Author:
Christy White
Date Of Creation:
4 May 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- To step
- Part 1 of 3: The basics
- Part 2 of 3: Calculating the standard deviation
- Part 3 of 3: Determining the standard error
- Tips
"Standard error" refers to the standard deviation of the sampling distribution of statistical data. In other words, it can be used to calculate the accuracy of a sample mean. In many cases, using the standard error implicitly assumes a normal distribution. If you want to calculate the standard error, read on at Step 1.
To step
Part 1 of 3: The basics
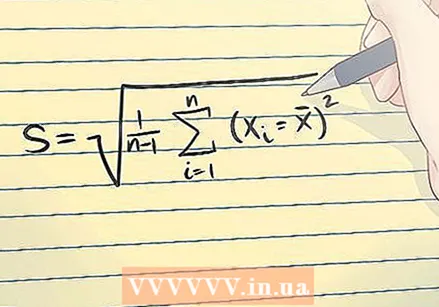 The standard deviation. The standard deviation of a sample indicates the degree of dispersion of the numbers. The standard deviation of a sample is usually denoted by an s. The mathematical formula for the standard deviation is shown above.
The standard deviation. The standard deviation of a sample indicates the degree of dispersion of the numbers. The standard deviation of a sample is usually denoted by an s. The mathematical formula for the standard deviation is shown above. 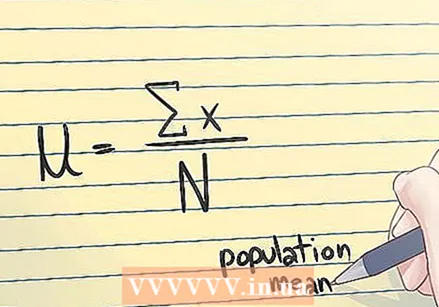 The population mean. The population mean is the mean of a set of numerical data that contains all the values of the entire group - in other words, the mean of a full set of numbers, rather than a sample.
The population mean. The population mean is the mean of a set of numerical data that contains all the values of the entire group - in other words, the mean of a full set of numbers, rather than a sample. 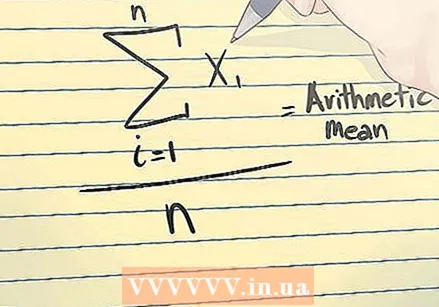 The arithmetic mean. This is just an average: the sum of a number of values divided by that same number of values.
The arithmetic mean. This is just an average: the sum of a number of values divided by that same number of values. 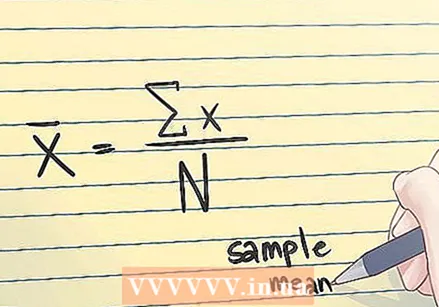 Recognize sample means. When an arithmetic mean is based on a series of observations obtained by sampling a statistical population, it is called a "sample mean." This is the average of a numeric series of data that includes part of the values within a group. It is referred to as:
Recognize sample means. When an arithmetic mean is based on a series of observations obtained by sampling a statistical population, it is called a "sample mean." This is the average of a numeric series of data that includes part of the values within a group. It is referred to as: 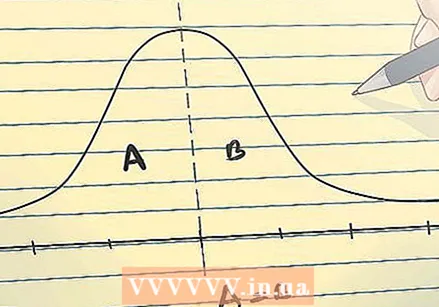 The normal distribution. The normal distribution, the most commonly used of all distributions, is symmetrical, with an outlier at the mean of the data. The shape of the graph is that of a clock, with the slope on both sides of the top being the same. Fifty percent of the distribution is on the left and fifty percent on the right. The spread of a normal distribution is determined by the standard deviation.
The normal distribution. The normal distribution, the most commonly used of all distributions, is symmetrical, with an outlier at the mean of the data. The shape of the graph is that of a clock, with the slope on both sides of the top being the same. Fifty percent of the distribution is on the left and fifty percent on the right. The spread of a normal distribution is determined by the standard deviation.  The standard formula. The formula for the standard error of a sample mean is given above.
The standard formula. The formula for the standard error of a sample mean is given above.
Part 2 of 3: Calculating the standard deviation
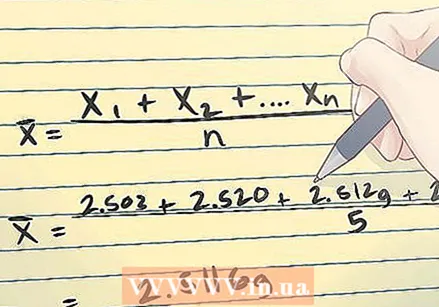 Calculate the sample mean. To determine the standard error, you will first have to calculate the standard deviation (because the standard deviation, s, is part of the formula for the standard error). Start by calculating the mean of the sample values. The sample mean is expressed as the arithmetic mean of the measurements x1, x2,. . . xn. This is calculated with the above formula.
Calculate the sample mean. To determine the standard error, you will first have to calculate the standard deviation (because the standard deviation, s, is part of the formula for the standard error). Start by calculating the mean of the sample values. The sample mean is expressed as the arithmetic mean of the measurements x1, x2,. . . xn. This is calculated with the above formula. - For example, suppose you need to calculate the standard error of a sample mean for the measurements of the weight of five coins, as listed in the table below:
You would then calculate the sample mean by entering the weight values into the formula, like this:
- For example, suppose you need to calculate the standard error of a sample mean for the measurements of the weight of five coins, as listed in the table below:
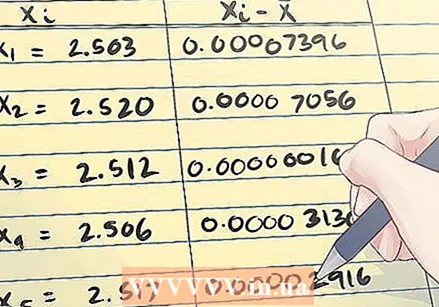 Subtract the sample mean from each measurement and square this value. Once you have the sample mean, you can expand the table by subtracting it from each individual measurement and squaring the result.
Subtract the sample mean from each measurement and square this value. Once you have the sample mean, you can expand the table by subtracting it from each individual measurement and squaring the result. - In the example above, it looks like this:
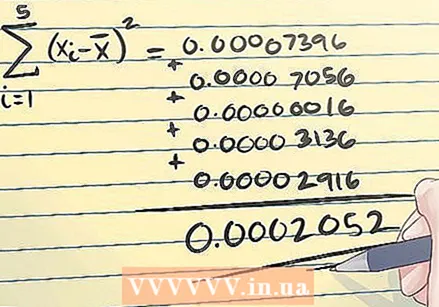 Determine the total deviation of your readings from the sample mean. The total deviation is the mean of the squared difference from the sample mean. Add up all the values to determine this.
Determine the total deviation of your readings from the sample mean. The total deviation is the mean of the squared difference from the sample mean. Add up all the values to determine this. - In the example above, you calculate this as follows:
This equation gives you the total squared deviation of the measured values from the sample mean. Note that the sign of the difference does not matter.
- In the example above, you calculate this as follows:
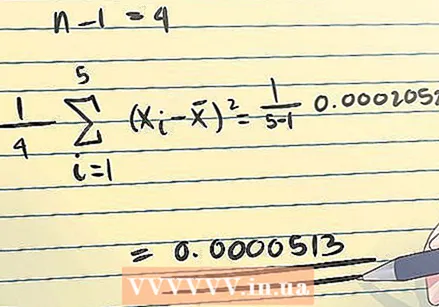 Calculate the mean square deviation of the measurements from the sample mean. Once you know the total deviation, you can find the average deviation by means of n -1. Note that n equals the number of measurements.
Calculate the mean square deviation of the measurements from the sample mean. Once you know the total deviation, you can find the average deviation by means of n -1. Note that n equals the number of measurements. - In the example above you have 5 measurements, so n - 1 = 4. Your calculation is done as follows:
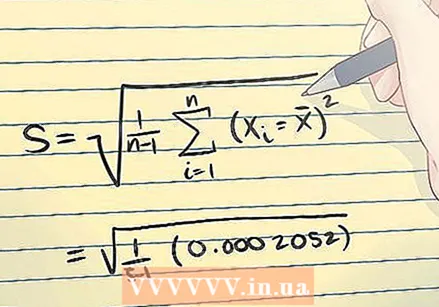 Determine the standard deviation. You now have all the necessary values to use the standard deviation formula (s).
Determine the standard deviation. You now have all the necessary values to use the standard deviation formula (s). - In the example above, calculate the standard deviation as follows:
So the standard deviation is 0.0071624.
- In the example above, calculate the standard deviation as follows:
Part 3 of 3: Determining the standard error
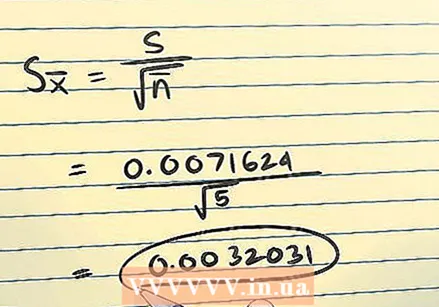 Use the standard deviation to calculate standard error with the standard formula.
Use the standard deviation to calculate standard error with the standard formula.- In the example above, calculate the standard error as follows:
The standard error (the standard deviation of the sample mean) is 0.0032031 grams.
- In the example above, calculate the standard error as follows:
Tips
- The standard error and the standard deviation are often confused. Note that standard error is a description of the standard deviation of the sampling distribution of a statistical value, not the distribution of individual values.
- In scientific journals, standard error and standard deviation are sometimes used interchangeably. A ± sign is used to add the two readings.