Author:
William Ramirez
Date Of Creation:
19 September 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024
Content
- Steps
- Method 1 of 3: Treating Mild Folliculitis with Home Remedies
- Method 2 of 3: Medication for folliculitis
- Method 3 of 3: Preventing folliculitis
Folliculitis is an inflammation of the hair follicles that can develop into a bacterial or fungal infection. It usually presents as itchy, painful pustules that develop around one or more inflamed follicles. Folliculitis can be caused by a variety of causes and vary in severity, so there are many treatment options. Whether you are faced with a mild form of folliculitis or it has developed in full force, in our article you will find tips on how to restore your skin to health.
Steps
Method 1 of 3: Treating Mild Folliculitis with Home Remedies
 1 Wash yourself periodically with antibacterial soap. As a rule, mild folliculitis will go away on its own, but the process can be accelerated. Wash the affected area twice a day with antibacterial soap. Rinse off the soap with water and dry clean dry towel.
1 Wash yourself periodically with antibacterial soap. As a rule, mild folliculitis will go away on its own, but the process can be accelerated. Wash the affected area twice a day with antibacterial soap. Rinse off the soap with water and dry clean dry towel. - Wash gently. Avoid using harsh soaps or rubbing heavily on your skin - this can irritate the skin and make the inflammation and redness worse.
- If folliculitis occurs on your face, use an antibacterial soap labeled “for the face”. These soaps are generally softer.
 2 Try a simple salt water compress. Warm compresses (cloth or other absorbent material soaked in warm water and placed on the affected area) soothe irritation, improve drainage, and speed healing.Salt, in turn, has antibacterial properties (although not very strong). Salt compress is done as follows: dissolve a few tablespoons of ordinary table salt in 1-2 glasses of warm water, then dip a towel or cotton ball into the solution and hold it, gently pressing it to the affected area.
2 Try a simple salt water compress. Warm compresses (cloth or other absorbent material soaked in warm water and placed on the affected area) soothe irritation, improve drainage, and speed healing.Salt, in turn, has antibacterial properties (although not very strong). Salt compress is done as follows: dissolve a few tablespoons of ordinary table salt in 1-2 glasses of warm water, then dip a towel or cotton ball into the solution and hold it, gently pressing it to the affected area. - Use compresses twice a day - morning and evening.
 3 Moisten the affected area with a solution of warm water and aluminum acetate. Actually, aluminum acetate is famous for its astringent and antibacterial properties, and therefore is often used as a cheap and OTC remedy for the treatment of various skin conditions (not very serious). Aluminum acetate can kill bacteria that cause inflammation and reduce swelling in the affected area, which can reduce irritation and speed up recovery.
3 Moisten the affected area with a solution of warm water and aluminum acetate. Actually, aluminum acetate is famous for its astringent and antibacterial properties, and therefore is often used as a cheap and OTC remedy for the treatment of various skin conditions (not very serious). Aluminum acetate can kill bacteria that cause inflammation and reduce swelling in the affected area, which can reduce irritation and speed up recovery. - It is very simple to prepare such a solution: dilute one packet of aluminum acetate in the recommended volume of warm water, then put a clean terry cloth in there, let it get wet, then take it back out, squeeze it a little and place it gently on the affected area. Keep the tissue on the affected area, wetting it again from time to time.
- When finished, wash the container in which you prepared the solution, and rinse the napkin under cold water. Then wash it in hot water and dry it thoroughly to keep bacteria or fungus free.
 4 Use oatmeal. Believe it or not, oatmeal has long been used to treat skin conditions. Take an oatmeal bath or simply apply an oatmeal lotion to the affected area. Enjoy the soothing sensation that oatmeal will give you, but remember not to overuse it to keep things from getting worse.
4 Use oatmeal. Believe it or not, oatmeal has long been used to treat skin conditions. Take an oatmeal bath or simply apply an oatmeal lotion to the affected area. Enjoy the soothing sensation that oatmeal will give you, but remember not to overuse it to keep things from getting worse. - Remember to gently dry the affected area with a clean towel.
 5 Go for holistic medicine and use vinegar. There are many holistic or natural remedies available for folliculitis and other mild skin problems. Some holistic advocates argue that these remedies are bound to help, although the medical community often disagrees. If you decide to try holistic methods, remember to use common sense and do not use anything that could worsen your condition. You can take vinegar, about which in a little more detail - below.
5 Go for holistic medicine and use vinegar. There are many holistic or natural remedies available for folliculitis and other mild skin problems. Some holistic advocates argue that these remedies are bound to help, although the medical community often disagrees. If you decide to try holistic methods, remember to use common sense and do not use anything that could worsen your condition. You can take vinegar, about which in a little more detail - below. - Dissolve 1 part white vinegar with 2 parts warm water and mix thoroughly. Then soak a clean washcloth or small towel in the solution, wring it out, and place over the affected area. Leave the compress on for 5-10 minutes, re-wetting it as it dries.
Method 2 of 3: Medication for folliculitis
 1 In serious cases, do not delay your visit to the doctor. As a rule, this disease does not cause anything but a slight, albeit painful, irritation. However, like any infection, folliculitis can develop into something more serious if left untreated. If folliculitis does not go away on its own, or if you have more troubling symptoms such as fever or severe swelling and irritation, see your doctor as soon as possible. It is better to play it safe - a timely visit can save you money, nerves, and health.
1 In serious cases, do not delay your visit to the doctor. As a rule, this disease does not cause anything but a slight, albeit painful, irritation. However, like any infection, folliculitis can develop into something more serious if left untreated. If folliculitis does not go away on its own, or if you have more troubling symptoms such as fever or severe swelling and irritation, see your doctor as soon as possible. It is better to play it safe - a timely visit can save you money, nerves, and health. - First, you can go to a therapist, he can also redirect you to a dermatologist.
- It is also worth seeing a doctor if a large area is affected by folliculitis.
 2 Use hydrocortisone ointments to relieve pain and itching. These products are topical preparations designed to soothe skin irritation and relieve itching. Try 1% hydrocortisone, which should be applied 2-5 times a day directly to the affected area, rubbing gently with clean fingers or a clean applicator. If you apply the product with your fingers, be sure to wash and dry your hands before doing so to keep out bacteria.
2 Use hydrocortisone ointments to relieve pain and itching. These products are topical preparations designed to soothe skin irritation and relieve itching. Try 1% hydrocortisone, which should be applied 2-5 times a day directly to the affected area, rubbing gently with clean fingers or a clean applicator. If you apply the product with your fingers, be sure to wash and dry your hands before doing so to keep out bacteria. - Keep in mind that hydrocortisone will relieve pain and inflammation, but will not kill bacteria.
 3 Use over-the-counter pain relievers or anti-inflammatory drugs. To manage the pain and inflammation caused by folliculitis, try an over-the-counter remedy. Common, inexpensive pain relievers like aspirin or paracetamol can help relieve mild pain caused by folliculitis. Anti-inflammatory pain relievers like ibuprofen are also great, and they will not only relieve pain, but also temporarily alleviate inflammation.
3 Use over-the-counter pain relievers or anti-inflammatory drugs. To manage the pain and inflammation caused by folliculitis, try an over-the-counter remedy. Common, inexpensive pain relievers like aspirin or paracetamol can help relieve mild pain caused by folliculitis. Anti-inflammatory pain relievers like ibuprofen are also great, and they will not only relieve pain, but also temporarily alleviate inflammation. - Do not give aspirin to children or adolescents without a doctor's prescription.
- Although most low-dose over-the-counter pain relievers are harmless, overdosing or taking longer (10 days or more) can sometimes lead to serious problems, such as liver damage. Therefore, always follow the instructions for their use.
 4 Take antibiotics for severe cases. If home remedies do not help treat folliculitis, you may need to treat the underlying bacterial infection with antibiotics. Antibiotic ointments are available over the counter. However, for oral antibiotics, you will need a doctor's prescription. Never prescribe them yourself.
4 Take antibiotics for severe cases. If home remedies do not help treat folliculitis, you may need to treat the underlying bacterial infection with antibiotics. Antibiotic ointments are available over the counter. However, for oral antibiotics, you will need a doctor's prescription. Never prescribe them yourself.  5 Use antifungal agents for fungal infections. As mentioned in the introduction to this article, sometimes it is not a bacterial infection, but a fungal infection that causes folliculitis. Accordingly, you will need an antifungal medication, either topical or oral. As with antibiotics, mild remedies can be purchased without a prescription, but stronger ones may require a prescription from a doctor.
5 Use antifungal agents for fungal infections. As mentioned in the introduction to this article, sometimes it is not a bacterial infection, but a fungal infection that causes folliculitis. Accordingly, you will need an antifungal medication, either topical or oral. As with antibiotics, mild remedies can be purchased without a prescription, but stronger ones may require a prescription from a doctor. - Your doctor will determine if your infection is bacterial or fungal and will prescribe appropriate treatment.
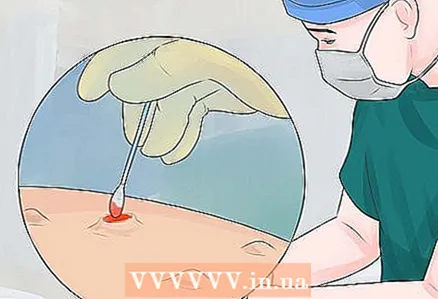 6 See a surgeon to open up abscesses and boils. In especially severe cases, folliculitis develops so much that purulent blisters and boils are formed. Then you need the help of a surgeon - he must open them, which will speed up the healing process and reduce scarring. However, do not try to do it yourself: in the absence of sterile conditions, this is almost a guaranteed way to get reinfection.
6 See a surgeon to open up abscesses and boils. In especially severe cases, folliculitis develops so much that purulent blisters and boils are formed. Then you need the help of a surgeon - he must open them, which will speed up the healing process and reduce scarring. However, do not try to do it yourself: in the absence of sterile conditions, this is almost a guaranteed way to get reinfection.
Method 3 of 3: Preventing folliculitis
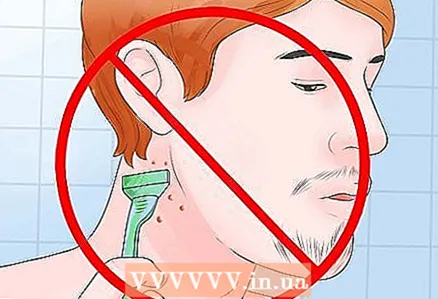 1 Do not shave the affected area. Folliculitis is often caused by irritation after shaving or dirty shaving utensils. If folliculitis appears in a place that you regularly shave, take a break and do not shave for a while. Constant shaving will only cause additional irritation, and possibly the spread of the disease to other follicles.
1 Do not shave the affected area. Folliculitis is often caused by irritation after shaving or dirty shaving utensils. If folliculitis appears in a place that you regularly shave, take a break and do not shave for a while. Constant shaving will only cause additional irritation, and possibly the spread of the disease to other follicles. - if you necessarily you need to shave, try to keep irritation to a minimum. In particular, shave with an electric razor rather than a hand razor, and shave on hair growth, not against. Keep your shaver clean at all times.
 2 Do not touch the affected area. Fingers and hands are one of the most common ways of carrying bacteria. You may feel itching or burning in the affected area, but resist the urge to scratch or poke at it. Handle the affected area with utmost care: wash your hands before touching, and try to touch only then, when you wash it, apply ointment or apply a compress.
2 Do not touch the affected area. Fingers and hands are one of the most common ways of carrying bacteria. You may feel itching or burning in the affected area, but resist the urge to scratch or poke at it. Handle the affected area with utmost care: wash your hands before touching, and try to touch only then, when you wash it, apply ointment or apply a compress.  3 Don't wear tight clothing. The friction that the skin is exposed to under tight clothing during the day can lead to the development of folliculitis. In addition, skin infections can also be caused by tight clothing blocking air from reaching the skin. If you have a tendency to develop folliculitis, try to wear soft, loose clothing to minimize possible irritation.
3 Don't wear tight clothing. The friction that the skin is exposed to under tight clothing during the day can lead to the development of folliculitis. In addition, skin infections can also be caused by tight clothing blocking air from reaching the skin. If you have a tendency to develop folliculitis, try to wear soft, loose clothing to minimize possible irritation. - Also, try not to dampen the clothing that covers the folliculitis area, so as not to increase the irritation.
 4 Avoid skin contact with irritants. Everyone's skin is different: some are easily covered with a rash from anything, some are not.If you have folliculitis (or are susceptible to it), try not to touch anything that might irritate you (especially substances or products to which you are allergic), as irritation can lead to a relapse or delay in the healing process.
4 Avoid skin contact with irritants. Everyone's skin is different: some are easily covered with a rash from anything, some are not.If you have folliculitis (or are susceptible to it), try not to touch anything that might irritate you (especially substances or products to which you are allergic), as irritation can lead to a relapse or delay in the healing process. - You may need to ditch certain cosmetics, oils, creams, lotions, and the like.
 5 Do not wash or swim in dirty water. Swimming or bathing in a pool or tub that is not properly cleaned is a common way to get folliculitis. Some bacteria that cause folliculitis, such as Pseudomonas aeruginosaare easily transmitted through dirty water. If you are susceptible to folliculitis, avoid contact with stagnant water of questionable purity.
5 Do not wash or swim in dirty water. Swimming or bathing in a pool or tub that is not properly cleaned is a common way to get folliculitis. Some bacteria that cause folliculitis, such as Pseudomonas aeruginosaare easily transmitted through dirty water. If you are susceptible to folliculitis, avoid contact with stagnant water of questionable purity.  6 Don't rely too heavily on topical steroids. A number of drugs, in the case of long-term use, can worsen the problem and increase the risk of developing folliculitis. In particular, the same hydrocortisone can become a factor in the development of infection. At the same time, paradoxically, hydrocortisone ointments are a common remedy. against mild cases of folliculitis. Therefore, if you are using hydrocortisone but do not see any improvement, make an appointment with your doctor before the infection becomes more serious.
6 Don't rely too heavily on topical steroids. A number of drugs, in the case of long-term use, can worsen the problem and increase the risk of developing folliculitis. In particular, the same hydrocortisone can become a factor in the development of infection. At the same time, paradoxically, hydrocortisone ointments are a common remedy. against mild cases of folliculitis. Therefore, if you are using hydrocortisone but do not see any improvement, make an appointment with your doctor before the infection becomes more serious.  7 Do not allow existing wounds to become infected. Hair follicles can become infected and inflamed if an irritated source of infection is nearby. Therefore, any skin infection must be treated quickly and professionally. Prevent the infection from spreading - when it is localized, it is much easier to deal with it.
7 Do not allow existing wounds to become infected. Hair follicles can become infected and inflamed if an irritated source of infection is nearby. Therefore, any skin infection must be treated quickly and professionally. Prevent the infection from spreading - when it is localized, it is much easier to deal with it.