Author:
Roger Morrison
Date Of Creation:
20 September 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- To step
- Part 1 of 3: Calculating the circumference
- Part 2 of 3: Calculating area
- Part 3 of 3: Calculating the area and perimeter with variables
The circumference (C) of a circle is its circumference, or the distance around it. The area (A) of a circle is how much space the circle occupies or the area enclosed by the circle. Both the area and the perimeter can be calculated using simple formulas using the radius or diameter of the circle and the value of pi.
To step
Part 1 of 3: Calculating the circumference
 Learn the formula for the circumference of a circle. There are two formulas that can be used to calculate the circumference of a circle: C = 2πr or C = πd, where π is the mathematical constant and approximately equal to 3.14,r is equal to the radius and d equal to the diameter.
Learn the formula for the circumference of a circle. There are two formulas that can be used to calculate the circumference of a circle: C = 2πr or C = πd, where π is the mathematical constant and approximately equal to 3.14,r is equal to the radius and d equal to the diameter. - Since the radius of a circle equals twice its diameter, these equations are essentially the same.
- The units for the circumference can be any unit for the measure of height: kilometers, meters, centimeters, etc.
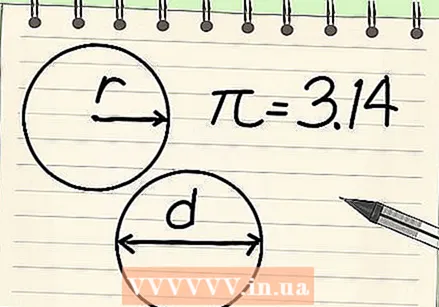 Understand the different parts of the formula. There are three components to finding the circumference of a circle: radius, diameter, and π. The radius and the diameter are related: the radius equals half the diameter, while the diameter equals double the radius.
Understand the different parts of the formula. There are three components to finding the circumference of a circle: radius, diameter, and π. The radius and the diameter are related: the radius equals half the diameter, while the diameter equals double the radius. - The radius (r) of a circle is the distance from one point on the circle to the center of the circle.
- The diameter (d) of a circle is the distance from one point on the circle to another point directly opposite the circle, passing through the center of the circle.
- The Greek letter pi (π) stands for the ratio of the circumference divided by the diameter and is represented by the number 3.14159265 ..., an irrational number that has neither a final digit nor a recognizable pattern of repeating digits. This number is often rounded to 3.14 for standard calculations.
 Measure the radius or the diameter of the circle. Place a ruler on one edge of the circle, through the center and to the other side of the circle. The distance to the center of the circle is the radius, while the distance to the other end of the circle is the diameter.
Measure the radius or the diameter of the circle. Place a ruler on one edge of the circle, through the center and to the other side of the circle. The distance to the center of the circle is the radius, while the distance to the other end of the circle is the diameter. - Radius or diameter is given in most math problems.
 Process and solve the variables. Once you have determined the radius and / or diameter of the circle, you can incorporate these variables into the correct equation. If you have the radius, use C = 2πr, but if you know the diameter, use C = πd.
Process and solve the variables. Once you have determined the radius and / or diameter of the circle, you can incorporate these variables into the correct equation. If you have the radius, use C = 2πr, but if you know the diameter, use C = πd. - For example: What is the circumference of a circle with a radius of 3 cm?
- Write the formula: C = 2πr
- Enter the variables: C = 2π3
- Multiply: C = (2 * 3 * π) = 6π = 18.84 cm
- For example: What is the circumference of a circle with a diameter of 9 m?
- Write the formula: C = πd
- Enter the variables: C = 9π
- Multiply: C = (9 * π) = 28.26 m
- For example: What is the circumference of a circle with a radius of 3 cm?
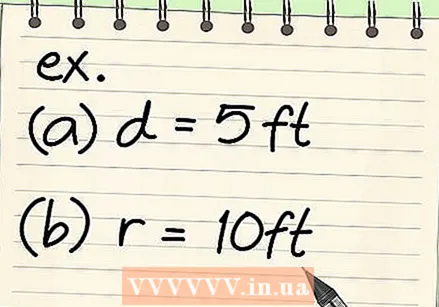 Practice with a few examples. Now that you've learned the formula, it's time to practice with a few examples. The more problems you solve, the easier it will be to solve them in the future.
Practice with a few examples. Now that you've learned the formula, it's time to practice with a few examples. The more problems you solve, the easier it will be to solve them in the future. - Determine the circumference of a circle with a diameter of 5 m.
- C = πd = 5π = 15.7 m
- Find the circumference of a circle with a radius of 10 m.
- C = 2πr = C = 2π10 = 2 * 10 * π = 62.8 m.
- Determine the circumference of a circle with a diameter of 5 m.
Part 2 of 3: Calculating area
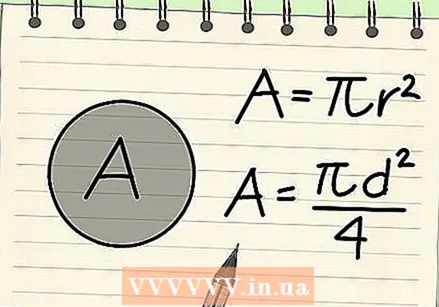 Learn the formula for the area of a circle. The area of a circle can be calculated using either the diameter or the radius, with two different formulas: A = πr or A = π (d / 2), where π is the mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14,r the radius and d the diameter.
Learn the formula for the area of a circle. The area of a circle can be calculated using either the diameter or the radius, with two different formulas: A = πr or A = π (d / 2), where π is the mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14,r the radius and d the diameter. - Since the radius of a circle equals half its diameter, these equations are essentially the same.
- The units for area can be any unit of length squared: km squared (km), meters squared (m), centimeter squared (cm), etc.
 Understand the different parts of the formula. There are three components to finding the circumference of a circle: radius, diameter, and π. The radius and the diameter are related to each other: the radius equals half the diameter, while the diameter equals double the radius.
Understand the different parts of the formula. There are three components to finding the circumference of a circle: radius, diameter, and π. The radius and the diameter are related to each other: the radius equals half the diameter, while the diameter equals double the radius. - The radius (r) of a circle is the distance from one point on the circle to the center of the circle.
- The diameter (d) of a circle is the distance from one point on the circle to another point directly opposite the circle, passing through the center of the circle.
- The Greek letter pi (π) stands for the ratio of the circumference divided by the diameter and is represented by the number 3.14159265 ..., an irrational number that has neither a final digit nor a recognizable pattern of repeating digits. This number is usually rounded to 3.14 for basic calculations.
 Measure the radius or the diameter of the circle. Place one end of a ruler on one point of the circle, through the center and to the other side of the circle. The distance to the center of the circle is the radius, while the distance to the other point on the circle is the diameter.
Measure the radius or the diameter of the circle. Place one end of a ruler on one point of the circle, through the center and to the other side of the circle. The distance to the center of the circle is the radius, while the distance to the other point on the circle is the diameter. - Radius or diameter is given in most math problems.
 Fill in and solve the variables. Once you have determined the radius and / or diameter of the circle, you can enter these variables into the correct equation. If you know the radius, use A = πr, but if you know the diameter, use A = π (d / 2).
Fill in and solve the variables. Once you have determined the radius and / or diameter of the circle, you can enter these variables into the correct equation. If you know the radius, use A = πr, but if you know the diameter, use A = π (d / 2). - For example: what is the area of a circle with a radius of 3 m?
- Write the formula: A = πr.
- Fill in the variables: A = π3.
- Square the radius: r = 3 = 9
- Multiply by pi: a = 9π = 28.26 m
- For example: what is the area of a circle with a diameter of 4 m?
- Write the formula: A = π (d / 2).
- Fill in the variables: A = π (4/2).
- Divide the diameter by 2: d / 2 = 4/2 = 2
- Square the result: 2 = 4
- Multiply by pi: a = 4π = 12.56 m
- For example: what is the area of a circle with a radius of 3 m?
 Practice with a few examples. Now that you've learned the formula, it's time to practice with a few examples. The more problems you solve, the easier it will be to solve other problems.
Practice with a few examples. Now that you've learned the formula, it's time to practice with a few examples. The more problems you solve, the easier it will be to solve other problems. - Find the area of a circle with a diameter of 7 m.
- A = π (d / 2) = π (7/2) = π (3.5) = 12.25 * π = 38.47 m.
- Find the area of a circle with a radius of 3 m.
- A = πr = π * 3 = 9 * π = 28.26 m
- Find the area of a circle with a diameter of 7 m.
Part 3 of 3: Calculating the area and perimeter with variables
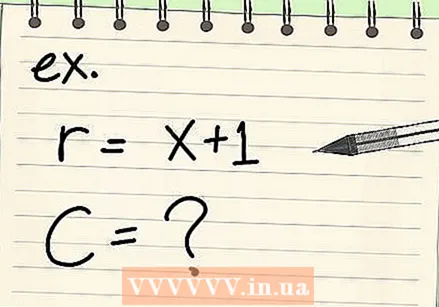 Determine the radius or the diameter of the circle. Some problems give a radius or diameter with a variable, such as r = (x + 7) or d = (x + 3). In this case, you can still determine the area or perimeter, but your final answer will also include that variable. Write down the radius or diameter as stated in the statement.
Determine the radius or the diameter of the circle. Some problems give a radius or diameter with a variable, such as r = (x + 7) or d = (x + 3). In this case, you can still determine the area or perimeter, but your final answer will also include that variable. Write down the radius or diameter as stated in the statement. - For example, calculate the circumference of a circle of radius (x = 1).
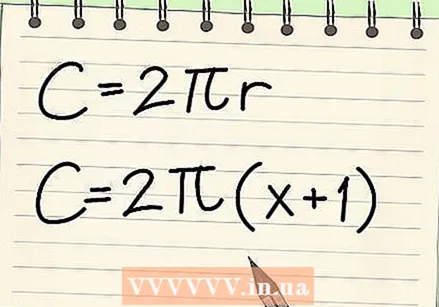 Write the formula with the given information. Whether you want to calculate area or perimeter, you still follow the basic steps of filling in what you know. Write down the area or perimeter formula and then fill in the given variables.
Write the formula with the given information. Whether you want to calculate area or perimeter, you still follow the basic steps of filling in what you know. Write down the area or perimeter formula and then fill in the given variables. - For example, calculate the circumference of a circle with a radius of (x + 1).
- Write the formula: C = 2πr
- Fill in the given information: C = 2π (x + 1)
 Solve the problem as if the variable were a number. At this point, you can just solve the problem as you normally would, treating the variable as if it were just another number. You may need to use the distributive property to simplify the final answer.
Solve the problem as if the variable were a number. At this point, you can just solve the problem as you normally would, treating the variable as if it were just another number. You may need to use the distributive property to simplify the final answer. - For example, calculate the circumference of a circle of radius (x = 1).
- C = 2πr = 2π (x + 1) = 2πx + 2π1 = 2πx + 2π = 6.28x + 6.28
- If the value of "x" is given later in the problem, you can plug it in and get a whole number.
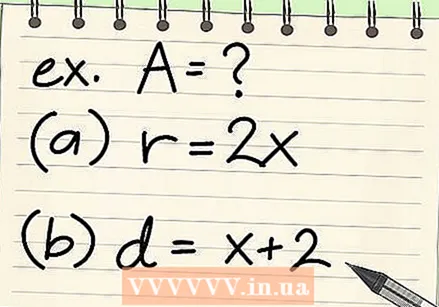 Practice with some examples. Now that you've learned the formula, it's time to practice with a few examples. The more problems you solve, the easier it will be to solve new ones.
Practice with some examples. Now that you've learned the formula, it's time to practice with a few examples. The more problems you solve, the easier it will be to solve new ones. - Find the area of a circle with a radius of 2x.
- A = πr = π (2x) = π4x = 12.56x
- Find the area of a circle with a diameter of (x + 2).
- A = π (d / 2) = π ((x +2) / 2) = ((x +2) / 4) π
- Find the area of a circle with a radius of 2x.