Author:
Tamara Smith
Date Of Creation:
23 January 2021
Update Date:
2 July 2024

Content
- To step
- Method 1 of 3: Format the layout of a document
- Method 2 of 3: Format the font
- Method 3 of 3: Add pictures and charts
- Tip
Microsoft Word is the world's most popular word processing program. Depending on the type of legal, formal, or personal text you are writing, each of these requires separate formatting guidelines. If you are using Microsoft Word, you will find that following these guidelines is quite easy given all the tools Word has. If you are just getting started with Microsoft Word, don't worry. You can format your document like a pro in no time.
To step
Method 1 of 3: Format the layout of a document
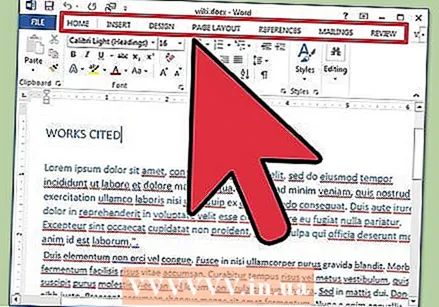 Explore the Word user interface. Familiarize yourself with the interface elements that contain all of your formatting tools. You may need to enable certain tools on your toolbar. You can do this in the "View" tab by selecting Toolbars and choosing "Standard".
Explore the Word user interface. Familiarize yourself with the interface elements that contain all of your formatting tools. You may need to enable certain tools on your toolbar. You can do this in the "View" tab by selecting Toolbars and choosing "Standard". - The menu bar is the area at the top of the screen where you will find File, Edit, View and other important menu items.
- The toolbar (depending on version) is located directly below the menu bar and shows common tasks such as saving, printing and opening a document.
- Located at the top of your workspace, below the toolbar, the ribbon organizes Microsoft Word features into categories, such as the Home tab and Page Layout.
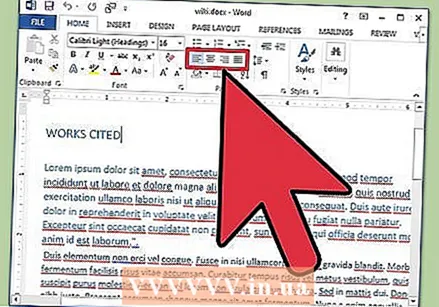 Adjust the alignment of your document. Different types of documents require different ways of alignment for the text. You can choose to align your entire document left, right, or center by clicking the Align buttons in the Alina group in the ribbon.
Adjust the alignment of your document. Different types of documents require different ways of alignment for the text. You can choose to align your entire document left, right, or center by clicking the Align buttons in the Alina group in the ribbon. - These are the buttons that look like a small version of a document, with small black lines indicating the alignment.
- You'll find the alignment buttons toward the center of the ribbon, after the Underline button, and before the Bullets button.
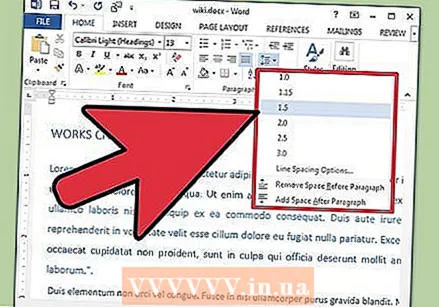 Set the line spacing of your document. Adjust the settings by clicking the Line and Paragraph Spacing button. Any text you type after using this tool will follow the distance you set.
Set the line spacing of your document. Adjust the settings by clicking the Line and Paragraph Spacing button. Any text you type after using this tool will follow the distance you set. - You'll find the Line and Paragraph Spacing button on the ribbon after the alignment buttons. This button looks like a row of lines with vertical arrows to the left of the lines pointing up and down.
- To edit the spacing of an existing line or paragraph, select the text and click the Line and Paragraph Spacing button to edit it.
- You can also edit the line and paragraph spacing by clicking the Page Layout tab in the menu bar at the top of the screen, selecting "Paragraph" from the list and specifying the desired spacing.
- Many professional documents, such as college essays and cover letters, require double spacing.
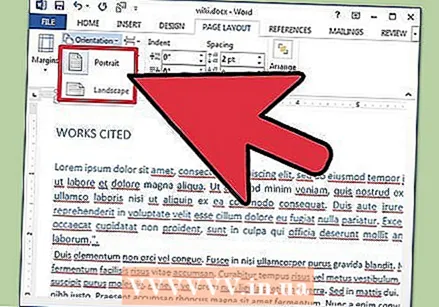 Adjust the page orientation. To write the document in a different orientation, click the "Orientation" option in the Page Setup group in the ribbon and select "Portrait" or "Landscape" from the drop-down list.
Adjust the page orientation. To write the document in a different orientation, click the "Orientation" option in the Page Setup group in the ribbon and select "Portrait" or "Landscape" from the drop-down list. 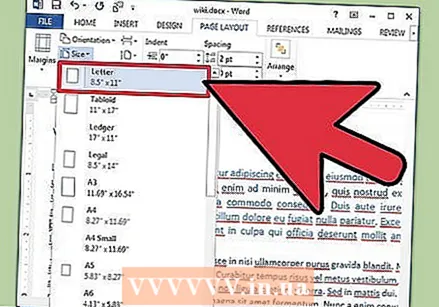 Change the size of the paper in the Page Setup group in the ribbon. If you need to print the document on a specific paper size, click the "Size" button and select the desired size from the drop-down list.
Change the size of the paper in the Page Setup group in the ribbon. If you need to print the document on a specific paper size, click the "Size" button and select the desired size from the drop-down list. - This changes the virtual size of the text document.
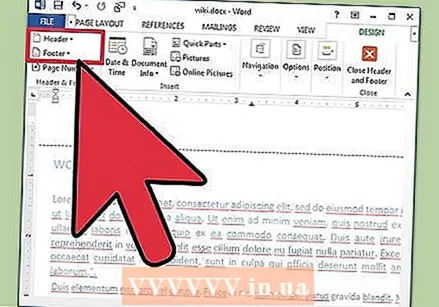 Customize the headers and footers of the document. A header contains information that appears on every page of the document.
Customize the headers and footers of the document. A header contains information that appears on every page of the document. - To set the header of your document, double-click the top part of the page and the header field will appear.
- Customize the document footers. Footers are just like document headers. All text in the footer appears at the bottom of every page of your document.
- To set the footer of your document, double-click the bottom part of the page and the footer field will appear.
- You can also format your headers and footers by selecting the "Insert" tab in the menu bar at the top of the screen and clicking Header or Footer in the group of the same name. This action allows you to create and edit headers and footers on your page.
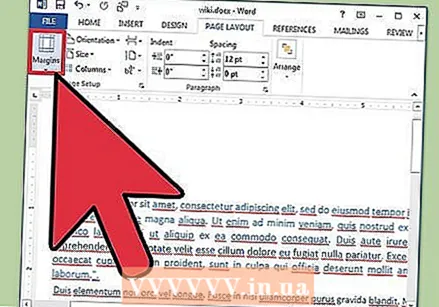 Adjust the margin. Click the "Margins" button in the Page Setup group of the Page Layout tab and select a margin from the predefined margin settings in the drop-down list.
Adjust the margin. Click the "Margins" button in the Page Setup group of the Page Layout tab and select a margin from the predefined margin settings in the drop-down list. - If you want to use your own margins, click "Custom Margins" at the very bottom of the drop-down list to set your own margins.
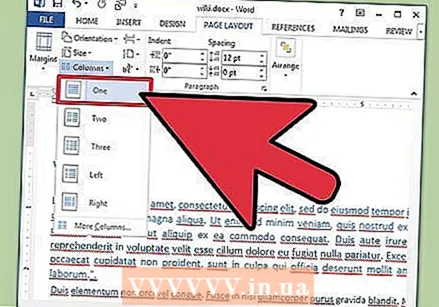 Add columns. If you want to create a newspaper-like document, you can do this by setting columns in the document. Select the "Columns" option from the Page Layout tab and choose the number and alignment of columns you want from the drop-down list. Depending on the Word version, you will also find the Columns button on the top row of the ribbon. This button has a green icon with a small rectangle divided in half.
Add columns. If you want to create a newspaper-like document, you can do this by setting columns in the document. Select the "Columns" option from the Page Layout tab and choose the number and alignment of columns you want from the drop-down list. Depending on the Word version, you will also find the Columns button on the top row of the ribbon. This button has a green icon with a small rectangle divided in half. - If you want to create one, two, or three columns, you can do that with the preset options. If you want to make more, you should choose "More Columns".
- Note that this column option is different from the columns you get when you insert items such as tables into your document.
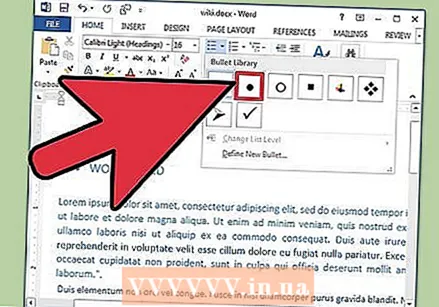 Add bullets and numbers. Highlight the text you want to number or bulleted in front of, and (depending on the version) click the Numbering or Bullets button in the ribbon.
Add bullets and numbers. Highlight the text you want to number or bulleted in front of, and (depending on the version) click the Numbering or Bullets button in the ribbon. - These buttons can be found next to each other in the ribbon, after the alignment buttons. The Numbering button shows three small lines of numbers to the left of the lines and the Bullets button shows three small lines of bullets to the left of the lines.
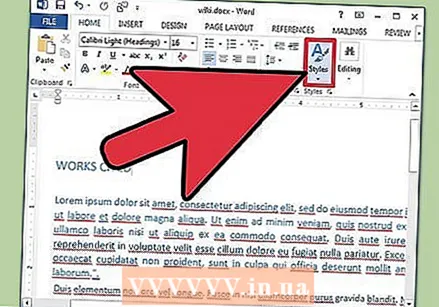 Choose your document style. All documents have built-in styles by default (for example: Normal, Title, Heading 1). The default style for text is Normal. The template on which a document is based (for example: Normal.dotx) determines which styles are displayed in the ribbon and in the Styles tab.
Choose your document style. All documents have built-in styles by default (for example: Normal, Title, Heading 1). The default style for text is Normal. The template on which a document is based (for example: Normal.dotx) determines which styles are displayed in the ribbon and in the Styles tab. - Before applying a style, you can see all the available styles and preview how they will look when you apply them.
- From the Home tab or the Format tab in the menu bar, under Styles, select a desired style.
- You can also click the Edit button on the Styles tab to create your own style.
- By default, Word applies a paragraph style (for example: Heading 1) to the entire paragraph. To apply a paragraph style to part of a paragraph, select only the specific part you want to change.
Method 2 of 3: Format the font
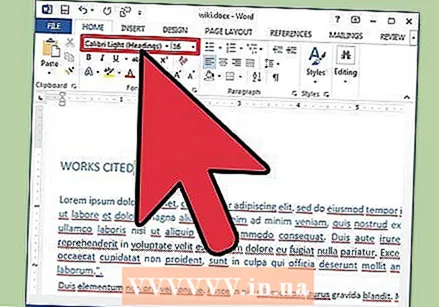 Adjust the font settings. In the ribbon you will see drop-down menus for font and size. To make changes to the text, you must first select the text you want to work with. You can select individual characters, specific words or entire paragraphs. After selecting text, you can format it. For example, you can change the font, size and color.
Adjust the font settings. In the ribbon you will see drop-down menus for font and size. To make changes to the text, you must first select the text you want to work with. You can select individual characters, specific words or entire paragraphs. After selecting text, you can format it. For example, you can change the font, size and color. - Click to the left of the first word you want to select and hold the cursor while dragging the cursor over all the words you want to select.
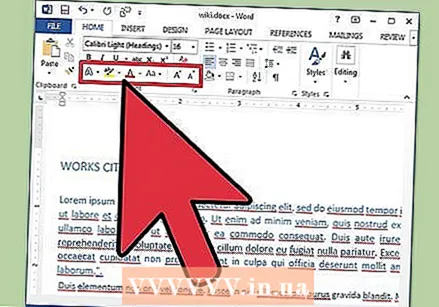 Change the size, color and marking. Navigate to the drop-down list on the ribbon to choose the desired font, size, color, and highlight. You will first see the font button, to the right after the Style button. Next you will find the font size button with the default size (usually 12).
Change the size, color and marking. Navigate to the drop-down list on the ribbon to choose the desired font, size, color, and highlight. You will first see the font button, to the right after the Style button. Next you will find the font size button with the default size (usually 12). - Always keep in mind the formatting guidelines of the document you are creating when choosing the font and size.
- The default font for most scientific and professional documents is Time New Roman, size 12.
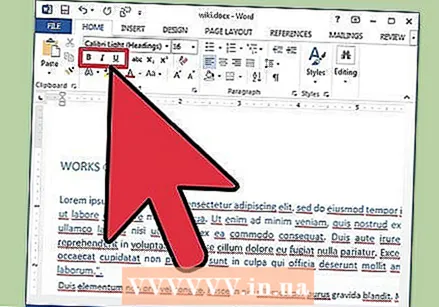 Choose the format of the text. In addition to setting the font style and size, you can also adjust the emphasis of words and lines in your document. Next to the size button you see the button Bold, Italic and Underline. The Bold button is a bold capital B, the Italic button is an italic capital I, and the Underline button is an underlined capital U.
Choose the format of the text. In addition to setting the font style and size, you can also adjust the emphasis of words and lines in your document. Next to the size button you see the button Bold, Italic and Underline. The Bold button is a bold capital B, the Italic button is an italic capital I, and the Underline button is an underlined capital U. - Once you've selected the font you want to change, click the buttons on the ribbon.
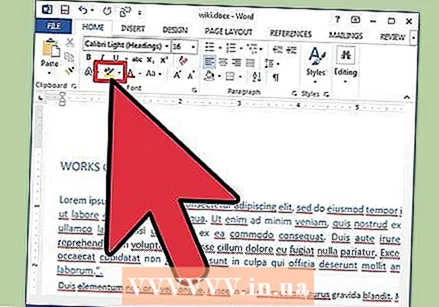 Set the text and font attributes and colors. If you want to add colors and highlights to your document, you can do this by selecting the part of the document you want to add colors to and clicking the Text Highlight Color or Text Color buttons in the ribbon.
Set the text and font attributes and colors. If you want to add colors and highlights to your document, you can do this by selecting the part of the document you want to add colors to and clicking the Text Highlight Color or Text Color buttons in the ribbon. - (Depending on version), go all the way to the right of the ribbon to find the button, a blue ABC with a white bar underlining it, and the text color button, a letter A with a black bar below it.
Method 3 of 3: Add pictures and charts
 Drag an image into the document. Place your image exactly where you want it. Once you've dropped the image, it can be a bit difficult to get it exactly where you want it. There are a few ways to manipulate your image more easily:
Drag an image into the document. Place your image exactly where you want it. Once you've dropped the image, it can be a bit difficult to get it exactly where you want it. There are a few ways to manipulate your image more easily: 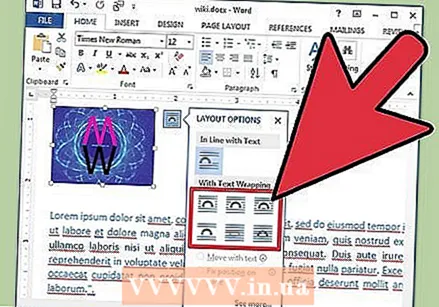 Activate text wrapping. Text wrapping changes the layout of your document so that text can flow around the image wherever it is.
Activate text wrapping. Text wrapping changes the layout of your document so that text can flow around the image wherever it is. - Right-click on the image and right-click over Wrap Text. Select the alignment that best fits your document. You will see a preview as you hover your mouse over each option.
- Select the image and then hold down the Ctrl key. While holding down the key, use the arrow keys to move the image in the document.
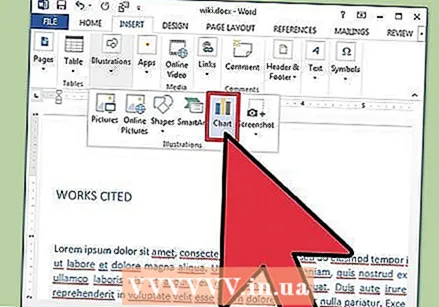 Add a chart. Click the "Insert" tab and then click the "Chart" option. When you select Graph, a new toolbar will appear on your ribbon with a range of graphs to choose from. Choose your preferred chart type, such as a pie.
Add a chart. Click the "Insert" tab and then click the "Chart" option. When you select Graph, a new toolbar will appear on your ribbon with a range of graphs to choose from. Choose your preferred chart type, such as a pie. 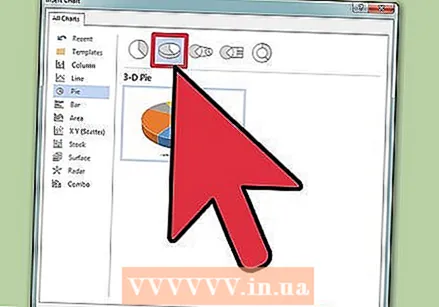 Change your chart. Scroll to that part of the window and then select from the different types of graphs, such as "Highlighted 3D Circle Segments".
Change your chart. Scroll to that part of the window and then select from the different types of graphs, such as "Highlighted 3D Circle Segments". - Click "OK" to insert the chart into your document and bring up the "Chart in Microsoft Word" window.
Tip
- Unless you are just writing a text, you should first consult the guidelines for that document before adjusting the layout of your document.
- Except for header, footer, and page formatting (which affects the entire document), all other formatting tools can only be applied to specific parts of the document.