Content
- To step
- Method 1 of 3: Sharp angle
- Method 2 of 3: Obtuse angle
- Method 3 of 3: Reflex angle (obtuse angle> 180)
- Tips
- Necessities
The easiest way to measure an angle is with a protractor. However, if you don't have a protractor handy, you can determine the size of an angle using the basic geometric principles of triangles. You need a scientific calculator to solve the equations. Most smartphones come with it, but you can also download free apps or use a free calculator online. The calculations you need to make depend on whether you are dealing with an acute angle (less than 90 degrees), obtuse angle (more than 90 degrees but less than 180), or a 'reflex angle' (more than 180 degrees but less than 360).
To step
Method 1 of 3: Sharp angle
 Draw a vertical line connecting the two rays of the corner. To determine the number of degrees in an acute angle, connect the two rays into a triangle. Align the short end of your ruler with the bottom radius, then draw a vertical line intersecting the other radius using the long side of your ruler.
Draw a vertical line connecting the two rays of the corner. To determine the number of degrees in an acute angle, connect the two rays into a triangle. Align the short end of your ruler with the bottom radius, then draw a vertical line intersecting the other radius using the long side of your ruler. - The vertical line creates a right triangle. The angle formed by the adjacent side (the bottom radius of the corner) of the triangle and the opposite side (the vertical line) is 90 degrees.
 Measure the length of the adjacent side to the adjacent or x value find. Place the end of your ruler on the corner point. Measure the length of the adjacent side from the vertex to the point where it intersects the opposite side.
Measure the length of the adjacent side to the adjacent or x value find. Place the end of your ruler on the corner point. Measure the length of the adjacent side from the vertex to the point where it intersects the opposite side. - This value is the x value in your slope equation, where slope = y / x. So if you measured 7, your equation becomes "slope = y / 7".
 We measure the length of the other side to find the opposite one. Line up the short end of your ruler with the adjacent side of the triangle. Measure the length of the vertical line from where it meets the adjacent side to the point where it meets the top radius of the corner (the hypotenuse of your triangle).
We measure the length of the other side to find the opposite one. Line up the short end of your ruler with the adjacent side of the triangle. Measure the length of the vertical line from where it meets the adjacent side to the point where it meets the top radius of the corner (the hypotenuse of your triangle). - This amount is the balance or y value in your slope equation. So if you measured 5, the equation becomes "slope = 5/7".
 Divide the opposite by the adjacent (the y value by the x value) to find the slope of the angle. The slope is the steepness of the diagonal line, or hypotenuse, of your triangle. Once you know this number, you can calculate the degrees of your acute angle.
Divide the opposite by the adjacent (the y value by the x value) to find the slope of the angle. The slope is the steepness of the diagonal line, or hypotenuse, of your triangle. Once you know this number, you can calculate the degrees of your acute angle. - So, to continue the example, the equation becomes "slope = 5/7", which is 0.71428571.
Tip: Do not round the number before converting it to degrees - otherwise the result will be less accurate.
 Use your calculator to calculate the angle in degrees. Type the value for the slope into your scientific calculator, then press the inverse tangent (tan) button. This will give you the angle in degrees.
Use your calculator to calculate the angle in degrees. Type the value for the slope into your scientific calculator, then press the inverse tangent (tan) button. This will give you the angle in degrees. - To continue with the example, a slope of 0.71428571 gives an angle of 35.5 degrees.
Method 2 of 3: Obtuse angle
 Extend the bottom radius of the corner in a straight line. Mark your vertex with a point, then use the long edge of your ruler to draw a straight line to the left of the vertex. The bottom radius of the corner should be a single long line extending below the open top radius of the corner.
Extend the bottom radius of the corner in a straight line. Mark your vertex with a point, then use the long edge of your ruler to draw a straight line to the left of the vertex. The bottom radius of the corner should be a single long line extending below the open top radius of the corner. - Make sure the line is perfectly straight. If the line is slanted up or down, it will ruin the accuracy of your equation.
Tip: If you're working on plain paper, you can line up the short edge of your ruler with the side of the paper to make sure your line extension is straight.
 Draw a vertical line connecting the top ray to the line. Align the short side of your ruler with the bottom radius at a point where the long side intersects with the top radius. Follow the long side to draw a line straight up from the bottom beam connecting the two.
Draw a vertical line connecting the top ray to the line. Align the short side of your ruler with the bottom radius at a point where the long side intersects with the top radius. Follow the long side to draw a line straight up from the bottom beam connecting the two. - Effectively, you've created a small right angle under the obtuse angle you want to measure, making the top radius of the obtuse angle the hypotenuse of your right angle.
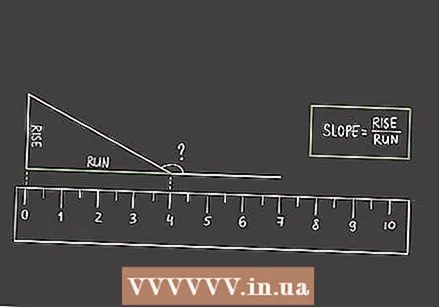 Measure the length of the bottom line from the vertex. Place your ruler below the bottom line, starting at the vertical line creating the right angle. Measure the length from that intersection to the vertex of the original angle.
Measure the length of the bottom line from the vertex. Place your ruler below the bottom line, starting at the vertical line creating the right angle. Measure the length from that intersection to the vertex of the original angle. - You determine the slope of the angle of the acute triangle, which you can use to calculate the degrees in the acute angle. The bottom line is the adjacent value in the equation "slope = opposite / adjacent".
 Measure the length of the vertical line. Line up the short end of your ruler with the bottom line of the small sharp triangle. Measure with the ruler to the point where the vertical line intersects the open radius of your obtuse corner. This is the length of your vertical line.
Measure the length of the vertical line. Line up the short end of your ruler with the bottom line of the small sharp triangle. Measure with the ruler to the point where the vertical line intersects the open radius of your obtuse corner. This is the length of your vertical line. - The length of your vertical line is the opposite value in the equation "slope = opposite / adjacent". If you know the values for both opposite and adjacent, you can calculate the slope of the acute angle.
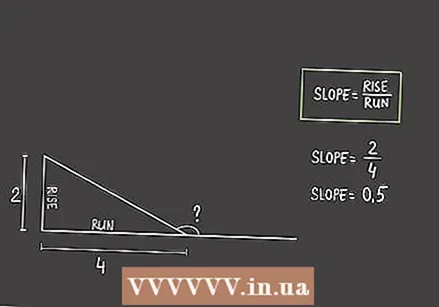 Determine the slope of the acute angle. Share the opposite value by the adjacent value to determine the slope of the acute angle. You will use this value to calculate the acute angle in degrees.
Determine the slope of the acute angle. Share the opposite value by the adjacent value to determine the slope of the acute angle. You will use this value to calculate the acute angle in degrees. - The equation "slope = 2/4" will then yield, for example, a slope of 0.5.
 Calculate the degrees of the acute angle. Enter the slope into your scientific calculator, then press the "inverse tan" (tan) button. The value displayed is the number of degrees of the acute angle.
Calculate the degrees of the acute angle. Enter the slope into your scientific calculator, then press the "inverse tan" (tan) button. The value displayed is the number of degrees of the acute angle. - To continue with the example, if your slope is 0.5, the acute angle is an angle of 26.565 degrees.
 Subtract the degrees of the acute angle from 180. A flat line is a right angle of 180 degrees. Since you drew a straight line, the sum of the acute angle you calculated and the obtuse angle will be 180 degrees. Subtracting the degrees of the acute angle from 180 will give you the degrees of your obtuse angle.
Subtract the degrees of the acute angle from 180. A flat line is a right angle of 180 degrees. Since you drew a straight line, the sum of the acute angle you calculated and the obtuse angle will be 180 degrees. Subtracting the degrees of the acute angle from 180 will give you the degrees of your obtuse angle. - To continue with the example, if you have an acute angle of 26.565 degrees, you have an obtuse angle of 153.435 degrees (180 - 26.565 = 153.435).
Method 3 of 3: Reflex angle (obtuse angle> 180)
 Determine the smaller acute angle associated with the obtuse angle that is greater than 180 degrees (hereinafter: reflex angle). A reflex angle is greater than 180 degrees but less than 360 degrees. This means that if you look at the reflex angle, you also see a sharp angle within it.
Determine the smaller acute angle associated with the obtuse angle that is greater than 180 degrees (hereinafter: reflex angle). A reflex angle is greater than 180 degrees but less than 360 degrees. This means that if you look at the reflex angle, you also see a sharp angle within it. - By determining the number of degrees of the acute angle, you can calculate the number of degrees of the reflex angle. You can use the basic slope equation and the inverse tangent function on your scientific calculator to find the degrees of the acute angle.
Tip: If you get confused because the angle is upside down, turn your paper and ignore the reflex angle until the last step.
 Draw a vertical line connecting the rays of the acute angle. Line up the short end of your ruler with the radius of the corner being horizontal instead of diagonal. Then draw a vertical line that intersects the horizontal radius of the corner.
Draw a vertical line connecting the rays of the acute angle. Line up the short end of your ruler with the radius of the corner being horizontal instead of diagonal. Then draw a vertical line that intersects the horizontal radius of the corner. - The horizontal line will be the opposite side of your triangle, and the vertical line will be the opposite side of the acute angle you want to measure.
 Measure the opposite and the adjacent line of the acute angle. In the equation "slope = opposite / adjacent", the opposite is the length of the vertical line, or the opposite side of your triangle. The adjacent is the length of the horizontal line, or the adjacent side of your triangle.
Measure the opposite and the adjacent line of the acute angle. In the equation "slope = opposite / adjacent", the opposite is the length of the vertical line, or the opposite side of your triangle. The adjacent is the length of the horizontal line, or the adjacent side of your triangle. - Measure the horizontal line from the vertex to the point where it intersects the vertical line. Measure the vertical line from the point where it intersects the horizontal line to the point where it intersects the diagonal line.
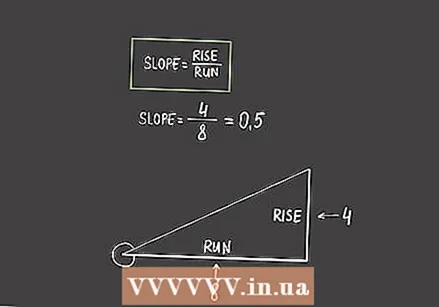 Divide the opposite by the adjacent to calculate the slope of the acute angle. Use the values found for the length of the vertical and horizontal lines in your slope equation. When you divide the length of the vertical line by the length of the horizontal line, you get the slope for the angle.
Divide the opposite by the adjacent to calculate the slope of the acute angle. Use the values found for the length of the vertical and horizontal lines in your slope equation. When you divide the length of the vertical line by the length of the horizontal line, you get the slope for the angle. - For example, if your horizontal line is 8 and the vertical line is 4, then your equation becomes "slope = 4/8". The slope of your angle is then 0.5.
 Use your calculator to find the degrees of the acute angle. Type the value you have for the slope of the angle into your scientific calculator, then press the "inverse tangent" (tan) button. The value displayed is the number of degrees of the smaller acute angle.
Use your calculator to find the degrees of the acute angle. Type the value you have for the slope of the angle into your scientific calculator, then press the "inverse tangent" (tan) button. The value displayed is the number of degrees of the smaller acute angle. - To continue with the example, if your slope is 0.5, the acute angle will be 26.565 degrees.
 Subtract the degrees of the acute angle from 360. A circle has 360 degrees. Since a reflex angle is an angle greater than 180 degrees, you consider it part of a circle. The degrees of the reflex angle and the degrees of the smaller acute angle add up to 360.
Subtract the degrees of the acute angle from 360. A circle has 360 degrees. Since a reflex angle is an angle greater than 180 degrees, you consider it part of a circle. The degrees of the reflex angle and the degrees of the smaller acute angle add up to 360. - To continue with the example, if the smaller acute angle is 26.565 degrees, the reflex angle is 333.435 degrees.
Tips
- Make sure your scientific calculator's trigonometric functions are set in degrees, not radians.
- The slope is the relationship between the x motion and the y motion. The unit of measure you use to quantify the lengths of the two lines is irrelevant - just make sure to use the same unit for both lines. In other words, if you measure the length of one line in centimeters, you should also measure the other in centimeters.
Necessities
- Scientific calculator
- Ruler