Author:
Frank Hunt
Date Of Creation:
13 March 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- To step
- Method 1 of 3: Naturally prevent a fungal infection from getting worse
- Method 2 of 3: Treating a yeast infection with medication
- Method 3 of 3: Understand what a yeast infection is
- Warnings
A yeast infection, also known as Candida, usually develops on the skin, in the mouth, or in the vagina. A fungal infection is caused by several of the bacteria Candida spp.family, of which there are more than 20 different types that you can get infected with. The most common cause of a fungal infection is an overgrowth of Candida albicans. Fungal infections can be very annoying, so it is important to start treatment immediately as soon as you experience symptoms. This form of infection is very common in people of all ages. If you think you are getting a fungal infection, there are a few methods you can use to combat this infection.
To step
Method 1 of 3: Naturally prevent a fungal infection from getting worse
 Eat yogurt with probiotics. There is a type of yogurt with good bacteria in it that can prevent the development of a fungal infection. Yogurt with lactobacillus acidophilus is often used by women, orally and vaginally, to fight fungal infections. You can buy this type of yogurt at most supermarkets. Be sure to check the label to see if it actually contains active and live lactobacillus acidophilus cultures.
Eat yogurt with probiotics. There is a type of yogurt with good bacteria in it that can prevent the development of a fungal infection. Yogurt with lactobacillus acidophilus is often used by women, orally and vaginally, to fight fungal infections. You can buy this type of yogurt at most supermarkets. Be sure to check the label to see if it actually contains active and live lactobacillus acidophilus cultures. - Research has shown that yogurt can be effective in relieving symptoms for some women. But other studies show that it doesn't work in all women.
 Wash yourself twice a day. While it may not quite fit into your daily schedule, it is important to keep yourself as clean as possible if you want to fight the yeast infection. When you wash, don't use chemical soap or shower gel. This type of soap kills the good bacteria you need to fight infection and does little to reduce it.
Wash yourself twice a day. While it may not quite fit into your daily schedule, it is important to keep yourself as clean as possible if you want to fight the yeast infection. When you wash, don't use chemical soap or shower gel. This type of soap kills the good bacteria you need to fight infection and does little to reduce it. - Women with a vaginal yeast infection are better off taking a bath than a shower. Taking a bath can help rid the vaginal area of the fungus.
- Make sure the bath is not too hot. Otherwise the fungus will grow.
 Use clean towels. When you bathe, go for a swim, or dry off with a towel, it's important to get as dry as possible. Mold thrives in a warm, humid environment, so use a clean, dry towel to remove as much moisture as possible. If you take a towel that you have used before, you can transfer the mold on it, as it will survive due to the moisture left in it from the previous wash. So throw your towel in the wash after using it.
Use clean towels. When you bathe, go for a swim, or dry off with a towel, it's important to get as dry as possible. Mold thrives in a warm, humid environment, so use a clean, dry towel to remove as much moisture as possible. If you take a towel that you have used before, you can transfer the mold on it, as it will survive due to the moisture left in it from the previous wash. So throw your towel in the wash after using it.  Wear loose clothing. If you have a yeast infection of the skin or vagina, it is important to wear loose clothing that allows the skin to breathe. This is especially important if you have a vaginal yeast infection. Wear cotton underwear and avoid silk or nylon underwear, as these fabrics do not allow air to pass through.
Wear loose clothing. If you have a yeast infection of the skin or vagina, it is important to wear loose clothing that allows the skin to breathe. This is especially important if you have a vaginal yeast infection. Wear cotton underwear and avoid silk or nylon underwear, as these fabrics do not allow air to pass through. - Avoid activities that cause unnecessary heat, sweat, and moisture in the affected areas to prevent further growth of the fungus.
 Avoid certain skin care products. If you get a yeast infection, don't use products that can make the infection worse. It is especially important to avoid soaps that get rid of the good bacteria, such as vaginal sprays or powders. Also, do not use lotions that keep the skin moist or that cause the skin to retain heat and moisture.
Avoid certain skin care products. If you get a yeast infection, don't use products that can make the infection worse. It is especially important to avoid soaps that get rid of the good bacteria, such as vaginal sprays or powders. Also, do not use lotions that keep the skin moist or that cause the skin to retain heat and moisture. - While you may want to use a spray or powder to combat the symptoms of the fungal infection, those products can irritate the skin even more.
Method 2 of 3: Treating a yeast infection with medication
 Use medicine for your skin. There are certain medications that help against fungal skin infections. For skin infections, doctors usually prescribe an anti-fungal cream that can be applied to the affected areas. These creams often clear up the infection within a few weeks. Two well-known anti-fungal creams for fungal skin infections are miconazole and clotrimazole. The package insert contains general instructions on how to use it, but make sure you follow the directions of your doctor carefully.
Use medicine for your skin. There are certain medications that help against fungal skin infections. For skin infections, doctors usually prescribe an anti-fungal cream that can be applied to the affected areas. These creams often clear up the infection within a few weeks. Two well-known anti-fungal creams for fungal skin infections are miconazole and clotrimazole. The package insert contains general instructions on how to use it, but make sure you follow the directions of your doctor carefully. - To use cream for a fungal infection, wash the affected areas with water and dry thoroughly afterwards. The skin should absolutely not be damp. Apply the recommended amount of cream as directed by your doctor or as stated in the package insert. Allow it to absorb well before putting on clothing again or before making any movements that could cause the area to rub against another object or material.
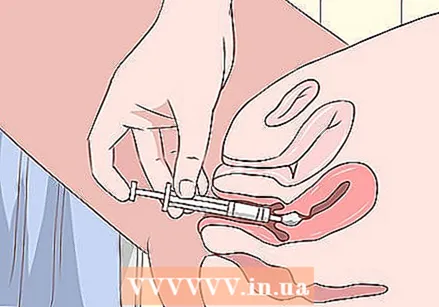 Treat a vaginal yeast infection. To fight a vaginal yeast infection, you can use over-the-counter or medications prescribed by your doctor. If you don't often get a yeast infection and the symptoms are mild, you can use an over-the-counter cream, tablet, or suppository that you insert directly into the vagina.
Treat a vaginal yeast infection. To fight a vaginal yeast infection, you can use over-the-counter or medications prescribed by your doctor. If you don't often get a yeast infection and the symptoms are mild, you can use an over-the-counter cream, tablet, or suppository that you insert directly into the vagina. - Well-known anti-fungal medications include miconazole and clotrimazole. These are generally administered as creams or suppositories to be inserted vaginally every day before going to bed, as long as indicated in the package insert.
- There are also oral antifungal medications, such as fluconazole and itraconazole. You take these pills by mouth.
- Clotrimazole is also available as a tablet, which must be inserted vaginally from one to seven days before going to sleep.
- Sometimes a fungal infection can cause complications. Then the treatment will take 14 days rather than one to seven.
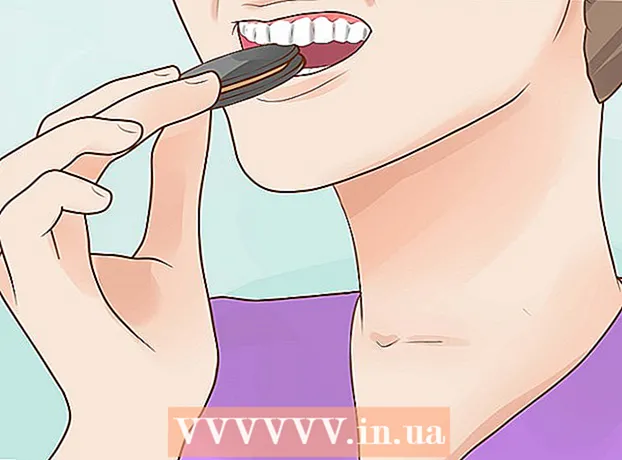
 Fight an oral yeast infection with a medicated mouthwash. If you have an oral yeast infection, you can treat it with an antifungal medicated mouthwash. To use this medicine, you have to rinse for a while and then swallow it. This remedy treats the surface of your mouth and works from the inside after you swallow it. Also talk to your doctor about additional oral medications you can use. Oral antifungal medications come in the form of tablets and lozenges.
Fight an oral yeast infection with a medicated mouthwash. If you have an oral yeast infection, you can treat it with an antifungal medicated mouthwash. To use this medicine, you have to rinse for a while and then swallow it. This remedy treats the surface of your mouth and works from the inside after you swallow it. Also talk to your doctor about additional oral medications you can use. Oral antifungal medications come in the form of tablets and lozenges. - If you have a severely weakened immune system and need to fight other illnesses such as cancer or HIV, your doctor may be able to prescribe Amphotericin B, a drug that can fight oral fungal infections that have become immune to other antifungal medications.
Method 3 of 3: Understand what a yeast infection is
 Recognize the signs. If you want to avoid getting a yeast infection, you need to know what the signs are. There are three types of fungal infections. There are infections affecting the skin, mouth and vagina.
Recognize the signs. If you want to avoid getting a yeast infection, you need to know what the signs are. There are three types of fungal infections. There are infections affecting the skin, mouth and vagina. - Symptoms of a yeast infection of the mouth, also called thrush, include creamy white patches in the throat or mouth and painful cracks in the corners of your mouth.
- Fungal infections of the skin cause blisters, red spots or a rash, usually between the toes and fingers, under the breasts and in the groin. A fungal skin infection can also occur on the penis. The symptoms may be the same, but the penis may also have white or moist patches, where a white substance builds up in the folds of the skin.
- Vaginal yeast infections are common, causing an increase in vaginal discharge that appears thick, white and curd-like. The vagina may be itchy and the skin on the inside may be irritated and red.
 Consider the general risk factors. There are many risk factors that can contribute to a fungal infection. If you have a condition that suppresses the immune system, such as HIV, you are more likely to get infections because the body cannot protect itself sufficiently against external attacks. If you take antibiotics you can also get a fungal infection more quickly. Anti-bacterial treatments, such as with antibiotics, serve to fight infections, but they also reduce the good bacteria that live on and in our bodies, which play an important role in protecting against other types of infections, such as fungal infections. In those cases, a yeast infection can develop if the fungus has found a surface on which to multiply, such as the skin, penis or vagina.
Consider the general risk factors. There are many risk factors that can contribute to a fungal infection. If you have a condition that suppresses the immune system, such as HIV, you are more likely to get infections because the body cannot protect itself sufficiently against external attacks. If you take antibiotics you can also get a fungal infection more quickly. Anti-bacterial treatments, such as with antibiotics, serve to fight infections, but they also reduce the good bacteria that live on and in our bodies, which play an important role in protecting against other types of infections, such as fungal infections. In those cases, a yeast infection can develop if the fungus has found a surface on which to multiply, such as the skin, penis or vagina. - Overweight people are also more likely to suffer from fungal infections. This is due to excess skin folds in which bacteria and fungi can grow.
- Babies are also more likely to suffer from a fungal infection, in the form of a diaper rash or thrush.
 Watch for gender-specific risk factors. Women who suffer from hormonal fluctuations, from menopause, the pill, pregnancy or PMS, are more prone to fungal infections due to physical stressors that trigger the hormonal changes. Women are also more likely to get a yeast infection from vaginal flushes and irritants. Although well-intentioned, these agents can unbalance the natural pH of the vagina, naturally creating an environment in which foreign bacteria cannot cause infections.
Watch for gender-specific risk factors. Women who suffer from hormonal fluctuations, from menopause, the pill, pregnancy or PMS, are more prone to fungal infections due to physical stressors that trigger the hormonal changes. Women are also more likely to get a yeast infection from vaginal flushes and irritants. Although well-intentioned, these agents can unbalance the natural pH of the vagina, naturally creating an environment in which foreign bacteria cannot cause infections. - Men are more prone to fungal infections if they are not circumcised. These men have an increased risk of fungal infections because bacteria can grow on and under the foreskin.
 Reduce the risk of a fungal infection. There are common ways to prevent a yeast infection. Only use antibiotics when absolutely necessary so that your body has enough good bacteria to fight a yeast infection. Since steroids can cause problems with the immune system, it is good to keep their use to a minimum. Try to avoid a damp environment or damp clothing. If your clothes are damp, change clothes as soon as possible.
Reduce the risk of a fungal infection. There are common ways to prevent a yeast infection. Only use antibiotics when absolutely necessary so that your body has enough good bacteria to fight a yeast infection. Since steroids can cause problems with the immune system, it is good to keep their use to a minimum. Try to avoid a damp environment or damp clothing. If your clothes are damp, change clothes as soon as possible. - A fungal infection can also develop in the mouth, especially in diabetics and people with dentures. To avoid this problem with dentures, keep your teeth clean and fit properly. In other cases, the fungus will remain dormant until it emerges from, for example, antibiotic use.
- Women should avoid vaginal showers as much as possible.
- If you have diabetes, do your best to control it and keep your skin healthy.
Warnings
- If you have recurring yeast infections, see the doctor instead of continuing to use over-the-counter remedies. It may not be a fungus, or it may be an unusual strain. You should also get tested for other conditions (such as diabetes).
- Although home remedies can sometimes help treat the symptoms of a yeast infection, and can sometimes partially remedy it, it is always better to combine them with medication that you get from your doctor. Always consult your doctor to understand the risks and benefits of alternative therapies. There are studies that have had positive results, but more research is needed before experts can recommend these remedies with certainty.