Author:
Charles Brown
Date Of Creation:
4 February 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
A function in mathematics (usually notated as f (x)) can be seen as some kind of formula or program where you put in a value "x", which then returns a certain value for y. The inverse of a function f (x) (notated as f (x)) is essentially the reverse: enter one yvalue and you will get the earlier Xvalue back again. Finding the inverse of a function may seem a bit complicated, but for simple equations, all you need is some knowledge of basic algebra operations. Read the following step-by-step instructions and take a good look at the example.
To step
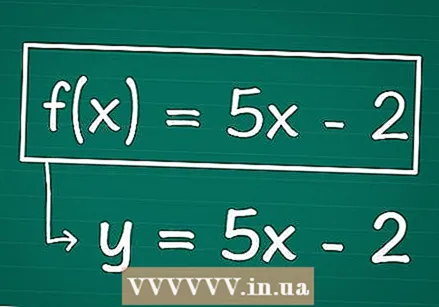 Write down your function, swapping f (x) with y if necessary. Your formula belongs y on one side of the equals sign and on the other side have the X-terms. If you have an equation already written in y and X terms (like for example 2 + y = 3x), then you just have to y by isolating it.
Write down your function, swapping f (x) with y if necessary. Your formula belongs y on one side of the equals sign and on the other side have the X-terms. If you have an equation already written in y and X terms (like for example 2 + y = 3x), then you just have to y by isolating it. - Example: We have a function f (x) = 5x - 2, and rewrite it as y = 5x - 2, simply by replacing "f (x)" with y.
- Note: f (x) is the standard function notation, but if you are dealing with multiple functions, each function will have a different initial letter to make them easier to distinguish from each other. For example g (x) and h (x) are commonly used letters for functions.
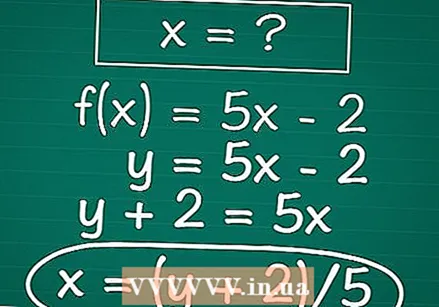 Loose X on. In other words, do the necessary edits X on one side of the equals sign. To do this, use the basic operations of algebra: if X has a coefficient (a number for the variable), divide both sides of the equation by this number to cancel it out; if there is a constant within the "x" term, cancel it out by adding or subtracting both sides of the equal sign, and so on.
Loose X on. In other words, do the necessary edits X on one side of the equals sign. To do this, use the basic operations of algebra: if X has a coefficient (a number for the variable), divide both sides of the equation by this number to cancel it out; if there is a constant within the "x" term, cancel it out by adding or subtracting both sides of the equal sign, and so on. - Remember that you must do any operation on one side of the equals sign on the other side as well.
- Example: To continue with our example, we first add 2 on both sides of the equation. This gives us y + 2 = 5x. Then we divide both sides of the equation by 5, leaving (y + 2) / 5 = x. Finally, to make it easier to read, we rewrite the equation with the "x" on the left: x = (y + 2) / 5.
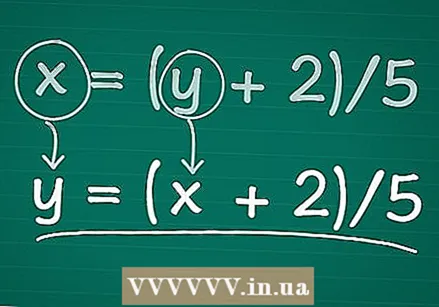 Switch the variables. Swap X with y and vice versa. The resulting equation is the inverse of the original function. In other words, if we have a value for it X in our original equation, then we can enter the answer in the inverse (again for "x"), which will return the original value!
Switch the variables. Swap X with y and vice versa. The resulting equation is the inverse of the original function. In other words, if we have a value for it X in our original equation, then we can enter the answer in the inverse (again for "x"), which will return the original value! - Example: After swapping x and y, we get y = (x + 2) / 5
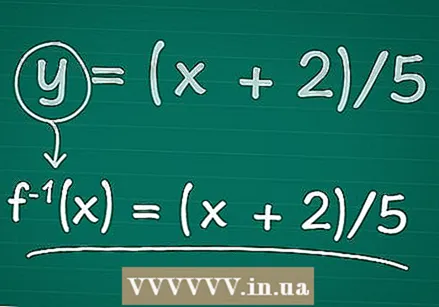 Replace y by "f (x)". Inverse functions are usually written as f (x) = (x terms). Remember that in this case the exponent -1 does not mean that we have to perform an exponential operation on the function. It's just a way of indicating that this function is the inverse of the original.
Replace y by "f (x)". Inverse functions are usually written as f (x) = (x terms). Remember that in this case the exponent -1 does not mean that we have to perform an exponential operation on the function. It's just a way of indicating that this function is the inverse of the original. - Because X is equal to 1 / x, you may also write f (x) as "1 / f (x)," another notation for the inverse of f (x).
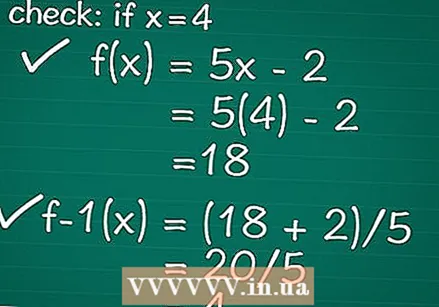 Check your work. Try to enter a constant in the original function for X. If you have found the correct inverse, you should see the original value of "x" again, if you enter the result in the inverse.
Check your work. Try to enter a constant in the original function for X. If you have found the correct inverse, you should see the original value of "x" again, if you enter the result in the inverse. - Example: Let's enter 4 as the value of X in our original comparison. This gives us f (x) = 5 (4) - 2, or f (x) = 18 as a result.
- Next, we are going to enter this result in the inverse. So we substitute 18 in the inverse function as the value of X. By doing this we get y = (18 + 2) / 5 as the result and this is equal to y = 4. So 4 is the x value we started with, and with that we know that we have found the correct inverse function.
Tips
- You can easily use both notations f (x) = y and f ^ (- 1) (x) = y if you let go of mathematical operations on the functions. But it is better to keep the original function and the inverse function apart, so try to stick to a commonly used notation. In the case of the inverse function, the notation f ^ (- 1) (x).
- Note that the inverse of a function is usually, but not always, a function itself.



