used terms:
Define the parts of a triangle. At its core, trigonometry is the study of relationships in triangles. A triangle has three sides and three corners. By definition, the sum of the angles of a triangle is 180 degrees. You must become familiar with triangles and triangle terminology to be able to master trigonometry properly. Some commonly used terms: - Hypotenuse - the longest side of a triangle.
- Obtuse angle - an angle greater than 90 degrees.
- Sharp angle - an angle of less than 90 degrees.
 Learn how to make the unit circle. With a unit circle, you can scale a triangle so that its hypotenuse is equal to one. This is useful because it can express trigonometric functions, such as the sine and cosine, in terms of percentages. Once you understand the unit circle, you can use the trigonometric values of a given angle to answer questions about triangles with those angles.
Learn how to make the unit circle. With a unit circle, you can scale a triangle so that its hypotenuse is equal to one. This is useful because it can express trigonometric functions, such as the sine and cosine, in terms of percentages. Once you understand the unit circle, you can use the trigonometric values of a given angle to answer questions about triangles with those angles. - Example 1: The sine of 30 degrees is 0.50. This means that the opposite side of a 30 degree angle is exactly half the length of the hypotenuse.
- Example 2: This relationship can be used to find the length of the hypotenuse in a triangle at an angle of 30 degrees with an opposite side of 18 cm. The sloping side would then be equal to 36 cm.
 Know the trigonometric functions. There are six functions essential to understanding trigonometry. Together they define the relationships within a triangle and allow you to understand the unique properties of a triangle. These six functions are:
Know the trigonometric functions. There are six functions essential to understanding trigonometry. Together they define the relationships within a triangle and allow you to understand the unique properties of a triangle. These six functions are: - Sine (Sin)
- Cosine (Cos)
- Tangent (Tan)
- Cutting line (Sec)
- Cosecans (Csc)
- Cotangent (Cot)
- Understanding relationships. One of the most important things to understand about trigonometry functions is that all functions are interrelated. While the values for the sine, cosine, tangent, etc. all have their own application, they are the most useful because of the relationships that exist between them. The unit circle limits these relationships so that they are easy to understand. Once you understand the unit circle, you can use the relationships it describes to model other problems.
Method 2 of 4: Insight into the applications of trigonometry
- Understand the basic scientific uses of trigonometry. In addition to studying trigonometric functions just because they enjoy trigonometry, these properties are also practically applied by mathematicians and scientists. Trigonometry can be used to find values for angles or line segments. You can also describe cyclic properties by drawing them as trigonometric functions.
- For example, the movement of a coil spring can be described as a sine wave by means of a graph.
- Think about the cycles in nature. Sometimes people struggle to understand abstract concepts in math or science. When you realize that these concepts are present in the world around you, you can often view them in a new light. Look for things in your life that occur in cycles and try to relate them to trigonometry.
- The moon has a predictable cycle of about 29.5 days.
- Visualize studying natural cycles. Once you realize that nature is full of cycles, you can start thinking about how you could study those cycles. Think about what a graph of these cycles would look like. From the graph you can then derive an equation for describing the phenomenon you have observed. This gives meaning to trigonometric functions so that you can better understand their usefulness.
- Consider measuring the tide on a particular beach. During high tide it reaches a certain height, and then drops to low tide. From low tide the water rises again on the beach, until the tide is out again. This cycle would go on indefinitely and can be graphed as a trigonometric function, such as a cosine.
Method 3 of 4: Study ahead
- Read the chapter. Trigonometric concepts are difficult for many people to understand right away. Reading the chapter prior to class treatment will help you become more familiar with the material. The more you see the material, the better you will be able to relate the different concepts in trigonometry to each other.
- This allows you to go through all the concepts you are having difficulty with prior to class.
- Keep a notebook. Browsing a book is better than nothing, but it's not the thorough kind of reading that will teach you trigonometry. Keep detailed notes for each chapter you are reading. Remember that trigonometry is cumulative and the concepts build on each other so your notes from previous chapters can help you understand the next chapter.
- Also write down any questions you want to ask your teacher.
- Do exercises from the book. Some people can visualize trigonometry well, but you will also have to do problems. To make sure you really understand the material, you can do a few exercises before class. This way you know exactly what you need help with during class, if you have trouble with something.
- Most books contain the answers for a number of exercises at the back. In this way you can check your work.
- Bring your study materials to class. Bringing your notes and practice exercises to class will give you something to refer to. This refreshes the things you already understand and points out concepts that need to be better explained. Get answers to all the questions you wrote down while reading.
Method 4 of 4: Take notes during class
- Make notes in the same script. Trigonometric concepts are all related to each other. It's best to keep all of your notes in one place so that you can refer to them at a later time. Designate a specific notebook or folder for your study of trigonometry.
- You can also make your practice assignments here.
- Make trigonometry your priority in class. Don't use your class time to chat or catch up on homework from another class. During the trigonometry lesson it is important to fully focus on the lesson and the assignments. Write down the notes that the teacher wrote on the board or that are marked as important.
- Stay involved in the classroom. Volunteer to solve problems on the board or share your answers to practice problems. Ask questions if you haven't heard something. Keep communication as open and flexible as possible, as far as your teacher allows. This will make learning and having fun with trigonometry a lot easier.
- If your teacher prefers to teach without interruptions, ask your questions before or after class.Remember, it's the teacher's job to help you learn trigonometry, so don't be too shy.
- Then do more practice exercises. Do all the homework you have been given. Homework assignments are good indicators of test questions. Make Sure You Understand Each Problem If you were not given homework, work on the exercises from the book that match the concepts covered in the last lesson.
Tips
- Remember that math is a way of thinking and not just formulas to remember.
- Learn about algebra and geometry.
Warnings
- You cannot learn trigonometry by stamping. You will have to understand the concepts behind it.
- Stamping for a test on trigonometry will practically never work.