Content
- To step
- Method 1 of 3: Identify genital warts
- Method 2 of 3: Treat genital warts with medication
- Method 3 of 3: Consider operations
Genital warts are small, raised skin lesions that can look like the top of a cauliflower. They can occur in both sexes, but men can get the warts on the testicles, penis, thighs and groin. Genital warts are caused by the very common human papilloma virus (HPV), of which more than 100 different types exist. Usually the warts cause no further symptoms, but sometimes the spots can be itchy, hurt or bleed. The most problematic types are HPV 16 and 18, which carry the risk of cancer. The virus is transmitted through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral. You can also get HPV spots in and around the mouth, on the lips, anus, tongue, nose, eyes, and throat. The HPV vaccine is an effective way to prevent this disease. Vaccination of men with the HPV vaccine not only prevents the virus from being passed on to others, but it can also prevent other related diseases and certain cancers.
To step
Method 1 of 3: Identify genital warts
 Assess your risk factors. Certain behaviors increase the risk of infection with HPV. Ask yourself the following questions, as your doctor will likely ask you the same questions when you undergo an examination:
Assess your risk factors. Certain behaviors increase the risk of infection with HPV. Ask yourself the following questions, as your doctor will likely ask you the same questions when you undergo an examination: - How many sexual partners do you have? The more partners, the more likely you are to contract the virus.
- Do you use condoms? This protection reduces the risk of sexually transmitted diseases, including HPV.
- How old are you? Genital warts mainly occur in adolescents, teenagers and young adults.
- Do you have a serious infection or cancer, or are you on medications that weaken your immune system? Infections such as HIV / AIDS reduce the body's ability to fight infections. Blood cancer such as leukemia changes your immune cells so that they work less well. Medicines such as steroids also weaken the immune system over time.
- Have you noticed damaged skin around your genitals? The virus can enter your body through small wounds.
- Do you have an uncircumcised penis? Men who have not had their foreskin removed are more likely to get HPV and are more likely to pass it on to their partners.
 Differentiate your symptoms from other infections or illnesses. You may mistake the warts for other conditions. It is best to make an appointment with your doctor to get the correct diagnosis. Pay attention to the following characteristics so that you can already make the distinction at home.
Differentiate your symptoms from other infections or illnesses. You may mistake the warts for other conditions. It is best to make an appointment with your doctor to get the correct diagnosis. Pay attention to the following characteristics so that you can already make the distinction at home. - HPV warts are flesh-colored wounds. Redder, fluid-filled blisters are more likely to be genital herpes.
- HPV warts do not contain moisture and do not burst. Genital herpes blisters are painful and can open - causing them to become inflamed - and secrete fluid before they heal. An ulcer (an open wound) on your penis can also indicate the first stage of syphilis. Sores from syphilis usually don't hurt.
- While the warts are not always completely painless, pain and itching are usually associated with herpes.
- Other symptoms - such as a red rash on the palms and soles of the feet, white patches in the mouth and on the genitals, hair loss and a sore throat - besides the warts, may be a sign of the second stage of syphilis.
- Multiple small bumps that circle the base of the glans and are flesh-colored, red, yellow, or translucent can indicate a harmless condition called pearly penile papules (PPP). This is considered a normal variety of penis skin and is not contagious.
- There is no dent in HPV warts. A dent on the top of the wart could indicate a viral infection called mollusca contagiosa. Mollusca can also be a sign of HIV infection.
 See your doctor. Ultimately, it is always best to go to the doctor with possible HPV warts. Your doctor can then determine the best treatment method. Typically, HPV warts get better after a few months, and about 90% disappear completely after two years without any form of treatment. Sometimes a doctor won't treat you unless you get more severe symptoms. If you decide not to see a doctor, pay attention to whether:
See your doctor. Ultimately, it is always best to go to the doctor with possible HPV warts. Your doctor can then determine the best treatment method. Typically, HPV warts get better after a few months, and about 90% disappear completely after two years without any form of treatment. Sometimes a doctor won't treat you unless you get more severe symptoms. If you decide not to see a doctor, pay attention to whether: - The warts increase in size
- The warts are increasing in number
- They appear in more places on your body
- You experience other symptoms such as itching, pain and bleeding, hair loss, fever, white patches in the mouth or around the genitals, sore throat or ulcers on the penis. As mentioned earlier, syphilis can also cause warts, so prompt antibiotic treatment is very important. Syphilis can eventually cause neurological problems if left untreated.
- Age and Cancer - HPV is responsible for about 63% of all penile cancer cases. The average age of diagnosis is 68, but you can get it as early as you're 30. If you experience other symptoms such as fatigue, weight loss, blood from the penis, bumps on the penis, a velvety rash, hardened skin on the penis, or foul-smelling discharge, see your doctor as soon as possible.
Method 2 of 3: Treat genital warts with medication
 Do not use over-the-counter products. It is inadvisable to use self-care products around the genitals. The skin in the pubic area is very sensitive and if you apply chemicals without proper knowledge and training, it can lead to serious damage.
Do not use over-the-counter products. It is inadvisable to use self-care products around the genitals. The skin in the pubic area is very sensitive and if you apply chemicals without proper knowledge and training, it can lead to serious damage.  See your doctor. Your doctor can perform a routine examination and examine the rest of your body for warts. The doctor may apply a small amount of trichloroacetic acid to the warts to make them white for better viewing and removal. First, talk to your doctor about the various options.
See your doctor. Your doctor can perform a routine examination and examine the rest of your body for warts. The doctor may apply a small amount of trichloroacetic acid to the warts to make them white for better viewing and removal. First, talk to your doctor about the various options. - The treatment depends on many factors, such as the size of the warts, where they are, previous treatments and whether the warts keep coming back or not.
- Remember that there is no cure for the virus, only the warts can be removed.
 Ask about immune response modifiers. These drugs can stimulate immune proteins in the body to get rid of the warts. There are different types of these drugs, such as:
Ask about immune response modifiers. These drugs can stimulate immune proteins in the body to get rid of the warts. There are different types of these drugs, such as: - Imiquimod - Your doctor can apply a 5% imiquimod cream to the warts using protective gloves and a cotton ball. Then he / she will prescribe the cream to use at home. Apply the cream in the evening before going to sleep with disposable gloves or a cotton ball. Wash the area in the morning (6-10 hours after application) with soap and water to remove it. Do this three times a week for the next 16 weeks.
- Interferon alpha - The doctor injects 3 million IU of interferon at the bottom of each wart. This process should be repeated three times a week for the next three weeks. Larger warts may require multiple injections. The warts disappear after four to eight weeks. If the warts are still not gone after 12 to 16 weeks, the doctor will suggest alternative treatment.
 Ask about cytotoxic drugs. These agents can destroy the warts and prevent them from spreading further. However, they can also damage healthy skin. If you accidentally spill such an agent on healthy skin, remove it immediately with soap and water. Side effects include pain, irritation, redness and itching. Options are:
Ask about cytotoxic drugs. These agents can destroy the warts and prevent them from spreading further. However, they can also damage healthy skin. If you accidentally spill such an agent on healthy skin, remove it immediately with soap and water. Side effects include pain, irritation, redness and itching. Options are: - Podofilox - This is the preferred treatment method for warts smaller than 10 cm². To make sure you are using the correct amount (0.5 ml or 0.5 g), your doctor will first show you how to apply it. Apply it with a cotton swab if you get a liquid, or with your finger if it's a gel. Repeat this twice a day for three days in a row, then stop the treatment for four days. Repeat this process for up to four weeks.
- Trichloroacetic acid (TCA) and bichloroacetic acid (BCA) are both medications that should only be applied by a doctor. Your doctor will apply the acid to the warts with a cotton ball. Your doctor may recommend repeating the treatment weekly for four to six weeks. This is one of the most commonly used treatment methods.
- Podofylline - This is an agent that should only be applied by the doctor to warts smaller than 10cm². Your doctor will apply it sparingly to the warts. after that, the area should air dry and avoid coming into contact with your clothing. The first time, let it sit on the skin for about 30-40 minutes. The following treatments can last from 1 to 4 hours, after which the agent should be removed with soap and water. This treatment should be repeated once a week for six weeks.
- This medicine should not be used during pregnancy or possible pregnancy. Do not let a female partner come into contact with it.
- 5-Fluorouracil - Your doctor will probably apply the first dose himself or provide a detailed explanation. Apply it to the warts with a cotton swab one to three times a week. Don't overuse. Let the cream air dry to prevent it from getting on your clothes. After 3 to 10 hours (as directed by your doctor), wash the area with soap and water to remove it.
- Veregen - Your doctor can prescribe this green tea extract. Apply a thin layer of ointment with your fingers on the warts. Repeat this three times a day for 16 weeks or until the warts are gone. Don't wash it off and avoid sexual contact.
 Research home remedies. There are several home remedies you can try to get rid of warts, although there is no scientific evidence that they work. Naturalists say you can try herbal creams like aloe vera and use vitamin A, C and E supplements. It is advisable to discuss the correct treatment with a natural doctor.
Research home remedies. There are several home remedies you can try to get rid of warts, although there is no scientific evidence that they work. Naturalists say you can try herbal creams like aloe vera and use vitamin A, C and E supplements. It is advisable to discuss the correct treatment with a natural doctor. - The idea behind this treatment method is that you supplement nutrient deficiencies, so that your immune system can better attack the warts. Antioxidants are also often recommended to fight infections.
Method 3 of 3: Consider operations
 Consult your doctor about the possibility of surgery. Your doctor may suggest surgery if you have a lot of warts or if a large area is infected. Your doctor may also recommend this if you have recurring genital warts.
Consult your doctor about the possibility of surgery. Your doctor may suggest surgery if you have a lot of warts or if a large area is infected. Your doctor may also recommend this if you have recurring genital warts.  Ask about cryosurgery. Liquid nitrogen freezes the moisture in the warts, destroying the cells that make them up. The doctor will clean the area with alcohol. Then a piece of foam rubber containing liquid nitrogen is held against the wart until a maximum of 5mm of the surrounding skin is frozen. The skin is then frozen for an additional thirty seconds until it is completely white, followed by a period of thawing during which the skin returns to its normal color. If the pain can be tolerated, the wart will be frozen again.
Ask about cryosurgery. Liquid nitrogen freezes the moisture in the warts, destroying the cells that make them up. The doctor will clean the area with alcohol. Then a piece of foam rubber containing liquid nitrogen is held against the wart until a maximum of 5mm of the surrounding skin is frozen. The skin is then frozen for an additional thirty seconds until it is completely white, followed by a period of thawing during which the skin returns to its normal color. If the pain can be tolerated, the wart will be frozen again. - Within 24 hours, a blister will form on the site of the wart. If necessary, the treatment can be repeated after one or two weeks.
- After two to four treatments within six to twelve weeks, 75-80% of the patients have completely gotten rid of the warts.
- You can also buy sets from the drug store that claim to do the same, but doctors recommend getting it done by an expert.
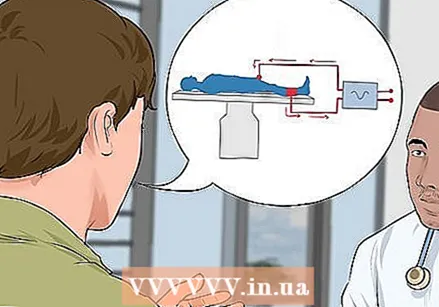 Request information about electrosurgery. The wart is cut away with high-frequency alternating current and a special needle electrode. The doctor first gives a local anesthetic. He / she can also prescribe painkillers for after surgery.
Request information about electrosurgery. The wart is cut away with high-frequency alternating current and a special needle electrode. The doctor first gives a local anesthetic. He / she can also prescribe painkillers for after surgery. - Electrosurgery is very effective for small warts on the penile shaft.
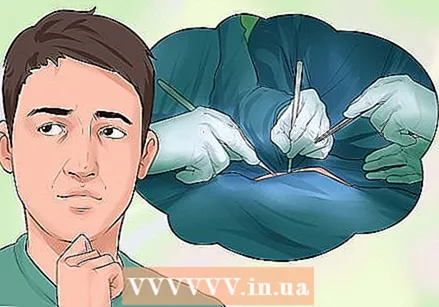 Decide if surgical removal is the right option. The doctor cuts away the warts with a scalpel. If you have few warts, the doctor will first give you a local anesthetic.In more severe cases, a general anesthetic may be chosen. Your doctor will then sew the two healthy pieces of skin back together, depending on the size of the cut wart.
Decide if surgical removal is the right option. The doctor cuts away the warts with a scalpel. If you have few warts, the doctor will first give you a local anesthetic.In more severe cases, a general anesthetic may be chosen. Your doctor will then sew the two healthy pieces of skin back together, depending on the size of the cut wart.  Ask your doctor about laser surgery. This method uses a carbon dioxide laser to vaporize the warts. This can work especially well for warts that keep coming back. It can usually be done on an outpatient basis. The doctor will give a local anesthetic to prevent pain from the laser treatment.
Ask your doctor about laser surgery. This method uses a carbon dioxide laser to vaporize the warts. This can work especially well for warts that keep coming back. It can usually be done on an outpatient basis. The doctor will give a local anesthetic to prevent pain from the laser treatment. - The doctor will probably also prescribe painkillers to use after the treatment, because most patients still experience a fair amount of pain after the operation.
- It is very important not to move when the laser is aimed at the skin, otherwise healthy skin can also be damaged.