Author:
Florence Bailey
Date Of Creation:
22 March 2021
Update Date:
27 June 2024

Content
- Steps
- Method 1 of 2: Treating ear plugs at home
- Method 2 of 2: Medical solution to the problem
- Tips
- Warnings
- What do you need
The Eustachian tube is a small canal that connects the ear to the nose. The patency of the Eustachian tube can be impaired by colds and allergies. Serious cases require observation by an otorhinolaryngologist. Mild cases can be managed at home with home remedies, over-the-counter drugs, and prescription solutions.
Steps
Method 1 of 2: Treating ear plugs at home
 1 Symptoms Colds, allergies, infections, and swelling cause airflow to be disrupted through the Eustachian tube. Due to the change in pressure, fluid accumulates in the inner ear, and then the following symptoms appear:
1 Symptoms Colds, allergies, infections, and swelling cause airflow to be disrupted through the Eustachian tube. Due to the change in pressure, fluid accumulates in the inner ear, and then the following symptoms appear: - ear pain or a feeling of fullness in the ear;
- ringing, clicking, and other sounds in the ears;
- children may describe a tickling sensation;
- hearing loss;
- dizziness or lack of coordination.
- Symptoms may worsen with rapid changes in body position, such as when flying, riding an elevator, hiking, or riding in a mountainous area.
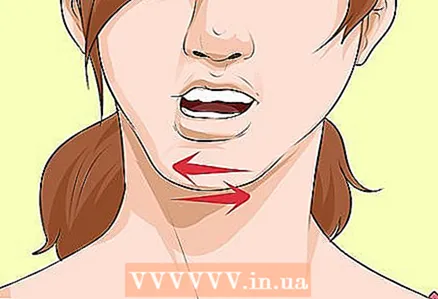 2 Lower jaw movements. This is a very simple technique called the Edmonds maneuver. Pull the lower jaw forward and move it from side to side. If the ear is not heavily stuffed up, this method will effectively restore normal airflow.
2 Lower jaw movements. This is a very simple technique called the Edmonds maneuver. Pull the lower jaw forward and move it from side to side. If the ear is not heavily stuffed up, this method will effectively restore normal airflow.  3 Use the Valsalva method. This method forces air to flow through the blocked passage, so it must be conducted carefully. A strong expiratory flow of air can cause rapid changes in blood pressure and heart rate.
3 Use the Valsalva method. This method forces air to flow through the blocked passage, so it must be conducted carefully. A strong expiratory flow of air can cause rapid changes in blood pressure and heart rate. - Take a deep breath and hold your breath with your mouth and nostrils closed.
- Try blowing air out through your closed nostrils.
- If the method is successful, you will hear a clicking sound in your ears.
 4 Try Toynbee's method. Like the Valsalva Method, the Toynbee Method is designed to relieve congestion in the ears. But instead of changing the air pressure when breathing, Toynbee's method uses the change in air pressure when swallowing. To perform Toynbee's method, do the following:
4 Try Toynbee's method. Like the Valsalva Method, the Toynbee Method is designed to relieve congestion in the ears. But instead of changing the air pressure when breathing, Toynbee's method uses the change in air pressure when swallowing. To perform Toynbee's method, do the following: - pinch your nostrils;
- take a sip of water;
- swallow;
- repeat the process until you feel the ear congestion is gone.
 5 Inflate the balloons with your nose. It sounds ridiculous, but this method effectively evens out the pressure in the ears. Unfortunately, a special device for this technique (Otovent) is not for sale in Russia, but it can be ordered via the Internet, or you can make it yourself. It is a ball with a nostril attachment. Perhaps at home you already have nozzles for a nasal aspirator - in this case, it will not be difficult to make such a device yourself.
5 Inflate the balloons with your nose. It sounds ridiculous, but this method effectively evens out the pressure in the ears. Unfortunately, a special device for this technique (Otovent) is not for sale in Russia, but it can be ordered via the Internet, or you can make it yourself. It is a ball with a nostril attachment. Perhaps at home you already have nozzles for a nasal aspirator - in this case, it will not be difficult to make such a device yourself. - Insert the nozzle into one nostril and close the other with your finger.
- Try inflating the ball of one nostril to the size of your fist.
- Repeat on the other side. Repeat the process until you hear a click in your ear.
 6 Swallow with a pinched nose. This is Lowry's method. Before you just swallow, you need to increase the pressure, as when straining. When holding your breath and straining, you will feel how the air tries to escape through all the passages. Some people find it difficult to swallow while doing this. Be patient and you will feel a popping sound in your ears.
6 Swallow with a pinched nose. This is Lowry's method. Before you just swallow, you need to increase the pressure, as when straining. When holding your breath and straining, you will feel how the air tries to escape through all the passages. Some people find it difficult to swallow while doing this. Be patient and you will feel a popping sound in your ears.  7 Place a heating pad or warm towel against your ear. This will relieve pain and may relieve congestion in the ear. The heat from the compress can relieve swelling and increase the patency of the Eustachian tube. If you are using a heating pad, place a cloth between the skin and the heating pad to avoid scalding.
7 Place a heating pad or warm towel against your ear. This will relieve pain and may relieve congestion in the ear. The heat from the compress can relieve swelling and increase the patency of the Eustachian tube. If you are using a heating pad, place a cloth between the skin and the heating pad to avoid scalding.  8 Use a vasoconstrictor for the nose. Ear drops will not help with congestion because the junction between the ear and nose is out of the reach of drops. Therefore, in such cases, vasoconstrictor nasal sprays are used. Position the spray dispenser in one nostril almost perpendicular to your face. Inhale vigorously after you spray - this should be done so vigorously that the liquid enters the back of your throat, but not enough to be swallowed or sucked into your mouth.
8 Use a vasoconstrictor for the nose. Ear drops will not help with congestion because the junction between the ear and nose is out of the reach of drops. Therefore, in such cases, vasoconstrictor nasal sprays are used. Position the spray dispenser in one nostril almost perpendicular to your face. Inhale vigorously after you spray - this should be done so vigorously that the liquid enters the back of your throat, but not enough to be swallowed or sucked into your mouth. - Try any of the above methods after using the drops - they may be more effective after using the spray.
 9 Take an antihistamine if your congestion is related to an allergy. Although antihistamines are not intended to treat ear congestion, they can be effective in relieving allergic swelling. Talk to your allergist about the most effective medication.
9 Take an antihistamine if your congestion is related to an allergy. Although antihistamines are not intended to treat ear congestion, they can be effective in relieving allergic swelling. Talk to your allergist about the most effective medication. - Note that antihistamines are not recommended for people with ear conditions.
Method 2 of 2: Medical solution to the problem
 1 Medicated nasal sprays. Conventional over-the-counter medications can be used, but prescription vasoconstrictors are most effective. If you have allergies, ask your doctor to prescribe steroid and / or antihistamine nasal sprays.
1 Medicated nasal sprays. Conventional over-the-counter medications can be used, but prescription vasoconstrictors are most effective. If you have allergies, ask your doctor to prescribe steroid and / or antihistamine nasal sprays.  2 Take antibiotics for an ear infection. Obstruction of the Eustachian tube is often not harmful and does not last long, but sometimes it can lead to ear infection. If the blockage does not go away for a long time, consult an otolaryngologist for treatment. The doctor will prescribe antibiotics at temperatures over 39 ° C for more than two days.
2 Take antibiotics for an ear infection. Obstruction of the Eustachian tube is often not harmful and does not last long, but sometimes it can lead to ear infection. If the blockage does not go away for a long time, consult an otolaryngologist for treatment. The doctor will prescribe antibiotics at temperatures over 39 ° C for more than two days. - Take your medications as directed. Drink a full course of antibiotics even if you feel better.
 3 Talk to your doctor about myringotomy. In severe cases, your doctor may recommend a surgical solution to the problem. There are two surgeries, and myringotomy is the fastest option. During this operation, the surgeon makes a thin incision in the eardrum and removes excess fluid from the middle ear. It may seem counterintuitive, but it is necessary for the incision to heal. slowly... If the incision is left open for a long enough period of time, the swelling of the Eustachian tube may subside. If the ear heals quickly (in less than 3 days), fluid will build up in the middle ear again and symptoms will return.
3 Talk to your doctor about myringotomy. In severe cases, your doctor may recommend a surgical solution to the problem. There are two surgeries, and myringotomy is the fastest option. During this operation, the surgeon makes a thin incision in the eardrum and removes excess fluid from the middle ear. It may seem counterintuitive, but it is necessary for the incision to heal. slowly... If the incision is left open for a long enough period of time, the swelling of the Eustachian tube may subside. If the ear heals quickly (in less than 3 days), fluid will build up in the middle ear again and symptoms will return.  4 Consider other pressure equalization methods. Another surgical method to get rid of congestion in the ear is used for advanced processes. Just like a myringotomy, the doctor makes an incision in the tympanic membrane and aspirates the fluid that has accumulated in the middle ear. A small tube is inserted into the incision to assess the condition of the middle ear during the healing period. The tubule is removed on its own after 6-12 months. This method is used in patients with chronic Eustachian tube disease.
4 Consider other pressure equalization methods. Another surgical method to get rid of congestion in the ear is used for advanced processes. Just like a myringotomy, the doctor makes an incision in the tympanic membrane and aspirates the fluid that has accumulated in the middle ear. A small tube is inserted into the incision to assess the condition of the middle ear during the healing period. The tubule is removed on its own after 6-12 months. This method is used in patients with chronic Eustachian tube disease. - Be sure to protect your ears from water if there are tubules in your eardrums. Use ear plugs or cotton balls when bathing and showering.
- If water gets through the tube into the middle ear, it can cause inflammation.
 5 Treat the cause. A congestion in the Eustachian tube usually indicates another disease, accompanied by mucus and edema. The most common illnesses are colds, flu, sinus infections, and allergies. Do not start these diseases to prevent ear inflammation. Treat colds and flu at the first symptoms and consult a doctor for allergies and sinus infections.
5 Treat the cause. A congestion in the Eustachian tube usually indicates another disease, accompanied by mucus and edema. The most common illnesses are colds, flu, sinus infections, and allergies. Do not start these diseases to prevent ear inflammation. Treat colds and flu at the first symptoms and consult a doctor for allergies and sinus infections.
Tips
- If you know you have fluid in your ears, do not use earwax removers. They can cause infection as they are liquid, not wax.
- For ear pain, do not lie down.
- Do not drink cold water, but some warm drink, such as tea.
- Try sucking a few papaya chewable tablets in your mouth. Papayotin, the main ingredient in unripe papaya, is an excellent mucus dissolver.
- You can also try fenugreek.
- Place an extra pillow under your head to help drain fluids from your nose while you sleep.
- For pain caused by stuffy ears, ask your doctor for prescription pain drops. You can also try over-the-counter medications such as ibuprofen, paracetamol, or naproxen to relieve pain.
- Wear a hat that covers your ears to keep your head cool.
Warnings
- Do not use over-the-counter nasal sprays for more than a few days. Longer use can cause congestion, which cannot be relieved with this spray. If the spray is ineffective, consult your doctor.
- Do not flush your ears with a nose flush or ear candles. These items are not recognized as safe by the medical community.
- Diving is contraindicated for Eustachian tube problems! Scuba diving can worsen ear pain due to pressure changes.
What do you need
- Vasoconstrictor nasal drops
- Glucocorticoid nasal drops
- Antihistamines
- Pressure equalization tubes



