Author:
Clyde Lopez
Date Of Creation:
19 June 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
Kudzu is a ground cover plant native to Japan but very common in the southern United States since its introduction in the 19th century. Kudzu is a grape well known for its incredibly fast growth. Growing up to a foot (30 cm) per day, this plant has acquired a reputation for being highly invasive. Learning the correct definition of kudzu will help you find it in your area. This is the first step to control kudzu.
Steps
 1 Look for a shamrock or three-leaf formations attached to each scion. All shamrocks must be attached to the stem on their own cuttings or stems. The stem of the central leaf is about "(19 mm) long, while the outer 2 leaves have shorter stems.
1 Look for a shamrock or three-leaf formations attached to each scion. All shamrocks must be attached to the stem on their own cuttings or stems. The stem of the central leaf is about "(19 mm) long, while the outer 2 leaves have shorter stems.  2 Look for an egg shape on a medium green leaf. In general, the center sheet has 3 parts or rounded projections. 2 outer leaves often have 2 rounded parts. However, the appearance of Kudza leaves may differ, and not all leaves are divided into parts. The leaves can also be quite large, about 5 or 6 inches (12-15 cm) long.
2 Look for an egg shape on a medium green leaf. In general, the center sheet has 3 parts or rounded projections. 2 outer leaves often have 2 rounded parts. However, the appearance of Kudza leaves may differ, and not all leaves are divided into parts. The leaves can also be quite large, about 5 or 6 inches (12-15 cm) long.  3 Touch the leaves to make sure they are fuzzy. Kudzu leaves have small hairs that are slippery to the touch.
3 Touch the leaves to make sure they are fuzzy. Kudzu leaves have small hairs that are slippery to the touch.  4 Look for a long vine, covered with small brown scales, stretching along the ground and climbing any vertical surface to form dense tufts of foliage. The main feature of kudzu is its tremendous growth rate. They can grow 1 foot (30 cm) in 1 day in a supportive environment. The kudzu can often be seen covering large trees, pillars, and other structures. As they grow, grapes can become a powerful tree. The kudzu vine is capable of climbing any height, and can also curl along the ground, rooting with each shoot.
4 Look for a long vine, covered with small brown scales, stretching along the ground and climbing any vertical surface to form dense tufts of foliage. The main feature of kudzu is its tremendous growth rate. They can grow 1 foot (30 cm) in 1 day in a supportive environment. The kudzu can often be seen covering large trees, pillars, and other structures. As they grow, grapes can become a powerful tree. The kudzu vine is capable of climbing any height, and can also curl along the ground, rooting with each shoot.  5 Look for purple or reddish purple flowers in clusters. Kudzu blooms in late summer, usually in August or September in the southern United States. The flowers form a cluster that can grow up to 8 inches (20 cm) long and emerge from a central leaf-bearing petiole.
5 Look for purple or reddish purple flowers in clusters. Kudzu blooms in late summer, usually in August or September in the southern United States. The flowers form a cluster that can grow up to 8 inches (20 cm) long and emerge from a central leaf-bearing petiole.  6 Measure the seed pods with a ruler. Kudzu produces small seed pods, usually about 2 inches (5 cm) long.
6 Measure the seed pods with a ruler. Kudzu produces small seed pods, usually about 2 inches (5 cm) long. 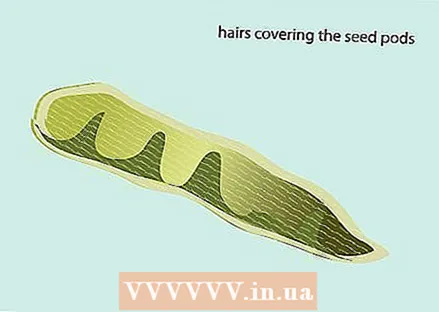 7 Look for the villi covering the seeds.
7 Look for the villi covering the seeds. 8 Cut open the seed pod and make sure the seeds are small and oval in shape.
8 Cut open the seed pod and make sure the seeds are small and oval in shape. 9 Look for green-bronze seed pods that turn brownish as they dry.
9 Look for green-bronze seed pods that turn brownish as they dry.
Tips
- Kudzu is classified as deciduous and sheds its leaves in winter.
Warnings
- Many local authorities may prohibit the landing of kudzu due to its increased invasive nature. Some authorities even ask you to report a kudzu sighting.